Melanocytic naevus
-
Upload
dr-yugandar -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
61 -
download
3
Transcript of Melanocytic naevus

DR .YUGANDAR

The term Naevus has been used to describe a
large variety of clinically dissimilar
lesions,often leads considerable confusion.
They usually present at birth or early
childhood.
Due to Genetic mosaicism.

Epidermal nevi
Melanocytic nevi
Dermal & Subcutaneous nevi

Melanocytic nevi
Cong. Melanocytic nevi
Acquired Melanocytic nevi
Dermal MN
Clinically atypical nevi
Special variants of acquired nevi

Synonyms like cellular nevi or
Pigmented nevi are best avoided, as not
all melanocytic nevi are pigmented ,nor
does the term cellular nevi define cell
type.

Present at birth
Greater malignant Potential
Larger size
Nevus cells have deeper penetration around
skin appendages, nerves and blood vessels


Small-sized congenital nevocytic nevus is
defined as having a diameter less than
2 cm.
Medium-sized congenital nevocytic nevus is
defined as having a diameter more than
2 cm but less than 20 cm.
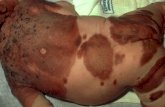
Giant congenital melanocytic nevus is
defined by one or more large, darkly
pigmented and sometimes hairy patches


Growth of cong. Nevi is very rapid and
disproportionate to the growth of particular
body area affected in first 6 months
In adults nevus remains static unless there is
infection ,trauma, development of
malignancy
Tardive nevi : early onset nevi, seen in first
2 yrs of birth.Less than 10mm size

The congenital melanocytic nevus appears as a
circumscribed, light brown to black patch or plaque,
potentially very heterogeneous in consistency, covering
any size surface area and any part of the body.
As compared with a melanocytic nevus congenital
melanocytic nevi are usually larger in diameter and may
have excess terminal Hair,condition called
hypertrichosis.
Giant variety chances are 0.002% of Births

As they mature, they often develop
thickness, and become elevated,
although Prominent terminal hairs
often form, especially after puberty.

Nevi become larger,darker and more rugose
as child grows
Finally develop warty, nodular surface
Certain other varieties
Cerebriform Cong Nevus
Spotted grouped pigmented nevus
Neurocutaneous melanocytosis

Common over scalp,
skin coloured plaque
Convoluted surface

Closely set brown to black plaques
forming clusters
Usually intradermal
Could be follicle or eccrine centred

Multiple nevi of head, neck, post
midline tumors ( Leptomeningeal
melanocytosis)
Epilepsy, MR, Inc ICT symptoms
Other spinal dysraphism, Club foot,
Lipoma, vascular nevi

Carney complex : Primary adrenocortical
disease, Lentigines, Blue nevi, Neuro
endocrine disorders
NAME: Nevi, atrial myxoma, myxoid
neurofibromata and Ephelides
LAMB : Lentigines,atrial myxoma,
mucocutaneous myxoma, Blue nevi

Depend on age,size of lesion
May be junctional, compound or
intradermal
At birth in first week – junctional
( hyperplasia seen in both epidermis
and adnexal area

Presence of nevus cells in reticular dermis
Extension of nevus cells in colleagen
bundles as single row/ sheets/ combinations
i.e. INDIAN FILE APPERANCE
Higher CONCENTRATIONS OF CELLS
around blood vessels,nerves and adnexal
structures
S100 protien by immunohistochemistry in
deep periadnexal structures

•single row/ sheets/ combinations
i.e. INDIAN FILE APPERANCE
•nevus cells in reticular dermis

Risk of melanoma in caucasians 4.5-10%
MC from large CMN than Medius and smal
size CMN
Other tumors with CMN
Neurosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Liposarcoma
Spindle cell sarcoma

Surgical excision of nevi performed as early as 3
weeks of birth
Others considered ideal time 10 to 14 months
Serial excision with use of tissue expanders and
grafting choice of therapy
Multiple medium size removed around puberty

Q switched Ruby laser
Dermabrasion
Pulsed Co2 laser
Use of artificial dermis
Fresh autologous cultured epithelium Under
trial

Defects in development of Epidermal
melanocytes
Depend on melanocytic distribution in
skin divide
Junctional N
Compound N
Intradermal N

Ackerman described it as Neoplasm b/c
they formed after Melanocytes achieved
maturity
With age, progressive maturation a/w
decrease in pigmentation
Most nevi become intradermal by early
adult life
Nevi on palms,soles and genitalia
remains junctional for long periods

15 to 40 %
Rarely present at birth
Appear in early childhood,
Progressively increase in number
Avg 15 in male, 20 to 29 in female
Rare beyond eighth decade

Formation of Nests of nevus cells in EpiDermis
Presence of Junctional activity in Junctional &
Compound types
Decrease in size & melanin content of nevus
cells as dermis downwards i.e. Process of
maturation
Formation of multinucleated giant cells
Mucinous,fibrosis,fatty change in regressive
stage

• Nests of nevus
•Decrease in size & melanin content of nevus cells

Junctional cells express both s100 &
melanoma associated antigens NK1/c-
3 ,HMB-45
Intraderma cells express only s100 antigens
In Loose nests nevus cells may demonstrate
Dendritic processes,In compact nest no
processes

Nevus cells-Upper dermis more
pigmented,cuboidal,abundant cytoplasm &
round nucleus i.e. Type A cells/epithelioid
In Mid dermis cells smaller,rounded,sparse
melanin i.e. Type B cell or Lypmoid cells
In Lower dermis Cells spindle shaped
resembling fibroblasts and schwann
cells,melanin absent i.e. Neuroid /type C
cells

J.Nevus: flat pigmented macule 3mm to 1cm
Colour varies from tan to brown – black
Skin surface markings preserved over nevus
90% of acquired nevi in children are J.N
J.N differentiated from freckles (s/o sun exposed
areas, fade on protection)
Lentigo simplex by HP examination

Compound Nevus: slightly raised circular
plaques
Pigment varies from brown to black
Centre being darker than periphery
Well established nevi often contain coarse
hair in centre
Irregular contour, variable color, irregular
perinevoid halo – risk of malignancy

Intradermal nevi: elderly adults
Difficult identify from compound nevi
Two variants
First seen after adolescence,dome
shaped,smooth surface over face.
Second seen inn adults sessile/soft
wrinkled sac seen over flexures
K/a cholinestrase nevus b/c of enzymes in
nevus


Melanomas arising from melanocytice
nevus better prognosis.
80% cases have sup. Spreading type
Junctional nevi got greater malignancy
potential
Acral lentiginous melanoma MC in asians
IL-1alfa,IL-1Beta,IL-6 protective role

Diametre > 7cm
Irregular edge
Variable color
Inflammation
Bleeding
Crusting
Oozing
Risk of melanoma in AMN

Removal by Esthetic prolems only
J.N over soles,palms,genitalis greater risk of
malignancy
Nevi at site of friction
Suddenly increase in size with pain indication
of removal
Inflamed nevi often excised
Incomplete excision- proliferation of remaining
tissue resembles melanoma: Psuedomelanoma

Similar to Melanocytic nevi Often observed on opposing eyelids
to form round shape when closed Indicates development of nevi b/w
2&6th month of fetal life Nevi : Caruncle,Limbal area,Eyeball. One conjuctival nevi transformed to
malignant melanoma

An active junctional nevus in the matrix gives rise to a single dark black band on the undersurface.

Rare,clinically compound or intradermal
Differing by collections of clear cells
Common in first three decades
Varying amount melanin in epi & Dermis
Balloon cells:single or groups,abundant
cytoplasm,small central nucleus. few multi
nucl.
DD: balloon cell melanoma,clear cell
hidradenoma,intradermal nevi

Thank You Very Much for Your Kind
Attention
















![Giant congenital melanocytic nevus - Naevus Global of neighboring, raised tubercles that began under her armpits and covered all her back to her kidneys. These outgrowths of skin …]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ac528497f8b9a220b8d345a/giant-congenital-melanocytic-nevus-naevus-global-of-neighboring-raised-tubercles.jpg)

