Male Reproductive System...Male Reproductive System •Sate the function and give an example for...
Transcript of Male Reproductive System...Male Reproductive System •Sate the function and give an example for...

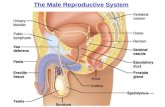
Male Reproductive System

Basic Reproductive Structures• Gonads are the organs that produce gametes and sex hormones.▫ Testes and ovaries
• Gametes are reproductive cells.▫ Sperm and ova.
• Ducts receive and transport gametes and fluids.• Accessory glands secrete fluid or mucus into the reproductive
system ducts.• External genitalia includes any reproductive structure visible
from the outside of the body.

Testes• The testes are the primary male
sex organs, where sperm and testosterone are produced.▫ Optimal sperm production
requires a 2°F cooler temperature.• The testes reside inside an
external pouch of skin called the scrotum.
• The cremaster muscle can contract and pull the testes closer to the body when warmth is needed.

• A dense fibrous capsule called the tunica albuginea covers each testis.
• Seminiferous tubules produce sperm.▫ About a half-mile of length of
tubules per lobe.• The rete testis is a network of
tubules that concentrates sperm.• The epididymis is a storage
reservoir for sperm.▫ Sperm undergo maturation for
2-3 weeks before ejaculation.• Interstitial cells produce
testosterone.

Seminiferous Tubule
Rete Testis
SeptumTunica albuginea
Lobule
Vas Deferens
Epididymis

Male Reproductive Tract• The vas deferens is a duct that
transports matured sperm from the epididymis towards the urethra in the penis.
• The vas deferens and duct of a seminal vesicle unite at the ejaculatory duct.
• The urethra transports sperm through the penis and out of the body.

The Penis• The penis contains three columns of vascular tissue that fills with
blood during an erection.▫ Two larger corpora cavernosa, and one smaller corpus spongiosum.
• The glans is the enlarged distal portion surrounding the opening of the urethra.

Accessory Glands• The male reproductive tract has three accessory glands that
add secretions to sperm, creating semen.▫ Two seminal vesicles▫ Prostate gland▫ Bulbourethral gland

Urinary Bladder
SymphysisPubis (Pelvis)
Seminal Vesicle
Ejaculatory Duct
RectumBulbourethral Gland
Epididymis
TesticleScrotum
Urethra
Erectile Tissue
Vas DeferensProstate

Ejaculation• Ejaculation is the
movement of sperm and semen out of the body, and takes place in a series of stages:
1. Sperm is forcefully moved from the epididymis through the vas deferens through peristalsis during orgasm.

2. Sperm enters the ejaculatory duct, where it receives fluid from the prostate and seminal vesicles.
3. Additional fluid is added by the bulbourethral gland.
4. The urinary sphincter closes off the bladder.
5. The semen exits the body via the urethra in the penis.

• Seminal plasma contains:▫ Fructose, a monosaccharide
that provides nourishment for sperm cells.▫ Prostaglandins are hormone-
like lipids that stimulate peristalsis along the male and female reproductive tract.▫ Fibrinogen is a clotting
protein that causes semen to temporarily clot inside the vagina.▫ Alkaline fluid neutralizes
acids produced by the prostate gland and vagina.

• The prostate gland produces a fluid that liquefies clotted sperm a short time after ejaculation.
• The bulbourethral gland adds a thick alkaline mucus (pre-ejaculate) that provides lubrication for sexual intercourse.

Sperm Anatomy• The head contains the DNA and a specialized lysosome called the
acrosome. ▫ The acrosome contains enzymes to help the sperm penetrate the
outer layer of the egg cell.• The midpiece is wrapped by mitochondria to generate ATP for
movement.• The tail is a flagella – used for movement.

Male Reproductive System •Sate the function and give an example for each of the following reproductive structures:
1.gonads2.gametes3.ducts4.accessory glands5.external genitalia
•Sate the function for each male reproductive structure:1.Prostate 2.Penis3.Seminal vesicles4.Testes5.Scrotum
•What organ and which cells produce testosterone hormone?•Explain the role of each structure in spermatogenesis:
1.Seminiferous Tubules –2.Epididymis –3.Vas Deferens4.Ejaculatory Canal
•Spermatogenesis begins in the _________________________ of the testes. The spermatozoa then travel to the _________________, where they mature and are stored. During an ejaculation, the sperm will travel through a long tube called the _________________ until they eventually reach the ejaculatory duct. Seminal plasma produced by the __________________ are added to the sperm. Additional secretions are then added by the _______________ and _________________ as the sperm move past them. The ________________ takes the sperm through the penis, where they exit the body.
•Explain the purpose of the four components of seminal fluid that the seminal vesicles and prostate gland contributes:1.Fructose2.Prostaglandins3.Fibrinogen4.Alkaline Fluid
•Explain how an erection occurs, using the terms corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum.•Explain the purpose of each of these structures in sperm cells. What region are they found in?
1.Head2.Acrosome3.Midpiece4.Tail
•Label each of the following structures: epididymis, rete testis, seminiferous tubules, vas deferens.

Bassick High School A&P2- Lab Quiz Dr. Camacho
Label the parts: ______ductus deferens ______scrotum ______seminal glands ______prostate gland______ testes ______epididymis ______penile urethra ______urinary bladder______glans penis ______ prepuce ______corpus cavernosum ______urethra orifice______corpus spongiosum ______membraneous urethra ______bulbourethral gland______prostatic urethra
____flagellum ____head ____mitochondria____nucleus ____neck
____acrosome ____ middle piece ____centrioles

Bassick HighSchool A&P Dr.CamachoMaleReproductionSystem
Name ________________•Why is the male reproductive anatomy external while the female is internal?•What is the function of the muscles within the scrotum? •What are the two functions of the testes?•Where do the sperm mature?•What is the function of the inguinal canal? What passes through there?• Why the inguinal canal is the weakest point of the abdominal wall in males?
•What happens during torsion of the testes?•The vas deferens loops up and around as it leaves the testes and eventually joins with the urethra. Why does it take such a circuitous path?
•What symptoms can occur in a male if the prostate becomes enlarged?
•Where does the penis attach to the rest of the body?•What causes an erection?•Why is it important that the entrance to the bladder closes off as ejaculation takes place?
•Label the two erectile tissues (corpora cavernosum) and the urethra in this cross-section of the penis.
•Label the seminal vesicles, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, and prostate on this diagram.
•Label the muscle layers and the lumen of this cross-section of the vas deferens.