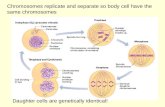
The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Cytokinesis.
Mitosis Tutorial
-
Upload
jbrander -
Category
Technology
-
view
2.671 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Mitosis Tutorial

Mitosis Tutorial
By Jon Brander
ED 205 Section 2 Quit

Mitosis- What is Mitosis?- Stages of Mitosis
- Interphase- Prophase- Prometaphase- Metaphase- Anaphase- Telophase- Cytokinesis
- Why Mitosis?- Authors Page- Resources Quit

What is Mitosis
• Mitosis is the division of the nucleus and is often followed by cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm. This creates two genetically identical cells.
• Mitosis occurs in a series of different stages.
• Mitosis occurs exclusively in eukaryotes, but occurs in different ways in other species.
• Mitosis and Cytokinesis are the shortest phases of the cell cycle. The longest phase being Interphase.
Quit

Interphase
- Interphase is not technically part of mitosis, but is often included.
- During interphase the cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division.
- Chromosomes are not clearly discerned, although a dark spot called the nucleolus may be seen.
- Also the cells may contain a pair of centrosomes, which are responsible for microtubule organization during mitosis.
Quit

Prophase
- Chromatin Fibers become tightly coiled and chromosomes become evident.
- The nucleolus disappears and the mitotic spindle begins to form.
- The mitotic spindle is composed of the centrosomes (centrioles) and the mitotic spindles that extend from them.
- Also the centrosomes begin to move away from one another
Quit

Prometaphase
- The Nuclear envelope dissapears and the mitotic spindles begin to interact with the chromosomes.
- Each of the two chromatids of the chromosome has a kinetochore attached to its centromere.
Quit

Metaphase
- Metaphase is the longest stage of mitosis.
- The centromeres are now at opposite ends of the cell.
- The chromosomes meet in the middle of the cell along the metaphase plate.
- Each sister chomatid is attached to a kinetochore from the opposite pole.
Quit

Anaphase
- Anaphase is the shortest phase of Mitosis.
- The two sister chromatids split to form chromosomes.
- The two chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell as the kinetochores shorten
- The cell elongates- At the end of anaphase each
side of the cell has equal amounts of chromosomes.
Quit

Telophase
- Two daughter nuclei begin to form in the cell and nuclear envelopes begin to form.
- Chromosomes become less condensed.
- Mitosis: The division of one nucleus into two genetically identical nuclei, is now complete.
Quit

Cytokinesis
- The division of the cytoplasm usually begins during late telophase, so two daughter cells appear shortly after mitosis.
- In animals cytokinesis involves a cleavage furrow, which pinches the cell in two.
Quit

Why Mitosis?- Mitosis allows for the reproduction of multiple identical
cells. - This allows for new skin cells to be produced when old
ones fall off or wounds to be repaired.- Mitosis also plays a role in ones growth and
development.
VIDEOS
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlN7K1-9QB0
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s1ylUTbXyWU
Interactive Animation
- http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm
Quit

The Author
- Hello, My name is Jon. I am a student at Grand Valley State University. I am studying for a secondary education degree with a major in biology and a minor in chemistry. I love to be outside and enjoy participating in many different sports, including wakeboarding.
EMAIL ME
Quit

Resources
-Biology 7th Edition. 2005. Campbell and Reece
- Google Images
http://images.google.com/imghp?hl=en&tab=wi- Interactive Animation
http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm- Videos
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlN7K1-9QB0
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s1ylUTbXyWU
Quit