Metamorphic rocks process of formation 2014
description
Transcript of Metamorphic rocks process of formation 2014

Learning Goal: Understand how metamorphic rocks are formed and classified.

S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formedc. Classify (group) rocks
(metamorphic) by their process of formation (formed)

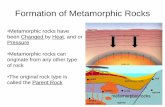
Rocks that have changed (metamorphism) due to HEAT and PRESSURE.
These rocks form
DEEP underground!
Pressure from plate movementfolds and buckles the crust.
Magma heats up surrounding rock.

Metamorphic rocks are formed by the effect of heat and pressure on existing rocks.
This can greatly affect the hardness, texture or layer patterns of the rocks.
Magma
metamorphic
rockforming
here
heat
Pressure from surface rocks

Metamorphic rocks are classified by texture in 2 ways…
1.Foliated2.Non-Foliated

The processes of compaction and recrystallization change the
texture of rocks during metamorphism. Compaction
The grains move closer together.The rock becomes more dense.Porosity is reduced.
Example: clay to shale to slate
RecrystallizationGrowth of new crystals. No changes in overall chemistry. New crystals grow from the minerals already present. A preferred orientation of minerals commonly develops under applied pressure. Platy or sheet-like minerals such as muscovite and biotite become oriented perpendicular to the direction of force. This preferred orientation is called foliation.

Mineral grains flatten and line up in parallel bands OR layers.
Slate:
Foliated (with layers)
Gneiss:
Foliated (with banding)
That are formed under directed pressure

Foliated TextureFoliated Texture

Foliated TexturesFoliated Textures• Slatey
- looks like blackboard> dull surface
- smooth, thin layering- breaks into flat slabs
> referred to as slatey cleavage
- no mineral grains visible
• Phyllitic
- looks like waxed surface> has a "sheen" to it
- may have little "waves" onsurface> referred to as crenulations
- some small grains visible
• Slatey
- looks like blackboard> dull surface
- smooth, thin layering- breaks into flat slabs
> referred to as slatey cleavage
- no mineral grains visible
• Phyllitic
- looks like waxed surface> has a "sheen" to it
- may have little "waves" onsurface> referred to as crenulations
- some small grains visible
• Schistose
- - visible grains
> garnets, staurolites
- may have shiny
> due to mica minerals
• Gneissic
- larger grains- may look like igneous rock- may have crude banding
> intensely distorted
- different minerals thanschistose
• Schistose
- distinct bands of minerals- visible mineral grains
> garnets, staurolites
- may have shiny
appearance > due to mica minerals
• Gneissic
- larger grains- may look like igneous rock- may have crude banding
> intensely distorted
- different minerals thanschistose

QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Foliated MM RocksFoliated MM Rocks
slateslate
schistschist gneissgneiss
phyllitephyllite
MM Rocks that could form as a shale (sedimentary) parent rock isMM Rocks that could form as a shale (sedimentary) parent rock isexposed to increasing directed pressure and temperature

Mineral grains change, grow, and rearrange, but don’t form bands or layers.
Quartzite Marble
Formed under uniform pressures

• Marble:- metamorphosed
limestone
•
Quartzite:-
metamorphosed sandstone
• -
Non-foliated RocksNon-foliated Rocks Examples
Quartzite forms in two different ways.
In the first way, under the high pressures and temperatures of deep burial, sandstone

Metamorphic ZonesMetamorphic Zones

• Metamorphism is common along most plate boundaries like this.
Metamorphic ZonesMetamorphic Zones

The Types of MetamorphismRead this slide
Then use the next two sides to complete the chart
Regional Orogenic Metamorphism is the type of metamorphism associated with convergent plate margins
• Dynamo-thermal: one or more episodes of orogeny with combined elevated geothermal gradients and deformation (deviatoric stress)
• Foliated rocks are a characteristic product

Depth,km
0
35
75
Asthenosphere
Continental crust
Regional metamorphism Oceanic
crust
Oceaniclithosphere
ShockShockmetamorphismmetamorphism
RegionalRegionalmetamorphismmetamorphism
RegionalRegionalhigh-pressurehigh-pressuremetamorphismmetamorphism
ContactContactmetamorphismmetamorphism
Continental mantle lithosphere
Water
SeafloorSeafloormetamorphismmetamorphism
Types of metamorphism

Depth,km
0
35
75
Asthenosphere
Continental crust
Regional metamorphism Oceanic
crust
Oceaniclithosphere
ShockShockmetamorphismmetamorphism
RegionalRegionalmetamorphismmetamorphism
RegionalRegionalhigh-pressurehigh-pressuremetamorphismmetamorphism
ContactContactmetamorphismmetamorphism
BurialBurialmetamorphismmetamorphism
Continental mantle lithosphere
Types of metamorphism



Sedimentary Igneous or Metamorphic
Pressure PressureHeat Heat
MetamorphismEffect
Classification based on Texture
G r a i n s
Heat & PressureFoliated Nonfoliated
NO
Layers Bands
Gneiss
Schist
Phyllite
Slate
PRESSURE
HEAT
↑ Flatten Grains ↑
Layers
Bands
Gneiss
SlateQuartzite Marble
Sedimentary Igneous or Metamorphic Rock
PressureHeat He
att
Heat


Learning Goal: Understand how metamorphic rocks are formed and classified.
Do Now Q: What features do foliate metamorphic rocks show?