LIPIDS I. Definition: Made up of C, H and O Lipids are hydrophobic compounds. Lipids are hydrophobic...
-
Upload
lorraine-rogers -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
3
Transcript of LIPIDS I. Definition: Made up of C, H and O Lipids are hydrophobic compounds. Lipids are hydrophobic...
DefinitionDefinition:: Made up of C, H and O
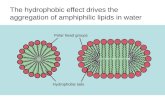
Lipids are hydrophobic compounds. Lipids are hydrophobic compounds.
insoluble or poorly soluble in water, insoluble or poorly soluble in water,
Readily soluble in non-polar solvents Readily soluble in non-polar solvents such as ( ether, benzene, acetone, such as ( ether, benzene, acetone, chloroform)chloroform)
Biological Functions of Biological Functions of LipidsLipids
As a major As a major source of energysource of energy, lipids provide 9 kcal of , lipids provide 9 kcal of energy per gramenergy per gram
Triglycerides provideTriglycerides provide energy storageenergy storage in adipocytes in adipocytes Phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and steroids are Phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and steroids are
structural componentsstructural components of cell membranes of cell membranes SteroidSteroid hormoneshormones are critical intercellular are critical intercellular
messengersmessengers Fat-soluble Fat-soluble vitaminsvitamins (A, E, D, K) (A, E, D, K) Dietary fat acts as a Dietary fat acts as a carrier of Fat-solublecarrier of Fat-soluble vitamins vitamins
into cells of small intestineinto cells of small intestine Fat stored in adipose tissue serves as thermal Fat stored in adipose tissue serves as thermal
insulator in the subcutaneous tissue and protective insulator in the subcutaneous tissue and protective around certain organs (e.g. kidney).around certain organs (e.g. kidney).
Lipids act as electrical insulators in Lipids act as electrical insulators in myelinated nerves to allow rapid myelinated nerves to allow rapid propagation of nerve impulses.propagation of nerve impulses.
Cholesterol is an important constituent of Cholesterol is an important constituent of the cell membrane and is essential for the the cell membrane and is essential for the synthesis of steroid hormones, bile acids synthesis of steroid hormones, bile acids and vitamin D.and vitamin D.
Fat-soluble vitamins, steroid hormones and Fat-soluble vitamins, steroid hormones and eicosanoids play important regulatory roles eicosanoids play important regulatory roles in the body.in the body.
Lipoproteins (e.g. LDL & HDL) are a mean for transporting lipids in blood. Imbalance in lipid metabolism can lead to major clinical problems such as obesity and atherosclerosis
Test your understandingTest your understanding1- All of the following are true about lipids except:A.They are energy sourceB.They are soluble in waterC.They are hydrophobic compoundsD.Serve as thermal insulatorsE.Structural components of cell membranes 2- Lipids share the property of being:A.Soluble in water.B.Soluble in organic solvents.C.Insoluble in water.D.Insoluble in organic solvents.E.Both b and c.
Test your understandingTest your understanding
3- Lipids are considered as:3- Lipids are considered as:
A.A.First source of energy in the body.First source of energy in the body.
B.B. Second source of energy.Second source of energy.
C.C. Third source of energy.Third source of energy.
D.D.Energy reserves in the body.Energy reserves in the body.
E.E. Both b and d.Both b and d.
Fatty AcidsFatty Acids Fatty acids are water-insoluble. Fatty acids are water-insoluble. Long straight-chain carboxylic acids Long straight-chain carboxylic acids
– no branchingno branching Most common chains range from 10–20 carbons in Most common chains range from 10–20 carbons in
lengthlength Can be saturated (containing no double bonds) or Can be saturated (containing no double bonds) or
unsaturated (containing one or more double bonds unsaturated (containing one or more double bonds that are always separated at 3 carbon intervals), but that are always separated at 3 carbon intervals), but usually no other functional groups presentusually no other functional groups present
The general formula of saturated fatty acids is:The general formula of saturated fatty acids is: CH CH3 3 - ( CH- ( CH22))n n – COOH – COOH– Any fatty acid that cannot be synthesized by the Any fatty acid that cannot be synthesized by the
body is called an body is called an essential fatty acidessential fatty acid
Fatty Acid Fatty Acid NomenclatureNomenclature
Nomenclature reflects location of Nomenclature reflects location of double bondsdouble bonds
also used are common names (e.g., also used are common names (e.g., oleic, stearic, palmitic)oleic, stearic, palmitic)
Carbon atoms in a fatty acid are Carbon atoms in a fatty acid are numbered by 2 different systemsnumbered by 2 different systems::
1.1. Beginning from the carboxyl carbonBeginning from the carboxyl carbon
((ΔΔ delta end) as carbon 1, where delta end) as carbon 1, where numeric designation of the fatty acid shows the numeric designation of the fatty acid shows the
number of carbon atomsnumber of carbon atoms
2- followed by the number of double bonds,2- followed by the number of double bonds,
3- then the site of unsaturation.3- then the site of unsaturation.
COOH
2
1 3
4
15
16
Palmitic acid: Palmitic acid:
CHCH33(CH(CH22))1414COOH ; 16:0COOH ; 16:0 (16:0 indicates a fatty acid with 16 (16:0 indicates a fatty acid with 16
carbons and no double carbons and no double bonds).bonds).
Oleic acid: Oleic acid:
CHCH33(CH(CH22))77C=C(CHC=C(CH22))77COOH ; 18:1 COOH ; 18:1 ΔΔ 99 (18:1 (18:1 ΔΔ 9 indicates a fatty acid with 9 indicates a fatty acid with
18 carbons and one double bond 18 carbons and one double bond between carbons 9 and 10).between carbons 9 and 10).
Linoleic acid:Linoleic acid:
CHCH33 (CH (CH22) ) 44C=CCHC=CCH22C=C(CHC=C(CH22) ) 77COOH ; 18:2 COOH ; 18:2 ΔΔ 9,129,12
(18:2 (18:2 ΔΔ 9,12 indicates a fatty acid with 18 9,12 indicates a fatty acid with 18 carbons and 2 double bonds between carbons and 2 double bonds between carbons 9 and 10 and carbons 12 and13).carbons 9 and 10 and carbons 12 and13).
Linolenic acid: Linolenic acid:
CHCH33CHCH22C=CCHC=CCH22C=CCHC=CCH22C=C(CHC=C(CH22) ) 77COOH; 18:3 COOH; 18:3 ΔΔ 9,12,15 9,12,15
(18:3 (18:3 ΔΔ 9,12,15 indicates a fatty acid with 9,12,15 indicates a fatty acid with 18 carbons and 3 double bonds between 18 carbons and 3 double bonds between carbons 9 and 10, carbons 12 and 13 and carbons 9 and 10, carbons 12 and 13 and carbons 15 and 16).carbons 15 and 16).
Arachidonic acid:Arachidonic acid:
CHCH33 (CH (CH22) ) 33(CH(CH22C=C) C=C) 44(CH(CH22) ) 33COOH; 20:4 COOH; 20:4 ΔΔ 5,8,11,145,8,11,14
(20:4 (20:4 ΔΔ 5,8,11,14 indicates a fatty acid with 20 5,8,11,14 indicates a fatty acid with 20 carbonscarbons
and 4 double bonds between carbons 5 and 6,and 4 double bonds between carbons 5 and 6,
carbons 8 and 9, carbons 11 and 12 and carbons 8 and 9, carbons 11 and 12 and
carbons 14 and 15).carbons 14 and 15).
2. Beginning with the terminal methyl 2. Beginning with the terminal methyl carbon carbon
(known as omega (known as omega ώώ carbon) as carbon 1, carbon) as carbon 1, where where ώώ-3 for example indicates that;-3 for example indicates that; The closest double bond to the terminal The closest double bond to the terminal
methyl methyl group begins after 3 carbons from that end. group begins after 3 carbons from that end. Therefore,Therefore, linoleic acid ; is an linoleic acid ; is an ώώ -6 fatty acid -6 fatty acidCHCH33 (CH (CH22) ) 44C=CCHC=CCH22C=C(CHC=C(CH22) ) 77COOHCOOH ώώ -6,18:2 -6,18:2 ΔΔ 9,12 9,12
linolenic acid ;is an linolenic acid ;is an ώώ -3 fatty acid. -3 fatty acid.CHCH33CHCH22C=CCHC=CCH22C=CCHC=CCH22C=C(CHC=C(CH22) ) 77COOHCOOH ώώ -3,18:3 -3,18:3ΔΔ9,12,159,12,15
Fatty Acid PropertiesFatty Acid Properties Melting point increases with increasing carbon Melting point increases with increasing carbon
numbernumber Melting point of a saturated fatty acid is higher Melting point of a saturated fatty acid is higher
than an unsaturated fatty acid with the same than an unsaturated fatty acid with the same number of carbonsnumber of carbons
Typical saturated fatty acids are tightly packed Typical saturated fatty acids are tightly packed togethertogether
ciscis double bonds prevent good alignment of double bonds prevent good alignment of molecules in unsaturated fatty acids leading to molecules in unsaturated fatty acids leading to poor packingpoor packing
Double bonds lower melting point relative to Double bonds lower melting point relative to saturated acidsaturated acid
Saturated & Unsaturated Fatty AcidsSaturated & Unsaturated Fatty AcidsA. Saturated Fatty Acids:A. Saturated Fatty Acids:
NameName No of No of CarbonCarbon Atoms Atoms
No of DoubleNo of Double Bonds Bonds
Lauric (12:0)Lauric (12:0) 1212 00
Myristic (14:0)Myristic (14:0) 1414 00
Palmitic (16:0)Palmitic (16:0) 1616 00
Stearic (18:0)Stearic (18:0) 1818 00
Saturated fatty acids do not have double bondsSaturated fatty acids do not have double bonds..
They are formed inside the bodyThey are formed inside the body..
B.B. Unsaturated Unsaturated FattyFatty Acids: Acids:NameName No of CarbonNo of Carbon
Atoms Atoms No of DoubleNo of Double Bonds Bonds
Palmitoleic (16:1)Palmitoleic (16:1) 1616 11
Oleic (18:1)Oleic (18:1) 1818 11
Linoleic (18:2)Linoleic (18:2) 1818 22
Linolenic (18:3)Linolenic (18:3) 1818 33
Arachidonic (20:4)Arachidonic (20:4) 2020 44
The first double bond is usually at the ninth carbonThe first double bond is usually at the ninth carbonThe double bond is normally in a The double bond is normally in a cis cis configuration configurationDouble bonds lower the melting temperatureDouble bonds lower the melting temperatureThe The ciscis configuration doesn’t allow fatty acids to configuration doesn’t allow fatty acids to pack as close togetherpack as close together
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fatty Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fatty AcidsAcids
saturatedsaturated: the SFA: the SFA’’s of a lipid have no s of a lipid have no double bonds between carbons in chaindouble bonds between carbons in chain
polyunsaturatedpolyunsaturated: more than one : more than one double bond in the chaindouble bond in the chain
most common polyunsaturated fats most common polyunsaturated fats contain the polyunsaturated fatty acids contain the polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) (PUFAs) oleicoleic, , linoleiclinoleic and and linoleniclinolenic acid acid
unsaturated fats have lower melting unsaturated fats have lower melting points points
stearic (SFA) melts at 70stearic (SFA) melts at 70ooC, oleic (PUFA) C, oleic (PUFA) at 26at 26ooCC
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds. There are 2 types:double bonds. There are 2 types:
Essential fatty acidsEssential fatty acids::These fatty acids are with more than one These fatty acids are with more than one double bond, e.g. linoleic, linolenic and double bond, e.g. linoleic, linolenic and arachidonic,arachidonic,
they are not formed in the body and should they are not formed in the body and should be obtained from the diet.be obtained from the diet.
Non-essential fatty acidsNon-essential fatty acids: : These can be synthesized in the body.These can be synthesized in the body.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 C OH
O1245678 3
CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 C OH
O1245678 3
3 - Octenoic Acid
3, 6 - Octadienoic Acid
Short hand: 8:1 (3)
8:2 (3,6)
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Linoleic acid: Cis, cis, 9, 12 - Octadecadienoic acid
Linolenic acid: Cis, cis, cis 9, 12, 15 - Octadecatrienoic acid
Arachidonic acid: Cis, cis, cis, cis 5, 8, 11, 14 - Eicosatetraenoic acid
Linoleic Acid
Linolenic Acid
Arachidonic Acid
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Saturated vs. Unsaturated FatsFats
saturated fats tightly packed, clog saturated fats tightly packed, clog arteries as arteries as atherosclerosisatherosclerosis
because of double bonds, because of double bonds, polyunsaturated fats do not pack well polyunsaturated fats do not pack well -- like building a wall with bricks vs. -- like building a wall with bricks vs. irregular-shaped objectsirregular-shaped objects
plant fats are much higher in PUFAplant fats are much higher in PUFA ’’s s than animal fatsthan animal fats
Cis 9 - Octadecenoic Acid (oleic)
Trans 9 - Octadecenoic Acid (elaidic acid)
O
CH3(CH2)7 C C (CH2)7 C OH
HH
910 O
CH3(CH2)7 C C (CH2)7 C OH
H
H
Cis And Trans Fatty Acids