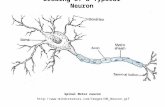
Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) and Lower Motor Neuron (LMN)
Transcript of Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) and Lower Motor Neuron (LMN)

Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) and Lower Motor Neuron (LMN)
UMN
♦ NervetractsthatoriginateorendinthesamecortexàButoncetheycometothepointofbecomingemergingnervestheynolongerarenervetracts,nutnowNERVES
♦ Interfacewithnuclei♦ SpinalNervesgototheSpinalCord♦ CranialNervesgototheBrainSteam♦ DamagetotheUMNResultsinacontralateraldamage:(BothSides,beforeCrossover)
LMN
♦ AKAthefinalcommonpathway♦ Thispathwayinnervatestheorgans♦ Thenervesmakecontactwithmusclesthatmoveorfeelsensation♦ CranialandSpinalNerves♦ ControlsvolitionalandSensoryMotorActivity
àEx:SpeakingandWalking♦ DamageinLMNresultsinipsilateraldamage:(Sameside,aftercrossover)

Let’s talk about the…. Spinal Nerves: 31 pairs
Theyinnervatebothsidesofourbodies
Theyarebothmotorandsensory♦ Partofmotortractoriginatingfromprimarymotorcortex♦ Corticalspinalakaspinalnerveswithinthepyramidaltract♦ Partofthesensorytractoriginatesfromtheprimarysensory
cortex
♦ Controls:àVoluntaryMovementsofmusclesinthebody
ex:walking,lifting,sittingàSensoryResponsestoexternalstimuli ex:touch,temp,pain,proprioception
♦ ApartoftheperipheralSomato-SensoryNervousSystem♦ Thesenervesarisefromthespinalcordinpairs
♦ Innervatemusclesonthesamesidethattheyarisefrom Therearethreedifferenttractsusingthespinalnerves:
1. PosteriorColumnTract2. SpinothalamicTract(ThalamustoSpinalCord)3. SpinocerebellarTract(InvolvestheCerebellum)
SpinalNervesaredivided
8Cervical-beginsfromtheneck
12Thoracic–fromthenecktoupperchest5Lumber–hipregion
5Sacral–tailboneregion1Coccygeal–tailboneregion
Spinal Nerves support in speech/language/hearing àHaveasmallcontributiontohelpingusbreath!
à This is a source of power!

http://www.pacemakerplus.com/diaphragmatic-pacing-phrenic-nerve-pacing-twitching-after-a-pacemakericd-implant/
Phrenic Nerve – Innervates the diaphragm
Cranial Nerves
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cranial_nerves
**NotallCranialNervesarerelatedtoSpeech!**

CranialNervesRelatedtoSpeech:V.TrigeminalNerve(Mixed,MotorandSensory)VII.FacialNerve(Mixed)VIII.AuditoryNerve(Sensory)IX.GlossopharyngealNerve(Mixed)X.VagusNerve(Mixed)XI.AccessoryNerve(Motor)XII.Hypoglossal(Motor)Let’sbrieflygooverallthenervesbutweshallgoindepthinthe
SpeechrelatednervesonlyV,VII,VIII,IX,X,XI,andXIIarespeechrelated.
http://courseimage.com/popular

12 Cranial Nerves:
♦ Theyarepartofthecorticonuclear/corticobulbartractwithinthepyramidaltract
♦ Receivesimputefromcortexandextrapyramidalpathways♦ CranialNerveswithBilateralUMNinnervation
àTheseInclude:V,VII(upperface),IX,X,XI♦ CranialNerveswithPrimaryContralateralUMNinnervation
àTheseinclude:VI,(lowerface),XII
Let’s talk about the Cranial Nerves Involved in
speech a little more!
http://kingessays.org/
Trigeminal (V): Motor & Sensory Function:Chewingandhelpswitharticulation
o FacialMusclesinvolved1. Masseter(HelpsChew)2. Temporalis(ForeHead)3. LateralandMedialPterigiods4. TensorTypana5. TensorVeliPalatini6. Mylohyliod7. Partsofdigastricmuscle

o Has3SensoryBranches1.Ophthalmic:Forehead,Eyes,Nose2.Maxillary:CheekArea,UpperLip,Palate,UpperTeeth,Gums3.Mandibular:Jaw(MandibleandMaxilla)
**If people have symptoms such as not being able to move there jaw
well and there ear is numb, this nerve might be damaged!**
Have you ever had a brain freeze? That’s because of this nerve!
Facial (VII): Sensory and Motor Function:movementoftheEyesandTongue
o àTaste(2/3anteriortongue)àEx:SweetorSaltyàHasalottodowithmusclesofthehearingpathwayàCansensemusclesvibratingsuchaseardrumàCancausestapediusmuscletocontract
http://erquiznpics.blogspot.com/2011/02/case-3.html

The picture above shows what could occur when there is damage in the facial nerve
Vestiblarcochlear/Auditory (VIII): Sensory Function:Hearing Glossopharyngeal (IX): Motor & Sensory Function:Salivation,Gagreflex,tastes(1/3)ofthetongueVagus (X): Sensory and Motor Function:Digestion,VocalFoldsforpitch,swallowing,andhelpsuskeepfoodawayfromourtrachea!
o **VagusNerveiswrappedaroundtheheart** àifthisnerveis“accidently”cutduringsurgerythenthe patientwillbenonverbal/vocal
http://www.canstockphoto.com/vector-clipart/couple-sad.html
Spinal Accessory (XI): Motor Function:neckandshouldermovementàEffectiveinPostureàTurningtheheadàRespiration Hypoglossal (XII): Motor
o Function:Innervationoftongue