Metamorphic Rocks
description
Transcript of Metamorphic Rocks

Metamorphic Rocks

C. Metamorphic Rocks
1. Metamorphism means to ______.change
changes to …SHALE
GNEISS

2) Form when a rock of any type (igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic) is put under ____ and _______ to become a new metamorphic rock.
3) The new metamorphic rock will be similar to its parent rock, but will be more _____ and less porous.
heat pressure
dense

F. Identification of Metamorphic rocks:1) ________: is when minerals begin to line up
at a ___degree angle to the direction of the pressure. Some minerals will have moved and changed into new types.
Foliation90

2) ________: is a type of foliation where enough minerals have ________ to make clearly visible ______.a. These bands are not to be confused
with the Layers of sedimentary rocks. If the rock has visible grains and particles, it is NOT metamorphic.
b. Metamorphic Banding will usually be curved, while Sedimentary Layers will usually be ____.
Bandinglined up
bands
flat

Banding, Foliation, or Sedimentary Layers?
FoliationBanding Sedimentary
Layers

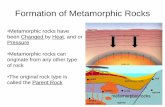
3) Metamorphic rocks are formed in two ways:a. _____________________: This happens
under ______ ________ as the rock is forced upward from the _______ of two crustal plates. This adds a great amount of ____ and _______ to the rock layers. The result is a high degree of _____________ (change).
Regional Metamorphismintense pressure
collision
heat pressuremetamorphism

Sandstone changes into _________. Limestone changes into ______. Siltstone changes into _______. Shale changes into ____, then ______, then _______, then finally ______.
QuartziteMarbleHornfels
Slate PhylliteSchist Gneiss

b. ____________________: This is where an igneous intrusion (such as a ‘sill’) forces and melts its way through the layers of old rock. Where the ______ touches the other layers of rock, they become hot, changed and then _____________ by the intense _____. There is not much ________ applied here, which results in a lower metamorphic change.
Contact Metamorphism
magma
metamorphisize HEATpressure