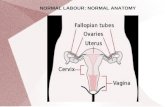
NORMAL LABOUR: NORMAL ANATOMY. NORMAL LABOUR: NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY Passenger Passage Power.
Normal labour
-
Upload
golden4host -
Category
News & Politics
-
view
4.993 -
download
1
Transcript of Normal labour

Normal labourNormal labour Definition of labour:-Definition of labour:- series of events that take place in the series of events that take place in the genital organs in an effort to expel the genital organs in an effort to expel the viable fetus out of the uterus through the viable fetus out of the uterus through the vagina in to the outer world.vagina in to the outer world.
Definition of delivery:-Definition of delivery:-Is the expulsion or extraction of a viable Is the expulsion or extraction of a viable fetus out of the uterusfetus out of the uterus..
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

NormallabourNormallabour
Labour is normal when it isLabour is normal when it is 1.1. Spontaneous in onset Spontaneous in onset 2.2. At termAt term3.3. single fetussingle fetus4.4. vertex presentation vertex presentation 5.5. Without undue prolongation Without undue prolongation 6.6. With no maternal complications or With no maternal complications or 7.7. Fetal complicationsFetal complications- Any deviation from this definition is abnormal - Any deviation from this definition is abnormal
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

OnOnset of labourset of labour Based on naegel’s formula labour starts Based on naegel’s formula labour starts
approximately as follow.approximately as follow. In the expected date of delivery in 4% of In the expected date of delivery in 4% of
cases cases One week on either side in 50% of cases One week on either side in 50% of cases Two weeks earlier and one week later on Two weeks earlier and one week later on
80% of cases 80% of cases At 42 weeks in 10% of cases At 42 weeks in 10% of cases At 43 weeks plus in 4% of cases At 43 weeks plus in 4% of cases
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Causes of the onset of labourCauses of the onset of labour Unknown the following theories were Unknown the following theories were
postulated postulated 1.1. Optimal distension theoryOptimal distension theory - When the uterus is distended to a certain When the uterus is distended to a certain
limit, it starts to contract to evacuate its limit, it starts to contract to evacuate its contents (multiple preg. Polyhydramnios)contents (multiple preg. Polyhydramnios)
2. 2. feto- placental theoryfeto- placental theory- Due to unknown factors fetal pituitary is - Due to unknown factors fetal pituitary is
stimulated with increase release of stimulated with increase release of ACTH that stimulate theACTH that stimulate the
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

fetal adrenal to produce cortisol which act in fetal adrenal to produce cortisol which act in the placenta to produce estrogen and the placenta to produce estrogen and prostaglandins.prostaglandins.
3- 3- estrogen theory:-estrogen theory:-
during the last trimester more free estrogen during the last trimester more free estrogen appears increasing the excitability of the appears increasing the excitability of the myometrium and prostaglandin synthesis myometrium and prostaglandin synthesis
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

4- progesterone:4- progesterone: Increase fetal production of Increase fetal production of
dehydroepiandro-sterone sulphate with dehydroepiandro-sterone sulphate with cortisol may inhibit the conversion of fetal cortisol may inhibit the conversion of fetal pregnenolone to progesterone there by pregnenolone to progesterone there by altering the estrogen progesterone ratio.altering the estrogen progesterone ratio.
5- prostaglandins5- prostaglandins:-:-
- Attracted much attention in recent years - Attracted much attention in recent years produced by-placenta –membrane –produced by-placenta –membrane –decidual cells and myometrium decidual cells and myometrium
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Synthesis is triggered bySynthesis is triggered by Rise in estrogen level Rise in estrogen level Altered estrogen. Progesterone ratio Altered estrogen. Progesterone ratio Mechanical stretching in later pregnancy Mechanical stretching in later pregnancy Infection or separation of membranes Infection or separation of membranes
↑↑ oxytocin receptors oxytocin receptors
6. Oxytocin theory:-6. Oxytocin theory:-
although oxytocin is a powerful stimulator of uterine although oxytocin is a powerful stimulator of uterine contraction its natural role in onset of labour is contraction its natural role in onset of labour is doubtful .doubtful .
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Diagnosis of labour :-Diagnosis of labour :-Pre labour (premonitory stage :-Pre labour (premonitory stage :-
- May begins two to three weeks before the - May begins two to three weeks before the onset of true labour in PG. and few days onset of true labour in PG. and few days before in multi gravida and may consist of before in multi gravida and may consist of the following .the following .
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

1)Lightening :- 1)Lightening :- A sense of relief from the A sense of relief from the upper abdominal pressure symptoms such upper abdominal pressure symptoms such as dyspnoea or dyspepsia due to sink of as dyspnoea or dyspepsia due to sink of the presenting part into the true pelvis .the presenting part into the true pelvis .
2.Pelvic pressure symptoms such as 2.Pelvic pressure symptoms such as frequency of micturition due to frequency of micturition due to engagement of the presenting part .engagement of the presenting part .
3.Cervical changes (ripening of the cervix) 3.Cervical changes (ripening of the cervix) become soft , less than 1.3cm in become soft , less than 1.3cm in length ,Admit tip of the finger and is length ,Admit tip of the finger and is dilatable .dilatable .
4.Appearance of false pain . 4.Appearance of false pain . www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

True LabourTrue Labour Features of true labour areFeatures of true labour are :-:-1)1) Labour pain:-Labour pain:-- Intermittened painful and regular .Intermittened painful and regular .- Increase progressively in frequency, Increase progressively in frequency,
duration and intensity .duration and intensity .- Felt in the abdomen and radiate to the Felt in the abdomen and radiate to the
back and thighback and thigh . .
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

2)The show2)The show Expulsion of the cervical mucus Expulsion of the cervical mucus plug mixed with blood –may occur few plug mixed with blood –may occur few days before the onset of labour .days before the onset of labour .
3) Progressive effacement and dilatation of 3) Progressive effacement and dilatation of the cervix .the cervix .
4) Formation of the bag of forewater ,the 4) Formation of the bag of forewater ,the lower pole of the fetal membranes become lower pole of the fetal membranes become unsupported and tend to bulge through the unsupported and tend to bulge through the cervical canal . cervical canal .
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Stages of labourStages of labour
Labour is divided into four Labour is divided into four stages:-stages:-
1- 1- First stage of labour:-First stage of labour:-- It is the stage of cervical It is the stage of cervical
dilatation .dilatation .- Starts with the onset of labour Starts with the onset of labour
pain and ends with full pain and ends with full dilatation of the cervix .dilatation of the cervix .
- It takes about 12 hours in a It takes about 12 hours in a Primipara, and 8hrs in a Primipara, and 8hrs in a multipara .multipara .
- It’s composed of two phases .It’s composed of two phases .
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

A) Latent phase:A) Latent phase:
Starts from the onset of labour and ends Starts from the onset of labour and ends when the cervix is (2 to3 cm) dilated . It when the cervix is (2 to3 cm) dilated . It occurs because the thinning of the lower occurs because the thinning of the lower segment and cervix take a lot of uterine segment and cervix take a lot of uterine work before rapid dilatation can begin . It work before rapid dilatation can begin . It takes about (6 to 8 hrs) . takes about (6 to 8 hrs) .
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

B) Active phase :-B) Active phase :- It is the phase of rapid dilatation of the cervix It is the phase of rapid dilatation of the cervix
from 3cm dilatation up to full dilatation it also from 3cm dilatation up to full dilatation it also take (6hrs) with a rate of cervical dilatation of take (6hrs) with a rate of cervical dilatation of (1.2cm/hour)in PG and (1.5cm/hour)in (1.2cm/hour)in PG and (1.5cm/hour)in multigravidamultigravida . .
It has three components:-It has three components:-
i) Accelerated phase of dilatation from i) Accelerated phase of dilatation from (2.5cmto4cm).(2.5cmto4cm).
ii) Phase of maximum slope of (4to9cm) dilatation .ii) Phase of maximum slope of (4to9cm) dilatation .
iii) Phase of deceleration of (9-10cm) dilatationiii) Phase of deceleration of (9-10cm) dilatation . .
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Causes of cervical dilation:-Causes of cervical dilation:-
1.1. Contraction and retraction of uterine Contraction and retraction of uterine musculature (primary force)musculature (primary force)
- Normal uterine contraction occur with - Normal uterine contraction occur with frequency of one every 2-3 minutes with frequency of one every 2-3 minutes with at least 1min between contraction. With a at least 1min between contraction. With a duration of 40-70 seconds and an duration of 40-70 seconds and an intensity of around 50 mmHg & a resting intensity of around 50 mmHg & a resting tone less than 15 mmHgtone less than 15 mmHg
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

The contraction begins in two pace The contraction begins in two pace makers near the utrotubal junction –only makers near the utrotubal junction –only one pace maker is operative in each one pace maker is operative in each contraction. It spread like a wave over the contraction. It spread like a wave over the whole uterus- strong in the funds (fundal whole uterus- strong in the funds (fundal dominance) less strong in the mid zone dominance) less strong in the mid zone and relatively in the lower segment. and relatively in the lower segment.
Relaxation begins simultaneously in all Relaxation begins simultaneously in all areas of the uterus.areas of the uterus.
The force generated by each contraction The force generated by each contraction is applied to the amniotic fluid and directly is applied to the amniotic fluid and directly www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Against the pole of the infant that occupies Against the pole of the infant that occupies the upper segment therefore each time the the upper segment therefore each time the muscle contracts the uterine cavity muscle contracts the uterine cavity becomes smaller and the presenting part or becomes smaller and the presenting part or the fore bag of water lying a head of it is the fore bag of water lying a head of it is pushed down ward in to the cervix this pushed down ward in to the cervix this tends to force it to open or dilatetends to force it to open or dilate..
A more potent factor in cervical dilatation A more potent factor in cervical dilatation however is the retraction of the upper however is the retraction of the upper segment. As this area of the uterus segment. As this area of the uterus becomes shorter and thicker it pulls the becomes shorter and thicker it pulls the lower segment and the dilating cervix lower segment and the dilating cervix upward around the presenting part at the upward around the presenting part at the same time thesame time the
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

uterus contracting directly against the uterus contracting directly against the infant tends to push it through the infant tends to push it through the cervicalcervical opening .opening .
Cervical dilatation in primigravida Cervical dilatation in primigravida occurs from above down ward occurs from above down ward causing progressive shortening of causing progressive shortening of the cervix.( effacement).the cervix.( effacement).
In multigravida effacement and In multigravida effacement and dilatation occurs simultaneously. dilatation occurs simultaneously.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

2. Second stage of labour2. Second stage of labour
It is the stage of expulsion of the fetusIt is the stage of expulsion of the fetus Begins with full cervical dilatation and Begins with full cervical dilatation and
ends with delivery of the fetusends with delivery of the fetus Its duration is about one hour in Its duration is about one hour in
primigravida and ½ an hour in primigravida and ½ an hour in multigravida.multigravida.
Delivery of the fetus is affected in addition Delivery of the fetus is affected in addition to the uterine contraction( primary force) to the uterine contraction( primary force) by voluntary contraction of the abdominal by voluntary contraction of the abdominal muscles with the diaphragm fixed after muscles with the diaphragm fixed after forced inspirationforced inspiration . .
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

This will increase intra abdominal This will increase intra abdominal pressure (secondary force).pressure (secondary force).
This secondary forces have no effect This secondary forces have no effect on cervical dilatation but they are of on cervical dilatation but they are of considerable importance in aiding the considerable importance in aiding the expulsion of the infant from the uterus expulsion of the infant from the uterus and vagina after the cervix is and vagina after the cervix is completely dilated.completely dilated.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

3- third stage of labour:-3- third stage of labour:- comprises the phase of placental separation comprises the phase of placental separation its descent to the lower segment and finally its descent to the lower segment and finally its expulsion with the membrane.its expulsion with the membrane.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

It begins after delivery of the fetus and end It begins after delivery of the fetus and end with expulsion of the placenta and with expulsion of the placenta and membrane.membrane.
Duration is about 10__20 minutes in both Duration is about 10__20 minutes in both primigravide and multigravida.primigravide and multigravida.
Placental separation is due to marked Placental separation is due to marked uterine muscle retraction which reduces uterine muscle retraction which reduces the surface area at the placental site to the surface area at the placental site to about its half but as the placenta is about its half but as the placenta is inelastic a shearing force in instituted inelastic a shearing force in instituted bringing about its separation. the plane of bringing about its separation. the plane of separation runs through the deep spongy separation runs through the deep spongy
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Layer of the decidua basalis Layer of the decidua basalis There are two mechanism of placental There are two mechanism of placental
separation.separation.
1- central separation (Schultz) occur in 80% 1- central separation (Schultz) occur in 80% of cases- detachment of placenta from its of cases- detachment of placenta from its uterine attachment starts at the centre.uterine attachment starts at the centre.
2- marginal separation( Mathews –Duncan) 2- marginal separation( Mathews –Duncan) occurs in 20% of cases. Separation starts occurs in 20% of cases. Separation starts at the margin as it is mostly un supported at the margin as it is mostly un supported
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

After complete separation of the placenta it is After complete separation of the placenta it is delivered by effective uterine contraction and delivered by effective uterine contraction and retraction and expelled out by either voluntary retraction and expelled out by either voluntary contraction of abdominal muscle (bearing contraction of abdominal muscle (bearing down effort) or by manipulative procedures.down effort) or by manipulative procedures.
After placental delivery the uterine sinuses and After placental delivery the uterine sinuses and arterioles are occluded by effective uterine arterioles are occluded by effective uterine contraction and retraction which is the principle contraction and retraction which is the principle mechanism of haemostasis, however mechanism of haemostasis, however thrombosis also occurs and is facilitated by the thrombosis also occurs and is facilitated by the hypercoagulable status of pregnancy.hypercoagulable status of pregnancy.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

4-fourth stage of labour4-fourth stage of labour
Begins immediately after expulsion of the Begins immediately after expulsion of the placenta and membranes and last for one placenta and membranes and last for one hour.hour.
Careful observation of the patient for signs Careful observation of the patient for signs of postpartum hemorrhage is essential.of postpartum hemorrhage is essential.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Mechanism of normal labour:-Mechanism of normal labour:-
It refers to the series of changes in position It refers to the series of changes in position and attitude which the fetus under goes during and attitude which the fetus under goes during its passage through the birth canalits passage through the birth canal
And it consist of the following.And it consist of the following.1)1) Descent of the fetus is a continuous movement Descent of the fetus is a continuous movement
it is slow or insignificant in the first stage of it is slow or insignificant in the first stage of labour but pronounced in the second stage. it labour but pronounced in the second stage. it is completed with the expulsion of the fetus. It is completed with the expulsion of the fetus. It is due to contraction and retraction of uterine is due to contraction and retraction of uterine muscle (primary force). Added in the second muscle (primary force). Added in the second stage by bearing down efforts (secondary stage by bearing down efforts (secondary force).force).
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

2- flexion:-2- flexion:- As the head meet the resistance of the As the head meet the resistance of the
birth canal during descent full flexion is birth canal during descent full flexion is achieved to bring the shortest sub-occipito achieved to bring the shortest sub-occipito bregmatic diameter. Of the head(9.5cm).bregmatic diameter. Of the head(9.5cm).
Flexion is essential for descent since it Flexion is essential for descent since it reduces the shape and size of the plane of reduces the shape and size of the plane of the advancing diameter of the head. the advancing diameter of the head.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

3- internal rotation3- internal rotation
In the second stage of labour the forces In the second stage of labour the forces propel the fetus progressively down the propel the fetus progressively down the birth canal, when the head meets the birth canal, when the head meets the resistance of the pelvic floor the occiput resistance of the pelvic floor the occiput rotates forward to lie under the sub pubic rotates forward to lie under the sub pubic arch with the sagittal suture in the antero-arch with the sagittal suture in the antero-posterior diameter of the pelvic out let . This posterior diameter of the pelvic out let . This internal rotation of the head occurs because internal rotation of the head occurs because with a well flexed head the occiput is with a well flexed head the occiput is leading and meets the slopping gutter of theleading and meets the slopping gutter of the
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Lavatores ani muscles which by their shape Lavatores ani muscles which by their shape direct it anteriorly.direct it anteriorly.
4. extension:-4. extension:- further advances of the head lead to its further advances of the head lead to its
passage through the vulva by a process of passage through the vulva by a process of extension. Once the occiput has escaped extension. Once the occiput has escaped from under the symphysis pubis the head from under the symphysis pubis the head extends with the nape of neck pressed extends with the nape of neck pressed firmly against the public arch. The firmly against the public arch. The successive parts of the fetal head to born successive parts of the fetal head to born through the stretched vulval .out let are through the stretched vulval .out let are vertexvertex , brow and face. , brow and face.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

5- restitution:-5- restitution:- As soon as the head is completely born it As soon as the head is completely born it
resumes its natural position with regard to resumes its natural position with regard to the shoulders by rotating 1/8the shoulders by rotating 1/8thth of a circle in of a circle in the direction opposite to that of internal the direction opposite to that of internal rotation. The neck becomes untwisted and rotation. The neck becomes untwisted and the head is restored to its natural relation the head is restored to its natural relation to the shoulder. to the shoulder.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

6.6. External rotationExternal rotation It is the movement of rotation of the head It is the movement of rotation of the head
visible externally due to internal rotation of visible externally due to internal rotation of the shoulders it carries the head in a the shoulders it carries the head in a movement through 1/8movement through 1/8thth of a circle in the of a circle in the same direction as restitution.same direction as restitution.
7- Birth of shoulders and trunk:-7- Birth of shoulders and trunk:- - Further descent takes place the anterior - Further descent takes place the anterior
shoulder escapes below the symphysis shoulder escapes below the symphysis pubis and by lateral flexion of the spine the pubis and by lateral flexion of the spine the posterior shoulder sweeps over the posterior shoulder sweeps over the perineum. Rest of the trunk is there perineum. Rest of the trunk is there expelled out expelled out
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Management of normal labourManagement of normal labour
First stage:-First stage:- On admission a complete history must be On admission a complete history must be
taken taken Antenatal record is reviewed to discover Antenatal record is reviewed to discover
whether there have been any abnormalities whether there have been any abnormalities during pregnancy during pregnancy
The women general condition is assessed The women general condition is assessed her pulse-blood pressure and temperature her pulse-blood pressure and temperature are recorded are recorded
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

on abdominal examination the on abdominal examination the presentation and position of the fetus and presentation and position of the fetus and the relation of the presenting part to the the relation of the presenting part to the brim of the pelvis are determined brim of the pelvis are determined
Abdominal examination will also show the Abdominal examination will also show the frequency and strength of uterine frequency and strength of uterine contraction .contraction .
The location, rate and regularity of the The location, rate and regularity of the fetal heart tones are also determined.fetal heart tones are also determined.
A vaginal examination will show the A vaginal examination will show the degree of cervical dilation, whether the degree of cervical dilation, whether the membranes are intact or rupture and themembranes are intact or rupture and the
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Position with station of the presenting part.Position with station of the presenting part. A urine specimen is examined for protein A urine specimen is examined for protein
and glucose and a hemoglobin or and glucose and a hemoglobin or haematocrit determination is made.haematocrit determination is made.
Enema:-Enema:- It’s routine use is unnecessary and has no It’s routine use is unnecessary and has no
particular benefit.particular benefit. Usually given early in the first stage of Usually given early in the first stage of
labour to empty the rectum to prevents labour to empty the rectum to prevents soiling of the perineum during the second soiling of the perineum during the second stage. stage.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Shaving or clipping of the Shaving or clipping of the vulval hairvulval hair
Is not necessary Is not necessary Awarm bath or shower is both hygienic Awarm bath or shower is both hygienic
and pleasant.and pleasant.Rest:-Rest:- there is no need for the women to remain there is no need for the women to remain
in bed during early labour. She is allowed in bed during early labour. She is allowed to walk about and to sit. This attitude to walk about and to sit. This attitude prevents venacaval compression and prevents venacaval compression and encourage descent of the presenting part. encourage descent of the presenting part.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Oral intakeOral intake The major risk to be avoided is aspiration The major risk to be avoided is aspiration
of gastric contents, this only occurs in the of gastric contents, this only occurs in the context of general anesthesia.context of general anesthesia.
Intake of solid food must be avoided, low Intake of solid food must be avoided, low fat, low residuce food and drink can be fat, low residuce food and drink can be given.given.
If dehydration needs to be corrected If dehydration needs to be corrected normal saline should be infused. normal saline should be infused.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Bladder care:-Bladder care:- The patient should be encouraged to empty The patient should be encouraged to empty
her bladder frequently as full bladder often her bladder frequently as full bladder often inhibits uterine contraction.inhibits uterine contraction.
If the patient fails to pass urine specially in If the patient fails to pass urine specially in late first stage catheterization is to be done late first stage catheterization is to be done with strict aseptic precautionwith strict aseptic precaution..
Relief of pain:-Relief of pain:- Pethidine (100) mg intramuscularly can be Pethidine (100) mg intramuscularly can be
given when the pains are well estabished. It. given when the pains are well estabished. It. www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

should not be given if delivery is anticipated should not be given if delivery is anticipated within two hourswithin two hours
Epidural analgesia is very effective & do Epidural analgesia is very effective & do not cause depression of fetal respiration not cause depression of fetal respiration
If epidural is not used towards the end of If epidural is not used towards the end of first stage a mixture of nitrous oxide & first stage a mixture of nitrous oxide & Oxygen (Entonox) may be started with the Oxygen (Entonox) may be started with the onset of each contraction.onset of each contraction.
Partogram:-Partogram:- One labour has become established all One labour has become established all
events during labour should be recorded events during labour should be recorded on the partogram.on the partogram.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Cervical dilatation marked in centimeters at Cervical dilatation marked in centimeters at the time of admission to ward and at every the time of admission to ward and at every subsequent examination(2 hourly)subsequent examination(2 hourly)
Descent of head (in cm above or below the Descent of head (in cm above or below the lschael spine).lschael spine).
Frequency, duration and strength of uterine Frequency, duration and strength of uterine contration in (10)min. each half an hour.contration in (10)min. each half an hour.
Fetal heart rate every ½ an hour.Fetal heart rate every ½ an hour. Condition of liquor and time and manner of Condition of liquor and time and manner of
membranes rupture.membranes rupture. moulding of the fetal skullmoulding of the fetal skull
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Dosage of Oxytocin if used Dosage of Oxytocin if used Maternal status (BP- pulse- temp-Maternal status (BP- pulse- temp-
urinalysis).urinalysis). Medication (including epidural block if Medication (including epidural block if
usedused
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Management of the second Management of the second stage:-stage:-
The transition from the first stage to the The transition from the first stage to the second stage is evidenced by the following second stage is evidenced by the following features.features.
- Appearance of bearing down effortsAppearance of bearing down efforts- Complete dilatation of the cervix on Complete dilatation of the cervix on
vaginal examination.vaginal examination.
Principles of management are:-Principles of management are:-
1. To assist in the natural expulsion of the 1. To assist in the natural expulsion of the fetus slowly fetus slowly
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

2- to prevent perineal injuries 2- to prevent perineal injuries General measuresGeneral measures::o FHR every 5 minutes FHR every 5 minutes o Maternal pulse and blood pressure every Maternal pulse and blood pressure every
15mins15minso If epidural block is not used to administer If epidural block is not used to administer
inhalation analgesia (entonox) to relieve pain inhalation analgesia (entonox) to relieve pain during contractionduring contraction
o Vaginal examination to confirm the on set of the Vaginal examination to confirm the on set of the second stage – to detect cord prolapse and to second stage – to detect cord prolapse and to know the position and station of the headknow the position and station of the head
o Nothing is given by mouthNothing is given by mouth
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Preparation for delivery:-Preparation for delivery:- Bearing down efforts, bulging of the Bearing down efforts, bulging of the
perineum and gaping of the anal opening perineum and gaping of the anal opening during contraction signify that delivery is during contraction signify that delivery is imminent so the patient should be shifted imminent so the patient should be shifted to the labour table to the labour table
Position of the patientPosition of the patient
Dorsal position is more widely preferred with Dorsal position is more widely preferred with the thighs flexed and separated . Some the thighs flexed and separated . Some however prefer delivery in lateral or however prefer delivery in lateral or lithotomy position lithotomy position
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Toileting the external genitalia and inner Toileting the external genitalia and inner Side of the thighs with cotton swabs Side of the thighs with cotton swabs soaked in savlon . And the area is covered soaked in savlon . And the area is covered with sterile sheet. Keeping only the with sterile sheet. Keeping only the external genitalia uncovered external genitalia uncovered
The delivery attendant should scrub put on The delivery attendant should scrub put on sterile gown ,mask and glovessterile gown ,mask and gloves
To catheterize the bladder if it is full.To catheterize the bladder if it is full.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Conduction of the deliveryConduction of the delivery The patient is encourage to intensify the The patient is encourage to intensify the
bearing down efforts during contractions.bearing down efforts during contractions. When the scalp is visible for about 5cm When the scalp is visible for about 5cm
diameter flexion of the head is maintained diameter flexion of the head is maintained during contraction by pushing the occiput during contraction by pushing the occiput down wards and back wards by using down wards and back wards by using thumb and index fingers of the left hand thumb and index fingers of the left hand while pressing the perineum by the right while pressing the perineum by the right palm with a sterile vulval pad. This palm with a sterile vulval pad. This process is repeated during subsequentprocess is repeated during subsequent
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

contraction until crowing of the head occurs contraction until crowing of the head occurs (biparietal diameter stretches the vulval (biparietal diameter stretches the vulval out let without any recession of the head out let without any recession of the head even after the contractions is over).even after the contractions is over).
When the perineum is fully stretched and When the perineum is fully stretched and threatens to tear specially in PG threatens to tear specially in PG episiotomy is done at this stage after prior episiotomy is done at this stage after prior infiltration with 10/ml of 1% lignocaine.infiltration with 10/ml of 1% lignocaine.
Slow delivery of the head is accomplished Slow delivery of the head is accomplished by pushing the chin with sterile gauze .by by pushing the chin with sterile gauze .by covered fingers of the right hand placed covered fingers of the right hand placed over the anococcygeal region over the anococcygeal region
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

While the left hand exerts pressure on the While the left hand exerts pressure on the occiput. the forehead, nose, mouth and occiput. the forehead, nose, mouth and the chin are thus born successively over the chin are thus born successively over the stretched perineum by extension.the stretched perineum by extension.
The mucus and blood in the mouth and The mucus and blood in the mouth and pharynx should be wiped with sterile pharynx should be wiped with sterile gauze or alternatively mechanical sucker gauze or alternatively mechanical sucker may be used.may be used.
The neck is then palpated to exclude the The neck is then palpated to exclude the presence of any loop of cord if it is found it presence of any loop of cord if it is found it should be slipped over the head or if it is should be slipped over the head or if it is sufficiently tight it is cut in between two sufficiently tight it is cut in between two pairs of kocher’s forceps.pairs of kocher’s forceps.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Wait for uterine contractions to come and for the Wait for uterine contractions to come and for the movements of restitution and external rotation of movements of restitution and external rotation of the head to occur, the anterior shoulder is born the head to occur, the anterior shoulder is born behind the symphysis. If there is delay the head behind the symphysis. If there is delay the head is grasped by both hands and is gently drawn is grasped by both hands and is gently drawn posteriorly until the anterior shoulder is released posteriorly until the anterior shoulder is released from under the pubis. by drawing the head in from under the pubis. by drawing the head in upward direction the posterior shoulder is upward direction the posterior shoulder is delivered out of the perineum.delivered out of the perineum.
After delivery of the shoulders the fore fingers of After delivery of the shoulders the fore fingers of each hand are inserted under the axillae and the each hand are inserted under the axillae and the trunk is delivered gently by lateral flexion.trunk is delivered gently by lateral flexion.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Some delay in clamping and cutting the Some delay in clamping and cutting the umbilical cord probably is beneficial to the umbilical cord probably is beneficial to the infant. As much as a 75 to 100ml increase infant. As much as a 75 to 100ml increase in fetal blood volume can be anticipated.in fetal blood volume can be anticipated.
The infant is placed in a heated crib with The infant is placed in a heated crib with its head slightly lower than its body. Its air its head slightly lower than its body. Its air passage should be cleared of Mucus by passage should be cleared of Mucus by sucker before vigorous respiratory efforts sucker before vigorous respiratory efforts are established.are established.
Apgar rating at 1 minute an at 5 minute is Apgar rating at 1 minute an at 5 minute is to be recorded to be recorded
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

A sterile cotton thread is applied to the A sterile cotton thread is applied to the cord 2.5cm away from the navel & the cord 2.5cm away from the navel & the cord is divided with scissors about 1 cm cord is divided with scissors about 1 cm beyond the ligature.beyond the ligature.
Episiotomy:-Episiotomy:- Defined as a planned surgical incision of Defined as a planned surgical incision of
the perineum made to increase the the perineum made to increase the diameter of the vulval outlet during diameter of the vulval outlet during childbirth (perineotomy)childbirth (perineotomy)
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Types of episiotomyTypes of episiotomy 1-midline:- 1-midline:-
the cut is made vertically from the fourchette the cut is made vertically from the fourchette down towards the anus.down towards the anus.
Advantages of this incision are less blood loss, Advantages of this incision are less blood loss, is easier to repair, the wound heals quicker, and is easier to repair, the wound heals quicker, and less postpartum pain and dyspareunia. The less postpartum pain and dyspareunia. The major disadvantage it carries a higher risk to major disadvantage it carries a higher risk to extend to involve the anal sphincter.extend to involve the anal sphincter.
2-mediolateral:-2-mediolateral:- This incision starts in the midline of the This incision starts in the midline of the
fourchette and then directed outwards to avoid fourchette and then directed outwards to avoid the anal sphincterthe anal sphincter
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

management of the management of the third stage:third stage:
Two methods of management are currently Two methods of management are currently in practice in practice
1.1. Watchful expectancy:-Watchful expectancy:-- In this management the placental - In this management the placental
separation and its descent into the separation and its descent into the vagina are allowed to occur vagina are allowed to occur spontaneously. When the features of spontaneously. When the features of placental separation at its descent into placental separation at its descent into
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

the lower segment are confirmed the patient the lower segment are confirmed the patient is asked to bear down simultaneously with is asked to bear down simultaneously with uterine contraction. The raised intra- uterine contraction. The raised intra- abdominal pressure is often adequate to abdominal pressure is often adequate to expel the placenta. If the patient fail to expel the placenta. If the patient fail to expel the placenta. controlled cord traction expel the placenta. controlled cord traction (Brandt- Andrews method) can be tried. (Brandt- Andrews method) can be tried. The palmer surface of the fingers of the The palmer surface of the fingers of the left hand is placed approximately at the left hand is placed approximately at the junction of upper and lower uterine junction of upper and lower uterine segment the body of the uterus is segment the body of the uterus is displaced upwards and backwards displaced upwards and backwards towards the umbilicus while by the right towards the umbilicus while by the right hand steady tension is given in hand steady tension is given in
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

Downwards and backward direction until the Downwards and backward direction until the placenta comes outside .placenta comes outside .
Signs of placental separation:-Signs of placental separation:-
1. A show of blood appears as the uterus 1. A show of blood appears as the uterus contracts.contracts.
2. Lengthening of the cord 2. Lengthening of the cord
3. The fundus become globular in shape, 3. The fundus become globular in shape, rises above the umbilicus, become rises above the umbilicus, become palatable. palatable.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

2. Active management:-2. Active management:- Is associated with reduced blood loss.Is associated with reduced blood loss. I.V ergometrine or syntometrine I.V ergometrine or syntometrine
(syntocinon 5 units +ergometrine 0.5mg) is (syntocinon 5 units +ergometrine 0.5mg) is given with delivery of the anterior given with delivery of the anterior shoulder.shoulder.
The placenta is immediately delivered The placenta is immediately delivered after delivery of the baby by controlled after delivery of the baby by controlled cord traction after insuring uterine cord traction after insuring uterine contraction contraction
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

As soon as the placenta passes through the As soon as the placenta passes through the introitus it is grasped between the hands and introitus it is grasped between the hands and twisted around and round with gentle traction so twisted around and round with gentle traction so that the membranes are stripped intact.that the membranes are stripped intact.
The placenta and the membranes should be The placenta and the membranes should be examined following their expulsionexamined following their expulsion
Vulva-vagina and perineum are inspected Vulva-vagina and perineum are inspected carefully for injuries and to be repaired if any. carefully for injuries and to be repaired if any. the episiotomy is sutured. The vagina is the episiotomy is sutured. The vagina is evacuated from blood clots . The area is evacuated from blood clots . The area is cleaned and a dry sterile vulval pad is placed.cleaned and a dry sterile vulval pad is placed.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd

The maternal condition –pulse –blood The maternal condition –pulse –blood pressure. Behavior of the uterus and any pressure. Behavior of the uterus and any abnormal vaginal bleeding is to be abnormal vaginal bleeding is to be watched at least for one hour after delivery watched at least for one hour after delivery (fourth stage of labour).(fourth stage of labour).
When fully satisfied that the general When fully satisfied that the general condition is good pulse and blood condition is good pulse and blood pressure are steady the uterus is well pressure are steady the uterus is well contracted and there is no abnormal contracted and there is no abnormal vaginal bleeding the patient is sent to the vaginal bleeding the patient is sent to the ward. ward.
www.doctor.sdwww.doctor.sd