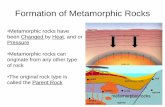
Metamorphic rocks
-
Upload
north-gwinnett-middle-school -
Category
Technology
-
view
3.481 -
download
0
Transcript of Metamorphic rocks

Meta=changeMorphic=form/
shape

I. Parent Rocks
Rocks that have been changed from an original “parent”
rock



II. How are Metamorphic Rocks Formed?
Formed under tremendous heat, great pressure, and chemical reactions
Can make new minerals Most are found on or near plate
boundariesMetamorphism is changing one type of
rock into another as a result of heat(from mantle), Pressure (from layers above) and/or chemical reactions.


III. Where does the Heat Come From?
The heat comes from: 1. Mantle2. Pressure of the
layers3. Movement of
the Plates on Earth

Earth’s Plates

IV. What does Metamorphism change?
Metamorphic rocks can change:
1. a rocks appearance, texture
2. crystal structure3. mineral content It can form from a/an: 1. Igneous2. Sedimentary3. Another
metamorphic rock!

a. Foliated – mineral crystals are arranged in parallel layers or bands
Examples: Schist, slate, and gneiss
b. Nonfoliated – rocks are not banded and do not break into layers Examples: Marble and quartizite
V. Types of Metamorphic Rocks


Foliated

Non-foliated
NON-Foliated

VI. Contact vs. Regional Metamorphism
Contact
Small AreaRegional
Large Area


Examples
Used in construction of buildings
and walkways
Used in tables, floors, and
roofing

Metamorphic Rockhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UrimDbTUalg

Tier 1 MetamorphicPicture
1 picture of foliated
1 picture of non-foliated
Must have correct rock
names Must be
presented in an organized/colorfu
l way
ChartComplete chart Must do research DOES NOT have
to be colorful