Lipids. Characteristics of Lipids NONPOLAR (neutral) DO NOT dissolve in water Hydrophobic...
-
Upload
marian-lane -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
3
Transcript of Lipids. Characteristics of Lipids NONPOLAR (neutral) DO NOT dissolve in water Hydrophobic...
Characteristics of LipidsCharacteristics of Lipids
NONPOLAR (neutral)NONPOLAR (neutral) DO NOT dissolve in water DO NOT dissolve in water
Hydrophobic Hydrophobic • (at least part of the molecule)(at least part of the molecule)
Will dissolve in Will dissolve in
nonpolar solvents nonpolar solvents
like ______like ______
EmulsifiersEmulsifiers
Can cause fats to mix with waterCan cause fats to mix with water Have polar and nonpolar endsHave polar and nonpolar ends Surround oil droplets with polar ends out to Surround oil droplets with polar ends out to
dissolve in waterdissolve in water• Ex- soaps and detergentsEx- soaps and detergents
Fats and OilsFats and Oils
made of glycerol and fatty acidsmade of glycerol and fatty acids Called-TRIGLYCERIDE:Called-TRIGLYCERIDE:
Made of a glycerol and 3 fatty acidsMade of a glycerol and 3 fatty acids linked through dehydration synthesis linked through dehydration synthesis
reactionsreactions
Fatty acids can be saturated or Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturatedunsaturated
Saturated Fatty Acids have no double Saturated Fatty Acids have no double covalent bonds between carbon atoms.covalent bonds between carbon atoms. (the C chain is “saturated” with all the H’s it (the C chain is “saturated” with all the H’s it
can hold)can hold) Solid at room temperatureSolid at room temperature
• Ex- butterEx- butter
Fatty acids can be saturated or Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturatedunsaturated
Unsaturated Fatty Unsaturated Fatty Acids Acids havehave double double covalent bonds covalent bonds between carbon between carbon atoms.atoms. Liquid at room Liquid at room
temperaturetemperature• Ex- oilsEx- oils
Hydrogenated?Hydrogenated?
Ever heard of hydrogenated fats? What Ever heard of hydrogenated fats? What do you think this means?do you think this means? Manufacturers add H’s to make fats saturatedManufacturers add H’s to make fats saturated
• Allows them to be solid and last longerAllows them to be solid and last longer• Can create TRANS FATSCan create TRANS FATS
Today show on fats
Kinds of LipidsKinds of Lipids
Fats and OilsFats and Oils
PhospholipidsPhospholipids
SteroidsSteroids
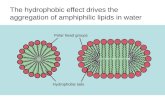
PhospholipidsPhospholipids
Have a phosphate in place of a fatty acidHave a phosphate in place of a fatty acid
PhospholipidsPhospholipids
Not electrically neutral like fatsNot electrically neutral like fats Have a POLAR HEAD (because of the Have a POLAR HEAD (because of the
phosphate ion) and a NONPOLAR TAILphosphate ion) and a NONPOLAR TAIL This property determines the structure of a This property determines the structure of a
cell membrane as we will see soon cell membrane as we will see soon
Kinds of LipidsKinds of Lipids
Fats and OilsFats and Oils
PhospholipidsPhospholipids
SteroidsSteroids
SteroidsSteroids
Backbone of 4 fused Carbon ringsBackbone of 4 fused Carbon rings
Ex- cholesterol (also important in cell Ex- cholesterol (also important in cell membranes)membranes)
What kind of lipid is shown below?What kind of lipid is shown below?
Fat
/Oil
Ste
roid
Phosp
holipid
33% 33%33%
11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 1010 1111 1212 1313 1414 1515 1616 1717 1818 1919 2020
2121 2222 2323 2424 2525 2626 2727 2828 2929 3030
1.1. Fat/OilFat/Oil
2.2. SteroidSteroid
3.3. PhospholipidPhospholipid
How would you describe the fatty How would you describe the fatty acid below?acid below?
.
.
.
..
1.1. HydrogenatedHydrogenated
2.2. SaturatedSaturated
3.3. UnsaturatedUnsaturated
11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 1010 1111 1212 1313 1414 1515 1616 1717 1818 1919 2020
2121 2222 2323 2424 2525 2626 2727 2828 2929 3030