Microbio - Agars and Media
description
Transcript of Microbio - Agars and Media

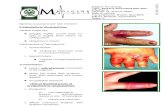
MacConkey Agar:
click image to enlarge
- Contains bile salts - Inhibit G(+) bacteriaLactose fermenters turn the colonies pink.Colonies of the non-lactose fermenters are colourless.
Eosin methylene blue:
click image to enlarge
click image to enlarge
- Inhibit G(+) bacteriaBacteria that ferment lactose, especially the coliform bacterium Escherichia coli, appear as colonies with green metallic sheen or blue–black to brown color. Bacteria that do not ferment lactose appear as colorless or transparent light purple colonies
Hektoen Enteric Agar:
click image to enlarge
Medium designed to isolate and differentiate members of the species Salmonella and Shigella from other Enterobacteriaceae. - Bile salts and the dyes bromthymol blue and acid fuchsin inihibit the growth of most G(+) organisms. - Lactose, sucrose, and salicin provide fermentable carbohydrates to encourage the growth and differentiation of enterics.- Sodium thiosulfate provides a source of sulfur. Ferric ammonium citrate also allows the visualiztion of hydrogen sulfide production by reacting with hydrogen sulfide gas to form a black precipitate. Salmonella typhi : Colorless colonies, black centers.
Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Salt Sucrose agar plate (TCBS)
click image to enlarge
- For the selective isolation of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus from a variety of clinical specimens and in epidemiological investigations.Vibrio cholerae : Growth (yellow colonies)Vibrio parahaemolyticus : Growth (green colonies)Staphylococcus aureus : No growth

Chocolate Agar:
click image to enlarge
Is prepared by adding sheep blood to an enriched agar base when the temperature of the medium is high enough to lyse the red cell without inactivating the NAD (V factor) and hematin (X factor) in the blood lysate (about 80C)
Thayer Martin VCN:
click image to enlarge
- with 5% chocolate sheep blood plus- Vancomycin, which is able to kill most Gram-positive organisms- Colistin, which is added to kill most Gram-negative organisms except Neisseria- Nystatin, which can kill most fungi.
Blood Agar:
click image to enlarge
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (extra)greenish-metallic appearing colonies (production of the pigments pyoverdin and pyocyanin)