Meiosis with Mitosis Review and Comparison (Chapters 8 and 10)
-
Upload
burton-wood -
Category
Documents
-
view
35 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Meiosis with Mitosis Review and Comparison (Chapters 8 and 10)
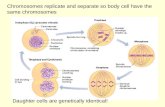
** Mitosis is asexual reproduction & occurs ONLY in regular old body cells called SOMATIC CELLS (skin, nails, your pancreas, etc..) NOT sperm and eggs
** Produces two identical diploid (2n) cells
Recall MitosisRecall Mitosis
Diploid Chromosomes
We call somatic cells diploid (2n) meaning you have 2 copies of each chromosome (1/2 from mom and ½ from dad)
Autosomal chromosomes are non-sex chromosomes› These contain genes that have nothing to do with
determining your sex Each of your cells contain 44 autosomal
chromosomes and 2 sex chromosomes (XX for female and XY for male) for a total of 46 chromosomes in each nuclei of your cells
Mitosis Produces Identical, Diploid Daughter Cells (46 chromosomes in the
nuclei of the cells)
Above are Homologous Chromosomes - Same chromosome with same types of genes on each chromosome, just different variations from each parent
Replicates
Meiosis Overview**Required for Sexual Reproduction
**Results in 4 NON-IDENTICAL haploid (n) cellsGenetic recombination creates genetic variability in
either sperm or egg For each meiotic division, 4 sperm are produced
but typically only 1 egg survives
**Produced in the ovaries (females) and testes (male)
**Diploid cells divide twice to produce haploid (n) sperm or egg (each have 23 chromosomes)
Meiosis Phases
**Meiosis II Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II and cytokinesis
**4 cells, the gametes!!
**Meiosis I Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, telophase I
**After interphase (DNA replication phase)
Fertilization When egg and sperm fuse we say the
egg is fertilized creating one, single diploid cell called a zygote
Although numerous sperm attempt to fertilize the egg, only one will succeed
Diploid zygote – will undergo mitosis
From your From yourDad Mom
Replication
Homologous chromosomes –
SAME chromosome
type (have the same types of
genes)
A tetrad is formed
Crossing Over between non-
sister chromatids
During Prophase 1 of
Meiosis 1 – Results in
genetic recombination
After Meiosis 1 After M
eiosis 2 o
ccurs th
e result is 4,
no
n-id
entical h
aplo
id sp
erm o
r egg
cells called
gam
etes
Meiosis occurs in 2 phases. Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2 with cytokinesis following. The process results in 4 non-identical haploid cells
Genetic Recombination During Meiosis
**independent assortment of homologous chromosomes
** A reassortment of chromosomes and genetic information they carry
**crossing over between non-sister chromatids during Prophase 1
Crossing Over
**Non-sister chromatids exchange
genetic information
**Pink is from your mom, blue
from your dad
Independent Assortment leads to genetic variability- homologous chromosomes are sorted before shipment to gametes independently of how
the other pairs were sorted
Non-Disjunction **chromosomes of a homologous pair (tetrad) fail to separate and move to the same pole of the cell. Some gametes may have an extra chromosome while others lacking
** Down syndrome occurs because of this. Called trisomy 21, there are 3 of chromosome #21 rather than a pair!
Karyotypes – Pictures of a person’s Chromosomes – Show Abnormalities
Male with no chromosomal abnormalities
Mitosis• Occurs in 1 stage
• Produces 2 genetically identical diploid cells
• It is Asexual Reproduction
• Produces “clones” with no genetic variability
• Occurs in body cells (autosomal) and creates two diploid cells
• 2n=46 22 pair of autosomal chromosomes and 1 pair sex chromosomes
Meiosis • Occurs in 2 stages
• Produces 4 genetically different haploid cells (genetic recombination)
• For Sexual Reproduction
• Produces genetically variability due to recombination
• Occurs in sex cells called gametes or germ cells and four haploid cells (sperm and egg)
• n=23 22 autosomal chromosomes and 1 sex chromosome
• Forms a tetrad
Mitosis (asexual reproduction) vs. Meiosis (sexual Reproduction)