Mitosis and Meiosis
-
Upload
amalina-ismail -
Category
Documents
-
view
75 -
download
2
Transcript of Mitosis and Meiosis

LAB 6
MITOSIS &
MEIOSIS
LAB 6

MITOSISMITOSIS

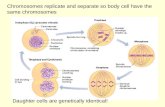
• A Process in which a parent nucleus produces 2 daughter nuclei• Each having the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent nucleus.
WHAT IS MITOSIS?

MITOSIS PERMITS GROWTH & TISSUE REPAIR.

MITOSIS REPAIRS DAMAGED TISSUE AND BONE.

CELL CYCLE

SGrowth DNA replications
G2Growth and final preparations for
division
G1Growth
Interphase
Mitosis
Cyt
okin
esis
Telo
phas
e
Ana
phas
e
Met
apha
se
Pro
met
apha
se
Prophase
G1
G2
M
Cell cycle checkpoint Apoptosis occur if DNA is damaged and cannot be repaired
Spindle assembly checkpoint if chromosome is not aligned properly mitosis will not occur
Mitosis checkpointApoptosis occur if DNA damaged and cannot be repaired.Mitosis occur if DNA replicate properly

MITOTIC STAGES

PROPHASE
• The chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes.
• Nucleolus disappears
• The nuclear envelope breaks down
• Spindles form at opposite "poles" of the cell.

METAPHASE
• The duplicated chromosomes are aligned at the
metaphase plate.
• Kinetochore spindle fiber attach to sister chromatids

ANAPHASE
• The sister chromatids part and become daughter
chromosomes that move to opposite ends of the cell.

TELOPHASE
• Nuclear envelopes and nucleolus reappear.
•Daughter cells form
•Chromosomes become indistinct chromatin.
• Cytokines has started between the two groups of chromosomes

CYTOKINESIS(Division of the cytoplasm)

IN ANIMAL CELLS
• Cleavage furrowing process occurs.
• A band of actin filaments slowly forms a circular contraction
between the 2 daughter cells

IN PLANTS CELLS
• Formation of new cell plate between the daughter cells, which eventually
becomes new plasma membrane between the daughter cells.


A process of reductional division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half.
A process of reductional division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half.
The word "meiosis" comes from the Greek verb meioun, meaning "to make small,"
The word "meiosis" comes from the Greek verb meioun, meaning "to make small,"



Prophase I takes the most time. Chromosomes begin to condense. Cell is 2N (diploid) and 2
chromatids/chromosomes (like before mitosis).
Synapsis occurs: homologous chromosomes pair, their DNA aligns.
Crossing over may occur: chromosomes exchange homologous loci (between homologous pairs). The point of crossing over is called the chiasma.

Homologous chromosomes align at cell equator to form tetrads.

Chromosomes are pulled to either side of the dividing cell; one of each pair is pulled toward each pole.

The nuclear envelope may form again.

Two daughter cells are formed.

Nuclear envelope disperses

Chromosomes align between poles

Chromatids segregate.

The former sister chromatids have reached the poles. A nuclear envelop is formed around each nucleus, while chromosome despiralize again.

After cytokinesis, four daughter cells are formed.

Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis
Chromosome behavior •Mitosis: Homologous chromosomes independent •Meiosis: Homologous chromosomes pair forming bivalents until anaphase I
Chromosome number•Mitosis- daughter cells diploid •Meiosis- daughter cells haploid
Genetic identity of progeny: •Mitosis: identical to parent cell•Meiosis: not identical to parents cell
Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis
Chromosome behavior •Mitosis: Homologous chromosomes independent •Meiosis: Homologous chromosomes pair forming bivalents until anaphase I
Chromosome number•Mitosis- daughter cells diploid •Meiosis- daughter cells haploid
Genetic identity of progeny: •Mitosis: identical to parent cell•Meiosis: not identical to parents cell