Menstruation
-
Upload
drangelosmith -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
48 -
download
6
Transcript of Menstruation
1. What is menstruation?2. Significance3. Which hormones play a role in
menstruation? 4. Significance of each hormone5. What medical conditions will arise due
to problems in hormones associated?
The process in a woman of discharging blood and other material from the lining of the uterus at intervals of about one lunar month (28 days) from puberty until the menopause, except during pregnancy.
Menstruation is not the same as the menstrual cycle.
The Menstrual cycle describes the cyclic changes in a woman’s body going through menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, the luteal phase and back to menstruation again to begin the cycle.
Menstruation is therefore one of the 4 phases of the menstrual cycle.
1. Cycle of natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovary as an essential part of making sexual reproduction possible.
2. Essential for the production of eggs.3. Preparation of the uterus for pregnancy.4. Fertile period of a woman’s life between
menarche and menopause.
Menarche: Age at onset of menstruation
Primary amenorrhea: Absence of menstruation despite signs of puberty
Secondary amenorrhea: Absence of menstruation for 3-6 months in a woman who previously menstruated
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding: Irregular bleeding due to anovulation or anovulatory cycle
Menarche age 129 years 16 years
Menorrhagia: Regular menstrual intervals, excessive flow and duration
Metrorrhagia: Irregular menstrual intervals, excessive flow and duration
Oligomenorrhea: Menstrual interval greater than 35 days
Anovulation / anovulatory: Menstrual cycle without ovulation
Dysmenorrhea: Menstrual cramping/pain
1. Duration of menstrual flow2. Quality of the menstruum,3. Amount of blood loss, 4. The flow pattern and 5. Associated symptoms.
Last from 3 to 7 days. The exact duration varies from woman to woman. It however shows little or no variation for the
same woman from cycle to cycle. Most women do not experience cycle to cycle
changes more than 1 or 2 days. It is unusual for the same woman to have wide
swings such as 3 days duration in one cycle and 7 days in another.
Menstrual blood is normally bright or light red in color like the bleeding that occurs after a knife cut or similar injury. It could look brown in some few
women and still be normal menstruation. It must not have a foul odor. Small clots may be a normal part of menstrual
blood.
The average blood loss during normal menstruation is about 35 ml, with arange of 10 to 80 ml. Usually understood from the number of
pads soaked.
Normally, as menses begin to flow, the amount of blood loss seems to increasegradually until it attains a maximum and then starts diminishing as the end of the flow draws near.
This pattern is described as crescendo-decrescendo pattern.
Normal menstruation may be accompanied by other symptoms such as Breasts fullness, Mild lower abdominal pain or Irritability. Fluid retention Cramping Mood swings Weight gain Breast tenderness Diarrhea Constipation
These symptoms are never debilitating.
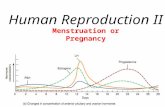
Begins when estrogen levels are lowAnterior pituitary secretes FSH and
LH, stimulation follicle to developCells around egg enlarge, releasing
estrogenThis causes this uterine lining to
thicken
LH and FSH still being released, for another 3-4 days
Follicle ruptures, releasing ova into the Fallopian tubes
Now empty follicle changes to a yellow colour, becomes corpus luteum
Continues to secrete estrogen, but now beings to release progesterone
Progesterone further develops uterine lining
If pregnant, embryo will release hormones to preserve corpus luteum
If no embryo, the corpus luteum begins to disintegrate
Progesterone levels drop, uterine lining detaches, menstruation can begin
Tissue, blood, unfertilized egg all discharged
Can take from 3-7 days
T r i g g e r s u t e r i n e l i n i n g t h i c k e n i n g
P r o d u c e sE s t r o g e n & O v u m
T r i g g e r s f o r m a t i o n o f t h eF o l l i c l e
W i t h i n t h e o v a r y
P r o d u c e sF S H
F o l l i c l e S t i m u l a t i n g H o r m o n e
P i t u i t a r yG l a n d
C o n t i n u e s u t e r i n e l i n i n g t h i c k e n i n g
P r o d u c e sP r o g e s t e r o n e
T r i g g e r s O v u l a t i o na n d t h e f o r m a t i o n o f t h e
C o r p u s L u t i u mW i t h i n t h e o v a r y
P r o d u c e sL H
L u t i n i z i n g H o r m o n e
P i t u i t a r yG l a n d
Hormonal Regulation
of MenstruationWITHOUT
ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE, ENDOMETRIUM
BREAKS DOWN – MENSTRUATION
OCCURS.