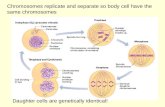
Chromosomes, Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosomes, Mitosis and Meiosis Chapter 10.
MEIOSIS By Diana Bivens. Meiosis vs. Mitosis Mitosis: period of nuclear division in which two...
-
Upload
justin-osborne -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of MEIOSIS By Diana Bivens. Meiosis vs. Mitosis Mitosis: period of nuclear division in which two...

MEIOSISMEIOSIS
By By
Diana BivensDiana Bivens

Meiosis vs. MitosisMeiosis vs. Mitosis
Mitosis: Mitosis: period of nuclear division in period of nuclear division in which two daughter cells are formed, which two daughter cells are formed, each identical to the parent celleach identical to the parent cell

Meiosis vs. MitosisMeiosis vs. Mitosis
Meiosis: Meiosis: type of division in which four type of division in which four cells are formed, each with half the cells are formed, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent number of chromosomes as the parent cellcell

Terms to KnowTerms to Know
Body cells (diploid, 2n)Body cells (diploid, 2n) contain two of each kind of contain two of each kind of
chromosome. chromosome. chromosomes are paired, one set chromosomes are paired, one set
from each parentfrom each parent Paired chromosomes are called Paired chromosomes are called
homologous chromosomeshomologous chromosomes Human body cell: 46 chromosomes/23 Human body cell: 46 chromosomes/23
pairspairs

Terms to KnowTerms to Know
Gamete (haploid, n)Gamete (haploid, n) Also called a “sex cell”Also called a “sex cell” Contains one of each kind of chromosome Contains one of each kind of chromosome
(or half the number of a body cells)(or half the number of a body cells) Human sex cell (sperm or egg): 23 Human sex cell (sperm or egg): 23
chromosomeschromosomes ZygoteZygote
the result of the fertilization of an egg the result of the fertilization of an egg cell with a sperm cell forming a diploid cell with a sperm cell forming a diploid cellcell

MeiosisMeiosis
fertilization is the process in which fertilization is the process in which two haploid cells come together to two haploid cells come together to form a unique diploidform a unique diploid
This is the premise of sexual This is the premise of sexual reproductionreproduction

MeiosisMeiosis
Interphase: stage in which Interphase: stage in which chromosomes duplicate themselves chromosomes duplicate themselves (same as mitosis)(same as mitosis)
Meiosis is then separated into two Meiosis is then separated into two division stagesdivision stages
Meiosis I and Meiosis IIMeiosis I and Meiosis II

Phases of MeiosisPhases of Meiosis
http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=9965DAF6-2344-4A14-8A87-085F0139FB50&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US

Meiosis IMeiosis I
Prophase IProphase I Chromosomes coil and spindle formsChromosomes coil and spindle forms Each pair of homologous chromosomes Each pair of homologous chromosomes
and their sister chromatids come and their sister chromatids come together to form a four-part together to form a four-part tetrad tetrad joined together by a centromerejoined together by a centromere

Meiosis IMeiosis I
Prophase IProphase I During this phase, an exchange of During this phase, an exchange of
genetic material may occur between genetic material may occur between two non-sister chromatids (crossing two non-sister chromatids (crossing over)over)
Crossing over allows for more variation Crossing over allows for more variation in sexual reproductionin sexual reproduction

Meiosis IMeiosis I
Metaphase IMetaphase I Chromosomes become attached to Chromosomes become attached to
spindlespindle Tetrads are pulled to the mid-line of the Tetrads are pulled to the mid-line of the
cellcell

Meiosis IMeiosis I
Anaphase IAnaphase I Homologous chromosomes, along with Homologous chromosomes, along with
their sister chromatids, separatetheir sister chromatids, separate

Meiosis IMeiosis I Telophase ITelophase I
Spindle breaks downSpindle breaks down Chromosomes uncoilChromosomes uncoil Cytoplasm divides to form two new cellsCytoplasm divides to form two new cells
* Each cell has * Each cell has halfhalf the genetic the genetic information as the original information as the original parent cell, parent cell, BUT BUT the the chromosomes are still doubled chromosomes are still doubled so another division must take so another division must take placeplace

Meiosis IIMeiosis II
Prophase IIProphase II A spindle forms and the chromosomes A spindle forms and the chromosomes
in each cell attachin each cell attach Sister chromatids are pulled to the Sister chromatids are pulled to the
center of the cellcenter of the cell

Meiosis IIMeiosis II Metaphase IIMetaphase II
Sister chromatids line up on the mid-Sister chromatids line up on the mid-line of the cellsline of the cells

Meiosis IIMeiosis II
Anaphase IIAnaphase II The centromere breaks allowing the The centromere breaks allowing the
sister chromatids to migrate to opposite sister chromatids to migrate to opposite ends the cellsends the cells

Meiosis IIMeiosis II
Telophase IITelophase II Nuclei reformNuclei reform Spindles break downSpindles break down Cytoplasm splitsCytoplasm splits

End of MeiosisEnd of Meiosis
Meiosis produces FOUR Meiosis produces FOUR haploid cells, each haploid cells, each containing one containing one chromosome from each chromosome from each homologous pairhomologous pair

MeiosisMeiosis
genetic recombination: genetic recombination: the the reassortment of chromosomes and reassortment of chromosomes and the genetic information they carry, the genetic information they carry, providing a major source of genetic providing a major source of genetic variationvariation

How much variation?How much variation?
““n”: The number of homologous pairs in n”: The number of homologous pairs in a cella cell
Human body cell contains 46 Human body cell contains 46 chromosomes (23 homologous pairs)chromosomes (23 homologous pairs)
2n=462n=46 Human sperm cell contains 23 Human sperm cell contains 23
chromosomes (one representative from chromosomes (one representative from each homologous pair) n=23each homologous pair) n=23
Human egg cell (same as sperm)Human egg cell (same as sperm) n=23n=23

WOW!!!WOW!!!
Possible different kinds of egg or sperm cells Possible different kinds of egg or sperm cells
created by a person = 2²³ or created by a person = 2²³ or 8.4 million8.4 million Fertilization of one egg by one sperm results Fertilization of one egg by one sperm results
in in
2²³ x 2²³ or 2²³ x 2²³ or 7070 trillion trillion possible zygote possible zygote combinationscombinations
* This does not take into consideration * This does not take into consideration possible crossovers that occur during possible crossovers that occur during prophase Iprophase I

End Result---We are ALL End Result---We are ALL truly uniquetruly unique