NEURON
description
Transcript of NEURON
PowerPoint Presentation
NEURON Lecture slides are Prepared by Dr.Mohammed Sharique Ahmed QuadriDr. Shaikh Mujeeb AhmedAssistant prof. PhysiologyAl Maarefa CollegeOBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture you should be able to
Describe the functional structure of neuron Cell body, Dendrites, Axon.
List the types of Nerve Conduction
List the factors that affecting nerve conduction
Illustrate the functional importance of is myelin sheath & Node of Ranvier
Discreminate between Contiguous Conduction and Saltatory Conduction
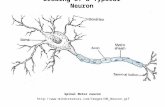
2Neuron (nerve cell) consists of Three Basic Parts : 1 Cell Body 2 Dendrites 3 Axon 3NEURONNeuronCell bodyHouses the nucleus and organellesDendrites Project from cell body and increase surface area available for receiving signals from other nerve cellsSignal toward the cell body
Dendrite and cell body serve as the neurons input zone. 4NeuronAxonNerve fiberSingle, elongated tubular extension that conducts action potentials away from the cell bodyConducting zone of the neuron5
Axon
Axon hillockFirst portion of the axon plus the region of the cell body from which the axon leavesNeurons trigger zone(where Action Potential are generated).
Axon terminalsRelease chemical messengers that simultaneously influence other cells with which they come into close associationOutput zone of the neuron
6Neuron
7REMEMBER Dendrites & cell body Input zone ( Receive) Axon -- Conducting zone Axon Terminals Output zone
Action Potential are initiated at Axon Hillock (trigger zone)8NEURON (cont)Action Potentials are propagated from the Axon Hillock to the Axon terminalIn cell body Graded Potentials (Local potentials) are produced in response to incoming signals.
Action potentials are Initiated at the Axon Hillock, and conducted throughout a nerve fiber
9Conduction of Action PotentialsTwo types of propagationContiguous conductionConduction in unmyelinated fibersAction potential spreads along every portion of the membraneSaltatory conduction Rapid conduction in myelinated fibersImpulse jumps over sections of the fiber covered with insulating myelin
10Contiguous Conduction
11Myelinated Fibers
12Saltatory Conduction
13Saltatory Conduction: Action Potential Propagation in a Myelinated Axon14
Saltatory ConductionPropagates action potential faster than contiguous conduction because action potential does not have to be regenerated at myelinated sectionMyelinated fibers conduct impulses about 50 times faster than unmyelinated fibers of comparable sizeMyelin Primarily composed of lipidsFormed by oligodendrocytes in CNSFormed by Schwann cells in PNS15
16Conduction depends on Two factors: 1) Diameter of the nerve fiber 2) Axon (Nerve fiber) is Myelinated or Unmyelinated 17CONDUCTION IN NERVE FIBERSDiameter of Nerve fiber Nerve fiber with small diameter conducts slowly Nerve fiber with large diameter conducts fast
18CODUCTION IN NERVE FIBERS (cont)Myelinated Nerve Fibers Myelinated nerve fibers conduct FAST then Unmyelinated nerve fibers. Why? Myelinated nerve fibers have saltatory conduction.19CONDUCTION IN NERVE FIBER (cont)20
SUMMARY
Small diameter fiber conduct SLOW Large diameter fiber conduct FAST Myelinated nerve fiber conduct VERY FAST.21CONDUCTION IN NERVE FIBER (cont)Regeneration of Nerve FibersRegeneration of nerve fibers depends on its locationSchwann cells in PNS guide the regeneration of cut axonsFibers in CNS myelinated by oligodendrocytes do not have regenerative abilityOligodendrocytes inhibit regeneration of cut central axons
22ReferencesHuman physiology by Lauralee Sherwood, seventh editionText book physiology by Guyton &Hall,11th editionText book of physiology by Linda .s contanzo,third edition
23