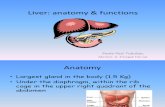
Liver Functions Part II
-
Upload
deepa-karthik -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Liver Functions Part II
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
1/39
Liver Functions Part II
3E1
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
2/39
From where we left off…
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
3/39
In the small intestines
• Complete digestion occurs in the smallintestines
• End products (glucose, amino acids, fattyacids, glycerol) diffuse into the blood vesselslining the small intestines.
• This process is called Absorption.
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
4/39
Some animal samples
• Guess what is the organ
shown!
• From which animal?
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
5/39
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
6/39
Adaptation of the
small intestine forabsorption
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
7/39
Structure of small intestine
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
8/39
What do you see in the intestinal walls?
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
9/39
How do the folds and villi help
in absorption?
• The presence of folds and villi
in the intestinal wall increase
surface area
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
10/39
More adaptations from the small
intestine
• the epithelial cell of the intestinal wall
• One-celled thick epithelial wall and microvilli
further increases
surface area
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
11/39
The small intestines• What makes the small intestines suitable for Absorption?
1) Elongated ileum, Innersurface of the ileum is folded
These features provide large surface area:vol for absorption
2) Villi andmicrovilli
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
12/39
The small intestines• What makes the small intestines suitable for Absorption?
3) Many blood
vessels lining thesmall intestines
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
13/39
Absorption• Absorption occurs by: – Diffusion
– Active transport
• After absorption,
Glucose and
amino acids enter
the blood
capilliaries
Glycerol and
fatty acids enter the
lacteals
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
14/39
How does absorption takes
place in the intestines
Absorption of fatty acids and glycerol
• Glycerol and fatty acids diffuse into theepithelium where they combined to formminute fat globules and enters the lacteals
•Fat globules mix with lymph in the lacteals toform chyle
• Liver is not involved *
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
15/39
Assimilation
and
function of the liver
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
16/39
Overview
Role of Digestion Mouth & Oesophagus
Gall Bladder &Pancreas
Stomach
Large Intestine & Others Small Intestine
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
17/39
Overview – 4 Stages
Ingestion Digestion
AbsorptionAssimilation
http://www.biotechlearn.org.nz/var/biotech/storage/images/home_page_images/children_eating_watermelon/4559-12-eng-GB/children_eating_watermelon_full.jpghttp://images.google.com.sg/imgres?imgurl=http://www.sciencebob.com/lab/bodyzone/stomach.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.discovervancouver.com/forum/topic.asp%3FTOPIC_ID%3D86784&h=251&w=301&sz=27&hl=en&start=4&tbnid=NlsB0oiXIvCe7M:&tbnh=97&tbnw=116&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dstomach%26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Denhttp://images.google.com.sg/imgres?imgurl=http://www.pediatriconcall.com/kidscorner/ScanImg/IntestineSmall.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.pediatriconcall.com/kidscorner/yourbody/our_digestive_system.asp&h=176&w=147&sz=7&hl=en&start=9&tbnid=ylhvcNEQkQLmOM:&tbnh=100&tbnw=84&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dsmall%2Bintestine,%2Bcartoon%26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DXhttp://images.google.com.sg/imgres?imgurl=http://lib.store.yahoo.net/lib/musclesurf/ab-man1.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.musclesurf.com/reports.html&h=196&w=233&sz=14&hl=en&start=7&tbnid=RDaR_yG4QEa3NM:&tbnh=92&tbnw=109&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dbuild%2Bmuscle%26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Denhttp://images.google.com.sg/imgres?imgurl=http://bio.bd.psu.edu/cat/Circulatory_System/vesels%2520of%2520small%2520intestine.jpg&imgrefurl=http://bio.bd.psu.edu/cat/Circulatory_System/arteries_and_veins_of_digestive_.htm&h=491&w=614&sz=79&hl=en&start=2&tbnid=vafghYkxmx9MDM:&tbnh=109&tbnw=136&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dsmall%2Bintestine%26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Denhttp://images.google.com.sg/imgres?imgurl=http://www.pediatriconcall.com/kidscorner/ScanImg/IntestineSmall.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.pediatriconcall.com/kidscorner/yourbody/our_digestive_system.asp&h=176&w=147&sz=7&hl=en&start=9&tbnid=ylhvcNEQkQLmOM:&tbnh=100&tbnw=84&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dsmall%2Bintestine,%2Bcartoon%26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DXhttp://images.google.com.sg/imgres?imgurl=http://www.sciencebob.com/lab/bodyzone/stomach.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.discovervancouver.com/forum/topic.asp%3FTOPIC_ID%3D86784&h=251&w=301&sz=27&hl=en&start=4&tbnid=NlsB0oiXIvCe7M:&tbnh=97&tbnw=116&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dstomach%26gbv%3D2%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Denhttp://www.biotechlearn.org.nz/var/biotech/storage/images/home_page_images/children_eating_watermelon/4559-12-eng-GB/children_eating_watermelon_full.jpg
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
18/39
Lesson objectives:
• Describe the fate of glucose, amino acids and fats inthe blood that leaves the intestines, after a meal.
• Describe the 5 major roles that the liver plays in the
human body – Regulation of blood glucose concentration
– Deamination of amino acids
– Production of bile
–
Detoxication – Iron storage
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
19/39
Fate of
glucose and
amino acids
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
20/39
Transport and utilization of absorbed foods
In the Liver!
Types of absorbed food products
Glucose
Amino acids
Fats
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
21/39
From the small intestines to the
liver! How??
Connected by a
vein called Hepatic
Portal Vein!
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
22/39
Guess which part the vein connects
to the intestine?
A
B
C
D
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
23/39
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
24/39
Carbohydrate metabolism
Hepatic portal veintransports sugars like glucose from
the intestines to the liver
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
25/39
Question!
Receives 5 glucose
molecules from the
intestines
Requires only 3
glucose molecules for
breathing
h l l f l d
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
26/39
how many molecules of glucose do you
think the liver would transport to the
lungs?
Receives 5 glucose
molecules from the
intestines
Requires only 3
glucose molecules for
breathing
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
27/39
Liver in Glucose metabolism
Hepatic portal vein
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
28/39
In the liver….
1. Some glucose carried in the blood to bedistributed to the rest of the body
- Tissue respiration
Carbohydrate metabolism
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
29/39
In the liver….
-Glucose (excess) Glycogen (stored)Hormone : Insulin
- If the glucose level is too low in the blood
Glycogen (stored) Glucose
Hormone: Glucagon
Insulin and glucagon
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
30/39
What about the amino acids
absorbed by the small intestines?
Similar route as sugars:
Intestines hepatic portal vein
liver general blood
circulation
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
31/39
Liver in Protein metabolism
Hepatic portal vein
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
32/39
Fate of amino acids
Amino acid metabolism
•Converted into
protoplasm•Used for growth
& repair of worn-
out parts•Formation of
enzymes &
hormones
•Excess amino
acids cannot bestored :
Deamination
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
33/39
Deamination
—N— H
H
C—OH||O
R
|—C—
|
H
Amino group Carbon residue
Ammonia (toxic)
Urea (non-toxic)
glucose
glycogen
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
34/39
Intestines lacteal lymphatic vessels blood rest
of the body
Fat metabolism
Fate of Fats
• maintenance of cell
membranes
•Production ofhormones
• Excess fats stored in
adipose tissues
When glucose supply is low,
fats will be oxidised in the liver
to provide energy
(Liver not involved)
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
35/39
Summary:
5 major roles that the liver plays
– Regulation of blood glucose
concentration
–
Deamination of amino acids – Iron storage
– Production of bile
– Detoxication
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
36/39
True/False
• Liver is part of the alimentary canal
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
37/39
True/False
• Carbohydrates are digested in the liver
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
38/39
True/False
• Excess amino acids are deaminated
-
8/15/2019 Liver Functions Part II
39/39
True/False
• Fats are absorbed in the liver and
transport to other parts of the body for
usage.







![[Splab8]Functions II](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/588121751a28abb9388b701d/splab8functions-ii.jpg)











