Membrane Potential 6 / 5 /10. The cell membranes of all body cells in the resting condition are,...
-
Upload
catherine-cain -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Membrane Potential 6 / 5 /10. The cell membranes of all body cells in the resting condition are,...

Membrane Potential
6 / 5 /10

• The cell membranes of all body cells in
the resting condition are, polarized
which means that they show an
electrical potential difference,
commonly used term for potential
difference is only potential.

• Membrane potential refers to a
separation of charges across the
membrane or a difference in the relative
number of cations and anions in the
ICF and ECF.
• Potential is measured is unit of volts
but because the membrane potential is
relatively low, the unit used is the
millivolt (mV) (1 mV = 1/1,000 volt).

Excitable Tissues
• Tissues of the body can generate and
propagate nerve impulses which are
waves of electro-chemical activity
along their membranes. These include
nerve cells and muscle cells.

Membrane Potentials Caused by Diffusion
• Diffusion Potential caused by an ion
concentration difference on the two
sides of the membrane.
• Potassium Ion
• Potassium concentration is great inside
a nerve fiber membrane but very low
outside the membrane.


Because of the large potassium
concentration gradient between inside
and outside the membrane.
There is a strong tendency for extra
numbers of potassium ions to diffuse
outward through the membrane as
the membrane at this instant is freely
permeable to the potassium ions but
not to any other ion.

• K-ions move outside i.e positive
electrical charges go to the outside,
thus creating electropositivity on the
outside the membrane and
electronegativity is created inside
because of negative anions that remain
behind that do not diffuse outward with
the potassium.


• Within a millisecond the potential
difference between the inside and outside,
called the diffusion potential, becomes
great enough to block further net outward
potassium diffusion .
• The potential difference is about 94
millivolts, with negativity inside the fiber
membrane. (in the normal mammalian
nerve fiber).

Sodium Ion :
At this time
• There is high concentration of
positively charged sodium ions on the
outside as compared to inside the
membrane.
• The membrane is highly permeable to
the sodium ions but impermeable to all
other ions.


• Diffusion of the positively charged
sodium ions to the inside creates a
membrane potential that is negativity
outside and positivity inside.
• Again, the membrane potential rises
high enough within milliseconds to
block further net diffusion of sodium
ions to the inside.


• The potential is about 61 millivolts
positive inside the fiber (in the
mammalian nerve fiber).


• The excitable tissues have the ability to
produce rapid, transient changes in
their membrane potential when excited.
• These brief fluctuations in potential
serve as electric signals.

Resting Membrane Potential
• The constant membrane potential
present in the cells of excitable tissue
when they are at rest i.e when they are
not producing electric signals is termed
as resting membrane potential.

Ions Involved In Memb. Potential
• The unequal disturbution of a few key
ions between the ICF and ECF and their
selective movement through the
plasma membrane are responsible for
the electrical properties of the
membrane.

• In the body, electric charge is carried
by ions. The ions primarily responsible
for the generation of the memb.
potential are K-ion, Na-ion, Cl-ion.
• Other ions ( calcium, magnesium,
phosphate , bicarbonate) do not make a
direct contribution to the memb.
potential.

• Potassium ions are present in much
higher concentration in the ICF
whereas, Sodium ions are present in
great conc. in the ECF. unit used for
these ions is mmol/L.

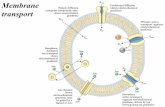
Transport Of Na And K-ions

Various ions tend to diffuse from one side
of the membrane to the other depending
upon their
• Electrochemical gradients.
• The permeability of cell membrane to
these ions which varies greatly.


• Diffusion of K+ and Na+ ions can take
place through the channels present in
the cell membrane which are called K+
and Na+ ion leak channels.
• Na and K-ion inaddition, to the active
carrier mechanism can passively cross
the memb. through protein channels
that are specific for them.

• K-ion can cross more easily as the
memb. has more channels open for it.
• Also at resting potential in a nerve cell
membrane is 50-70% more permeable
to K-ion than Na-ion.

There are still other processes by
which these ions can move across the
cell membrane these are:
• The voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels.
• The electrogenic Na+ K+ ATPase pump.

• The effects of an unequal concentration of
ions on the two sides of semipermeable
membrane can be analyzed as.
• Suppose the membrane is only permeable
to K+ ions. K+ ions are present in higher
concentration inside, therefore, they tend
to diffuse along their concentration
gradient into the extracellular fluid.

• But soon an equilibrium is reached at
which the efflux of K+ ions out of the cell
stops. The membrane potential at which
this equilibrium will exist is called the
Equilibrium potential for K+.

• Other names for equilibrium potential
are Nernst or reversal or diffusion
potentials.
• It is obvious that at the equilibrium
potential for K+ ions, the cell
membrane will become impermeable to
K-ions.

• The magnitude of the net forces
tending to move each ion across the
membrane is determined by the resting
potential of the cell membrane and the
equilibrium potential for that ion.
• Actually it is the difference between
these two values.

• The diffusion potential level across a
membrane that exactly opposes the net
diffusion of a particular ion through the
membrane is called the Nernst potential
for that ion.

• The magnitude of this Nernst potential
is determined by the ratio of the
concentrations of that specific ion on
the two sides of the membrane.

• End Of Todays Lecture!!!!