Dr. Ahmed Fathalla Ibrahim. MITOSIS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MITOSIS & MEIOSIS.
Mitosis&CellCycle
description
Transcript of Mitosis&CellCycle
-
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
-
MitosisMitosis is the dividing of the cell after Nuclear Replication.
-
The Body is Composed of 2 Types of Cells
-
Germ CellsGerm Cells are the sex cells.They are specialized and capable of going under meiosis.They are found only in the gonads.Results in half of the number of original chromosomes in each new cell.
-
Somatic CellsThese are the body cellsThey compose tissues and organs and other parts of the body.
-
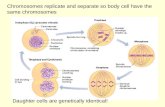
The Cell CycleThe Cell Cycle consists of 4 phases. It also includes interphase.The 4 phases are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
-
InterphaseCell will spend almost 90% of it time in the normal cellular cycle in interphase.Late in interphase the nucleus is well defined and contains one or more nucleoli.Chromosomes can not be distinguished although they have been replicated.
-
ProphaseIn the nucleus the chromatin fibers become more tightly coiled.The nucleoli disappearMitotic Spindle begins to form.Spindle fibers appear between the centrioles
-
Prophase (cont)The centrioles split and then move to different sides of the nucleus.
-
PrometaphaseThe nuclear membrane dissolves.Proteins attach to the centromeres creating kinetochores.The chromosomes begin moving.
-
MetaphaseSpindle Fibers align the chromosomes along the middle of the cells nucleus.The line is called the metaphase plate.
-
AnaphaseThe paired chromosomes separate at the kinetochores and move to opposite side of the cell.Each Chromatid is now considered a chromosome.
-
Anaphase (cont)The cell becomes longer because the poles move farther apart lengthening the microtubules.In the end of Anaphase, both poles have the exact same and full collection of chromosomes.
-
TelophaseThe spindles fibers disappear.Chromosomes disperse.Cytokenesis Begins in this stage.
-
CytokinesisIn cytokinesis the cell splits and two daughter cells reamain, to regrow and then reproduce more cells.It pinches off the cytoplasm of the original cell and creates two new cells.
-
G1 PhaseThe G1 stage is for growth and preparation of the chromosomes for replication.
-
S PhaseCell growth happens in this phase.Chromosomes are duplicated only during this stage.
-
G2 Phase
Cell is still growing and in this phase, it completes the preparations for cell division.
-
M or Mitotic PhaseThis is where the cell actually undergoes mitosis.This phase also includes cytokinesis.
-
G0 PhaseThis is a stage where the cell is not able to replicate itself. Many of the human bodys cells are in G0 like specialized muscle cells, which do not replicate themselves.
-
VocabA kinetochore is a specialized region on the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the the mitotic spindle.
-
VocabAster=Microtubules that extend from the centrosomes in radial arrays.Furrowing(cytokinesis)=Indention of the cytoplasm until the seperation of the duaghter cells is complete.Tetraploid=an organism that has four pair of homologous chromosomes. This is mostly found in plants
-
Vocab (cont)Chromatin= A mass of genetic material composed of DNA and proteins that condense to form chromosomes in eukaryotic cell division. Located in the cells nucleus.Chromosome= Condensed version of a chromatin in a dividing cell.
-
Vocab (cont)Diploid= Total number of chromosomes in the cells nucleusHaploid= Total number of each kind of chromosomes. This equals half the number of diploid cells.
-
Vocab (cont)Centromere= The protein structure that connects the two indentical halves of the chromosome.Different ChromosomesHumans have 22 autosomes which are responsible for protein synthesis.Sex chromosomes are the chromosomes that determine the sex of the individual.
-
Vocab (cont)Homologous PairsThese are chromosomes that are paired.They have the same function and responsibilities as the other it is paired with.They are usually the same size