Metamorphic Rocks:
description
Transcript of Metamorphic Rocks:

Metamorphic Rocks:• Meta = change Morph = form• Metamorphic rocks form from changes to pre-
existing rock caused by heat and pressure• Metamorphism can occur locally over a small area,
or over a large area covering many kilometers


Two Types of Metamorphism...• Regional Metamorphism - heat and pressure are
significant over a wide area (many kilometers)• Contact Metamorphism - occurs over a small area
when pre-existing rocks come into contact with hot liquid magma from an igneous intrusion.

Metamorphic Rocks...• Classified on the basis of type of metamorphism
(Regional or Contact) and texture:– Foliated (occurs w/regional metamorphism)– Non-foliated (usually occurs w/ contact metamorphism)


Regional Metamorphism• Changes to rock over a large area• Layers of rock deep in the Earth’s crust experience the
following:– 1. High temperatures (depth and friction)– 2. High pressures (weight and crustal movement)– 3. Exposure to hot liquids, water, and gases
• Results:– Mineral grains are compressed– minerals “migrate” through rock and begin to separate– minerals are aligned within rock in response to
pressures to produce foliation

Regional Metamorphism...• Foliation - the alignment of minerals within a
rock caused by heat and pressure
This sample is clearly foliated. see the mineral alignment???

Draw the foliation that results from regional metamorphism
BEFORE AFTER

Metamorphic Grade (degree of metamorphism)
Clearly “banded” appearance as
minerals separate into alternating
bands
Visible mica grains; foliation obvious;
other minerals may be seen.
Micas still microscopic, but begin to reflect
more light; “silky” sheen in appearance
Harder, microscopic mica minerals begin to
form, less air space; dull shine
Clay minerals, stratified, soft, and
fragile, dull in appearance
GNEISSSCHISTPHYLLITESLATESHALE
Sedimentary Rock
Low-Grade Metamorphic
Rock
Medium-Grade Metamorphic
Rock
Medium-Grade Metamorphic
Rock
HIGH-Grade Metamorphic
Rock

This nice piece of schist has large, visible garnet crystals in it.
This sample of schist shows mica minerals that have grown large enough to reflect light.

Here is another gneiss which shows distinct banding due to mineral alignment. The arrows indicate how this sample was squeezed by pressure at great depth below ground.

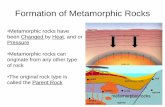
Contact Metamorphism• Occurs over as small area around magma (igneous
bodies)– country rock (pre-existing, in-place) is baked by the hot
temperatures associated with magma– hot liquids and gases mix with country rock
• Results:– minerals migrate and fuse together– no foliation or alignment since pressure is not significant

Contact metamorphism has occurred around this igneous intrusion.

Draw layers of rock getting metamorphosed by coming into contact with magma

Metamorphism – Parent Rock Definition• Parent Rock - the pre-existing rock from which a
metamorphic rock forms

MetamorphismSedimentary
MaterialSedimentary
RockMetamorphic
RockPebbles, gravel, sand Conglomerate Quartzite, Gneiss
Sand Grains (usuallyquartz)
Sandstone Quartzite
Clay (usually kaolin),Silt
Shale, Mudstone Slate, Phyllite,Hornfels, Schist
Lime (shells,fragments, grains)
Limestone Marble

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• Metamorphic Rocks form from changes to other rocks in response to pressure and heat
• TRUE

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• Metamorphic rocks are classified by their mineral composition primarily
• FALSE. Metamorphic rocks are classified on the basis of texture and type of metamorphism

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• Foliation in metamorphic rocks is the alignment of minerals in response to high temperatures along with great pressure.
• TRUE!

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• Only contact metamorphic rocks experience foliation.
• FALSE. Regional metamorphic rocks become foliated due to high pressure in addition to high temperatures

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• Shale is a low-grade metamorphic rock
• FALSE. Shale is a sedimentary rock.

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• Middle to high grade metamorphic rocks appear shiny because as mica minerals crystallize they begin to reflect light.
• TRUE!

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• Extremely high grade metamorphic rocks experience more alignment of minerals into distinct bands.
• TRUE.

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• Rocks that come into contact with an igneous intrusion will only change into igneous rocks.
• FALSE. The high heat near an igneous intrusion will “burn” the surrounding rock and change it into metamorphic rock.

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• The pre-existing rock that was changed into a metamorphic rock is called the “Grandma” rock.
• FALSE. The original rock is called the parent rock.

Metamorphic Rock Quiz...
• The sedimentary rock limestone can become changed by metamorphism into a metamorphic rock called marble.
• TRUE.