M. Sc. in GEOLOGY FACULTY OF SCIENCE SECOND … and classification of sedimentary rocks. ......
Transcript of M. Sc. in GEOLOGY FACULTY OF SCIENCE SECOND … and classification of sedimentary rocks. ......
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
M. Sc. in GEOLOGY FACULTY OF SCIENCE
SECOND SEMESTER (EVEN SEMESTER)
Eligibility
Criteria
(Qualifying
Exams)
Course
Code Course Type Course (Paper/Subjects)
Credi
ts
Contact Hours
Per WeeK
EoSE
Duration
(Hrs.)
L T P Thy P
Aft
er a
pp
eari
ng
in
th
e F
irst
sem
este
r ex
am
inati
on
ir
resp
ecti
ve
of
an
y n
um
ber
of
ba
ck/
arr
ear
pap
ers
MSG201 CCC SEDIMENTARY AND METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY 5 4 2 00 3 0
MSG202 CCC IGNEOUS PETROLOGY 5 4 2 00 3 0
MSG203 CCC STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY 5 4 2 00 3 0
MSG211 CCC SEDIMENTARY AND METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY-
LAB 2 00 00 3 0 3
MSG212 CCC IGNEOUS PETROLOGY-LAB 2 00 00 3 0 3
MSG213 CCC STRUCTURAL GEOPLOGY-LAB 2 00 00 3 0 3
MSGSO2 PRJ/FST/EST SOCIAL OUT REACH AND SKILL DEVELOPMENT
(GEOLOGICAL EXCURSION TOUR) 6 00 00 9 0 4
MSGB01 ECC/CB ENVIRONMENTAL AND FOREST LAWS
6 4 3 00 3 00 MSGB02 ECC/CB TOPOGRAPHIC SURVEY
MSGB03 ECC/CB ENVIRONMENTAL LAW AND POLICIES
MSGB04 ECC/CB MINERAL ECONOMICS
33
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
M.Sc (GEOLOGY) 2nd
SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: MSG201 COURSE TYPE: CCC
COURSE TITLE:SEDIMENTARY AND METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY
CREDIT:7 HOURS:135
THEORY: 5 PRACTICAL:2 THEORY:90 PRACTICAL: 45
MARKS
THEORY: 100(30+70) PRACTICAL:100
OBJECTIVE: This course is aimed towards generating fundamental knowledge, concepts and dimensions
of Sedimentary and Metamorphic Petrology.
UN
IT-1
-
18
Hou
rs Unit-1
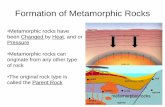
Character and classification of sedimentary rocks. Origin of sediments, classification of
sediments. Sedimentary differentiation.Environments of deposition.
UN
IT-2
-
18H
ou
rs Unit-2
Mineral stability in sedimentary rocks. Lithification and diagenesis. Mechanical analysis of
sediments: Presentation and processing of sedimentary analytical data. Textural structural and mineralogical characters of sedimentary rocks. Provenance and palaeogeography.
UN
IT-3
-
18 H
ou
rs Unit-3
Metamorphic Structures Equilibrium in Metamorphism. Experimental Work in Metamorphic
equilibria. Metamorphic Facies. Facies Series of Tectonic and Non Tectonic Domain.
UN
IT-4
-
18H
ou
rs
Unit-4 Facies of Contact and Regional. Metamorphism Retrograde Metamorphism. Metasomatism.
Metamorphic Differentiation and Diffusion. Granitization.
UN
IT-5
-
15
Hou
rs Unit-5
Metamorphic texture. Fabric analysis of metamorphic rocks. Relationship between metamorphic
rocks. Relationship between metamorphism and deformation.
LA
BO
RA
TO
RY
WO
RK
(MS
G2
11
)
Sedimentary petrology practical:- 1. Megascopic & Microscopic Examination of Sedimentary rocks
2. Sedimentary Mechanical Analysis Interpretations
3. Determination of Roundness of Grains, grain size analysis.
Metamorphic petrology practical:- 1. Identification of various metamorphic rocks in hand specimen through megascopic
characters.
2. Identification of various metamorphic rocks through microscopic characters. 3. Plotting of mineral assemblages in ACF, AKF and AFM diagrams
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
SU
GG
ES
TE
D R
EA
DIN
GS
1. Winter, J.D. 2001 : An introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Prentice
Hall.
2. Philpotts, A.R. 1994 : Principles of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Prentice Hall.
3. Bucher, K. and Martin, F. 2002 : Petrogenesis of Metamorphic Rocks, Springer –
Verlag, 7th Revised Edition.
4. Yardley, B.W.D. 1989 : An introduction to Metamorphic Petrology, Longman Scientific & Technical, New York.
5. Spear, F. S. 1993 : Mineralogical Phase Equilibria and pressure – temperature – time
Paths, Mineralogical Society of America. 6. Powell, R. 1978 : Equilibrium thermodynamics in Petrology: An Introduction,
Harper & Row Publishers, London.
7. Wood, B.J. and Fraser, D.G. 1976: Elementary Thermodynamics for Geologists, Oxford University Press, London.
8. Rastogi, R.P. and Mishra, R.R. 1993: An Introduction to Chemical Thermodynamics,
Vikash Publishing House.
9. Yardley, B.W.D., Mackenzie, W.S. and Guilford, C. 1995 : Atlas of Metamorphic Rocks and their textures, Longman Scientific & Technical, England.
10. Spry, A. 1976 : Metamorphic Textures, Pergamon Press.
11. Blatt, H. and Tracy, R.J. 1996 : Petrology (Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic), W.H. Freeman & Co., New York.
12. Kerr, P.F. 1959 : Optical Mineralogy, McGraw Hill Book Company Inc., New York.
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
M.Sc (GEOLOGY) 2nd
SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: MSG202 COURSE TYPE: CCC
COURSE TITLE: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY
CREDIT:7 HOURS:135
THEORY: 5 PRACTICAL:2 THEORY:90 PRACTICAL: 45
MARKS
THEORY: 100(30+70) PRACTICAL:100
OBJECTIVE: This course is aimed towards generating fundamental knowledge, concepts and dimensions
of Structural Geology.
UN
IT-1
-
18
Hou
rs
Unit-1 Concept of Line and Plane; Attitude of Plane and a line; Bedding plane; Plungeand trend; Dip and
strike and their measurement. Criteria for determination of Top & Bottom of sedimentary,
metamorphic and igneous rocks in a structurally deformed terrain. Field techniques of lithological and structural mapping. Unconformity and its type. Onlap. Offlap, Outlier, Inlier and Tectonic
Window.
UN
IT-2
-
18H
ou
rs Unit-2
Rock deformation: Stress & strain, their relationship; Factors controlling rockDeformation.
Properties of elastic, plastic and brittle materials; Progressive deformation. Strain analysis: types
of strain; strain ellipse; strain ellipsoid; geological application of strain theory.Stress analysis: compressive and shear stress; biaxial and triaxial stress. Mohr’s Circle and envelope.
UN
IT-3
-
18 H
ou
rs Unit-3
Fold: Definition; classifications - geometrical and genetic; its types. Mechanism of Fold
formation. Superimposed fold; outcrop pattern of superimposed structure comprising of two fold
system. Stereographic Projection: Principles, Schmidt Net. Plotting a line, plane, intersection of
plane.
UN
IT-4
-
18H
ou
rs
Unit-4 Fault: types and mechanism of faulting; Principal stress orientation for the threemain fault types; Relationship between stress and strain ellipsoid. Joints and its types; their analysis and relationship
to major structures. Petrofabric Analysis: Field and laboratory techniques; Preparation of
petrofabric diagrams and their interpretation. Structure and tectonics of India
UN
IT-5
-
15
Ho
urs
Unit-5
Cleavage &Schistosity: definition and types. Mechanism of formation of Cleavage &Schistosity; its relationship with deformation and major structures. Lineation: definition and its types; their
mode of development and relation to major structures. Plutons: Definition & description; Role in
progressive deformation
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
LA
BO
RA
TO
RY
WO
RK
(MS
G2
12
)
Structural Geology Practical:-
1. Stereographic projection – problems in angular relationship true dip, apparent dip plunge and rake of the intersection of planes.
2. Study of minor structures in hand specimens.
3. Preparation & Interpretation of geological maps & structure contour maps.
4. Three point problems geometric solutions for three point problems & fault. 5. Measurement of strain in rock.
SU
GG
ES
TE
D R
EA
DIN
GS
1. Ghosh, S.K. (1993): Structural Geology: Fundamental and Modern Development.
Pergamon Press. 2. Hobbs, B.E., Means, W.D. and Williams, P.F. (1976): An outline of Structural Geology,
John Wiley and Sons, New York.
3. Ramsay, J.G. (1967): Folding and fracturing of rocks, McGraw Hill.
4. Ramsay, J.G. and Huber, M.I. (1983): Techniques of Modern Structural Geology, Vol. I, Strain Analysis, Academic Press.
5. Ramsay, J.G. and Huber, M.I. (1987): Techniques of Modern Structural Geology, Vol. II,
Folds and Fractures, Academic Press. 6. Ramsay, J.G. and Huber, M.I. (2000): Techniques of Modern Structural Geology, Vol. III
(Application of continuum mechanics), Academic Press.
7. Turner, F.J. and Weiss, L.E. (1963): Structural analysis of Metamorphic Tectonites,
McGraw Hill. 8. Windley B. (1973): The Evolving continents, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
M.Sc (GEOLOGY) 2ND
SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: MSG203 COURSE TYPE: CCC
COURSE TITLE: IGNEOUS PETROLOGY
CREDIT:7 HOURS:135
THEORY: 5 PRACTICAL: 2 THEORY:90 PRACTICAL: 45
MARKS
THEORY: 100(30+70) PRACTICAL:100
OBJECTIVE: This course is aimed towards generating fundamental knowledge, concepts and dimensions
of Igneous Rocks (Primary Rocks).
UN
IT-1
-
18
Hou
rs Unit-1
Magma: Its physics, nature, factors affecting magma and evolution. Petrology and melting of
mantle. Generation of magmas in different tectonic environments.
UN
IT-2
-
18H
ou
rs Unit-2
The Phase equilibrium of binary (Ab-An, Ab-Or, Di-An, Fo-Si) and ternary (Di-Ab-An, Di-
Fo-Si, Di-Fo-An, Ne-Ks-Si, Fo-An-Si) systems and its relation to magma genesis and crystallization in the light of modern experimental works.
UN
IT-3
-
18 H
ou
rs Unit-3
Interpretation of igneous textures in terms of rate of nucleation and crystal growth. IUGS
classification of the Igneous rocks. CIPW Norm.
UN
IT-4
-
18H
ou
rs
Unit-4 Petrology and petrogenesis of major igneous rock types giving Indian examples of Ultramafic,
Basaltic, Granitic, Alkaline, Ophiolite, Carbonatite, Nephelinite-Ijolilte, Lammproits, and Layered igneous rocks.
UN
IT-5
-
15H
ou
rs
Unit-5 Plume magmatism and hot spots. Mantle metasomatism. Mantle heterogeneities. Partial melting (batch and fractional melting), crystal fractionation [equilibrium and fractional
(Rayleigh) crystallization], contamination (AFC process) and dynamic melting
LA
BO
RA
TO
R
Y W
OR
K
(MS
G2
13
)
Igneous petrology practical:-
1. Identification of various igneous rocks in hand specimen through megascopic
characters. 2. Identification of various igneous rocks through microscopic characters.
3. Simple CIPW norms calculations
4. Harker’s and niggli’s variation diagrams and their interpretation.
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
SU
GG
ES
TE
D R
EA
DIN
GS
1. Bose, M.K., 1997. Igneous Petrology, World Press, Kolkata.
2. Best, Myron G., 2002. Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Blackwell Science.
3. Cox, K.G., Bell, J.D. and Pankhurst, R.J.,1993: The Interpretation of Igneous Rocks. Champman& Hall, London.
4. Faure, G. : Origin of Igneous Rocks, Springer.
5. Hall,A., 1997 : Igneous Petrology, Longman.
6. LeMaitre, R.W., 2002. Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms, Cambridge University Press.
7. McBirney, 1994. Igneous Petrology, CBS Publishers, Delhi.
8. Phillpotts, A.R., 1994. Principles of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Prentice Hall of India.
9. Sood, M.K., 1982: Modern Igneous Petrology. Wiley-Interscience Publ., New
York. 10. Srivastava, Rajesh K. and Chandra, R., 1995: Magmatism in Relation to Diverse
Tectonic Settings.
11. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam.
12. Wilson, M., 1993: Igneous Petrogenesis. Chapman & Hall, London. 13. Winter, J.D., 2001: An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology.
Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
M.Sc (GEOLOGY) 2ND
SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: MSG B01 COURSE TYPE : ECC
COURSE TITLE: FOREST AND ENVIRONMENTAL LAWS
CREDIT: 06
THEORY: 06
HOURS : 90
THEORY: 90
MARKS : 100
THEORY: 70 CCA : 30
OBJECTIVE:
- Understands the concept and place of research in concerned subject
- Gets acquainted with various resources for research
- Becomes familiar with various tools of research
- Gets conversant with sampling techniques, methods of research and techniques of analysis
of data
- Achieves skills in various research writings
- Gets acquainted with computer Fundamentals and Office Software Package .
UN
IT -
1
1
8 H
rs
EVOLUTION OF FOREST AND WILD LIFE LAWS
a) Importance of Forest and Wildlife
b) Evolution of Forest and Wild Life Laws
c) Forest Policy during British Regime
d) Forest Policies after Independence.
e) Methods of Forest and Wildlife Conservation.
UN
IT -
2
18 H
rs
FOREST PROTECTION AND LAW
a) Indian Forest Act, 1927
b) Forest Conservation Act, 1980 & Rules therein
c) Rights of Forest Dwellers and Tribal
c) The Forest Rights Act, 2006
d) National Forest Policy 1988
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
UN
IT -
3
18 H
rs
WILDLIFE PROTECTION AND LAW
a) Wild Life Protection Act, 1972
b) Wild Life Conservation strategy and Projects
c) The National Zoo Policy
UN
IT -
4
1
8 H
rs
CHAPTER – BASIC CONCEPTS
a. Meaning and definition of environment.
b. Multidisciplinary nature of environment
c. Concept of ecology and ecosystem
d. Importance of environment
e. Meaning and types of environmental pollution.
f Factors responsible for environmental degradation.
CHAPTER– INTRODUCTION TO LEGAL SYSTEM
a. Acts, Rules, Policies, Notification, circulars etc
b. Constitutional provisions on Environment Protection
c. Judicial review, precedents
d. Writ petitions, PIL and Judicial Activism
CHAPTER – LEGISLATIVE FRAMEWORK FOR POLLUTION CONTROL LAWS
a) Air Pollution and Law.
b) Water Pollution and Law.
c) Noise Pollution and Law.
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
UN
IT -
5
18 H
rs
CHAPTER- LEGISLATIVE FRAMEWORK FOR ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION
a) Environment Protection Act & rules there under
b) Hazardous Waste and Law
c) Principles of Strict and absolute Liability.
d) Public Liability Insurance Act
e) Environment Impact Assessment Regulations in India
CHAPTER – ENVIRONMENTAL CONSTITUTIONALISM
a. Fundamental Rights and Environment
i) Right to Equality ……….Article 14
ii) Right to Information ……Article 19
iii) Right to Life …………..Article 21
iv) Freedom of Trade vis-à-vis Environment Protection
b. The Forty-Second Amendment Act
c. Directive Principles of State Policy & Fundamental Duties
d. Judicial Activism and PIL
SU
GG
ES
TE
D R
EA
DIN
GS
Bharucha, Erach. Text Book of Environmental Studies. Hyderabad : University Press (India) Private limited, 2005.
Doabia, T. S. Environmental and Pollution Laws in India. New Delhi: Wadhwa and Company, 2005.
Joseph, Benny. Environmental Studies, New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company
Limited, 2006.
Khan. I. A, Text Book of Environmental Laws. Allahabad: Central Law Agency, 2002.
Leelakrishnan, P. Environmental Law Case Book. 2nd
Edition. New Delhi: LexisNexis
Butterworths, 2006.
Shastri, S. C (ed). Human Rights, Development and Environmental Law, An Anthology. Jaipur:
Bharat law Publications, 2006.
Environmental Pollution by Asthana and Asthana, S,Chand Publication
Environmental Science by Dr. S.R.Myneni, Asia law House
Gurdip Singh, Environmental Law in India (2005) Macmillan.
Shyam Diwan and Armin Rosencranz, Environmental Law and Policy in India –
Cases, Materials and Statutes (2nd
ed., 2001) Oxford University Press.
JOURNALS :-
Journal of Indian Law Institute, ILI New Delhi.
Journal of Environmental Law, NLSIU, Bangalore.
MAGAZINES :-
Economical and Political Weekly
Down to Earth.
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
M.Sc (GEOLOGY) 2ND
SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: MSGB02 COURSE TYPE: ECC
COURSE TITLE: TOPOGRAPHIC SURVEY
CREDIT: 6 HOURS: 90
THEORY: 6 PRACTICAL:0 THEORY:90 PRACTICAL:00
MARKS
THEORY: 100(30+70) PRACTICAL:100
OBJECTIVE: This course is aimed towards generating fundamental knowledge, concepts and dimensions
of Topographic Survey for geological mapping.
UN
IT-1
-
18
Hou
rs Unit-1
Working principle of prismatic compass. Measurement of distance, chain surveying, prismatic
compass and chain traversing. Introduction to toposheet, Brunton Compass, Clinometer and
Geological Maps.
UN
IT-2
-
18H
ou
rs Unit-2
Working principle of dumping level and its application in geological mapping. Levelling with
dumpy level and contouring.
UN
IT-3
-
18
Hou
rs Unit-3
Plane table surveying and three point problems geological maps: Geometric solution and fault
problem.
UN
IT-4
-
18H
ou
rs
Unit-4
Working principal of Theodolite. Measurement of horizontal and vertical angles with transit
theodolite, triangulation, tacheometric survey with theodolite and plane table with telescope
alidade.
UN
IT-5
-
15H
ou
rs Unit-5
Working principle of GPS and DGPS. Use of global positioning system (GPS) in surveying and
their application in Geological Mapping.
SU
GG
ES
TE
D
RE
AD
ING
S
1. Lahee. F.H, Geological Field Geology 2. Roy Chowdhary, K.P. (1987): Surveying (Plane and Geodetic) Oxford & IBH Pub. Co.,
New Delhi.
3. Shahani, P.B. (1978): Text Book of Surveying, vol.I. Oxford & IBH Pub. Co., New Delhi
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
M.Sc (GEOLOGY) 2ND
SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: MSGB03 COURSE TYPE: ECC
COURSE TITLE: ENVIRONMENTAL LAW AND POLICIES
CREDIT:6 HOURS:90
THEORY: 6 PRACTICAL: 00 THEORY: 90 PRACTICAL:00
MARKS
THEORY: 100(30+70) PRACTICAL:00
OBJECTIVE: This course is aimed towards generating fundamental knowledge, concepts and dimensions
to analyse the basic principles of IndianEnvironmental Law And Policy
UN
IT-1
-
18 H
ou
rs
Unit-1
To critically analyse the role of Indian Judiciary in evolution of Indian environmental law, To
familiarize the laws relating to pollution control, forest and wildlife, hazardous substances and
processes, coastal protection, and climate change, Climate Change, Basic concepts UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, Kyoto Protocol. International Organizations and
Institutions: WMO, IPCC, Trade and Climate change Negotiations National Scenario: National Action Plan on Climate Change, Energy Conservation Act, 2001
UN
IT-2
-
18H
ou
rs Unit-2
Introduction to environmental laws in India, Constitutional provisions, Stockholm conference; Bhopalgas tragedy; Rio conference. General principles in Environmental law. Environment
protection laws and large projects, Legal framework on environment protection-Environment
Protection Act as the framework legislation – strength and weaknesses; National Environment Appellate Authority Act,1995. EIA.
UN
IT-3
-
18 H
ou
rs Unit-3
Air, Water and Marine Laws.National Water Policy and some state policies.Laws relating to prevention of pollution, access and management of water and institutional mechanism: Water
Act, 1974; Water Cess Act,1977, EPA, 1986. Ground water and law Judicial remedies and
procedures Marine laws of India; Coastal zone regulations. Legal framework on Air pollution: Air Act,1981; EPA, 1986
UN
IT-4
-
18
Ho
urs
Unit-4
Forest, Wildlife and Biodiversity related law. Evolution and Jurisprudence of Forest and Wildlife laws;Colonial forest policies; Forest policies after independence, Statutory framework on Forests,
Wildlife and Biodiversity: IFA, 1927; WLPA, 1972; FCA, 1980; Biological Diversity Act,2002;
Forest Rights Act, 2006. Forest policy and Joint forest management Strategies for conservation – Project Tiger, Elephant, Rhino, Snow leopard. Role of NGOs. National Biodiversity Action
Plan, Role of judiciary
UN
IT-5
-
15H
ou
rs
Unit-5
Hazardous Substances and Activities. Legal framework: EPA and rules made there under;
NETA, 1988; PLI Act, 1991. Principles of strict and absolute liability, International
Environmental law An introduction to International law; sources of international law; law of treaties; signature,
ratification. Evolution of international environmental law, Customary international law, Common
but differentiated responsibility, Polluter pays.
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
SU
GG
ES
TE
D
RE
AD
ING
S 1. Divan S. andRosencranz A(2005).;Environmental Law and Policy in India.2nd edn.,
Oxford, New Delhi.
2. Leelakrishnan, P. (2008), EnvironmentalLaw in India, 3rd edn., Lexis Nexis, India
M.Sc Geology/ 2nd SEMESTER/SU
M.Sc (GEOLOGY) 2ND
SEMESTER
COURSE CODE: MSGB04 COURSE TYPE: ECC
COURSE TITLE: MINERAL ECONOMICS
CREDIT:6 HOURS: 90
THEORY: 6 PRACTICAL: 00 THEORY: 90 PRACTICAL: 00
MARKS
THEORY: 100(30+70) PRACTICAL: 00
OBJECTIVE: This course is aimed towards generating fundamental knowledge, concepts and knowledge
of mineral economics of India and foreign.
UN
IT-1
-
18
Hou
rs
Unit-1 Definition: importance of minerals in national economy, pattern of mineral relationships,
geographic and political factors in mineral use, features peculiar to mineral industries,
economics factors, common to mineral and manufacturing industries. Demand and supply of minerals, cartels, substitutes, market speculations and production cost, international nature and
movement of minerals.
UN
IT-2
-
18H
ou
rs Unit-2
Mineral production and economics of Indian minerals and metals. Diamonds, coal, petroleum, uranium, thorium, iron manganese, chromium, nickel, tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium,
titanium, copper, lead, zinc, tin, zirconium, gold, silver, sulphur, fertilizer minerals. Insulating
minerals and mica.
UN
IT-3
-
18 H
ou
rs Unit-3
Trade restrictions, tariff, quotas and embargoes, production incentives, foreign development
and exploitation of minerals. Total world resources, reserves, and production of important
minerals.
UN
IT-4
-
18H
ou
rs Unit-4
Tenor, grade and specification. Strategic, critical and essential minerals. Conservation and substitution. Changing pattern of mineral requirement. UNFCC Minerals Classification.
UN
IT-5
-
15H
ou
rs Unit-5
Importance of minerals in national economy. National mineral policy. Indian mineral policy and legislation. Chhattisgarh state mineral policy.
SU
GG
ES
TE
D
RE
AD
ING
S 1. Sinha, R.K. and Sharma, N.L. (1976) Mineral Economics.
2. Arogyaswami, R.P.N. (1996) Courses in Mining Geology.