1 Lipids Lipids are the hydrophobic compounds of C, H and O With much higher ratio of hydrogen to...
-
Upload
dwayne-collins -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
7
Transcript of 1 Lipids Lipids are the hydrophobic compounds of C, H and O With much higher ratio of hydrogen to...

1
LipidsLipids are the hydrophobic compounds of C, H and OWith much higher ratio of hydrogen to oxygen than carbohydrates
Most are insoluble in water but soluble in non polar compounds

2
Lipids
Types of Lipids
Fatty Acids
Fats, and Oils
Chemical Properties of Triglycerides

3
Properties of fats and oils
• fats are solids or semi solids• oils are liquids• melting points and boiling points are not
usually sharp (most fats/oils are mixtures)• when shaken with water, oils tend to emulsify• pure fats and oils are colorless and odorless
(color and odor is always a result of contaminants) – i.e. butter (bacteria give flavor, carotene gives color)

4
Examples of oils
• Olive oil – from Oleo europa (olive tree)• Corn oil – from Zea mays• Peanut oil – from Arachis hypogaea• Cottonseed oil – from Gossypium• Sesame oil – from Sesamum indicum• Linseed oil – from Linum usitatissimum• Sunflower seed oil – from Helianthus annuus• Rapeseed oil – from Brassica rapa• Coconut oil – from Cocos nucifera

5
Non-drying, semi-drying and drying oils
• based on the ease of autoxidation and polymerization of oils (important in paints and varnishes)
• the more unsaturation in the oil, the more likely the “drying” process– Non-drying oils:
• Castor, olive, peanut, rapeseed oils
– Semi-drying oils• Corn, sesame, cottonseed oils
– Drying oils• Soybean, sunflower, hemp, linseed, tung, oiticica oils

6
Types of Lipids
• Lipids with fatty acids
Waxes
Fats and oils (trigycerides)
Phospholipids
Sphingolipids
• Lipids without fatty acids
Steroids

7
Fatty Acids
• Long-chain carboxylic acids• Insoluble in water• Typically 12-18 carbon atoms (even number)• Some contain double bonds
corn oil contains 86% unsaturated fatty acids and 14% saturated fatty acids

8
Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Saturated = C–C bonds
Unsaturated = one or more C=C bonds
COOH
COOH
palmitoleic acid, an unsaturated fatty acid
palmitic acid, a saturated acid

9
Structures
Saturated fatty acids• Fit closely in regular pattern
Unsaturated fatty acids• Cis double bonds
COOHCOOHCOOH
C CH H
COOHcis double bond

10
Properties of SaturatedFatty Acids
• Contain only single C–C bonds
• Closely packed
• Strong attractions between chains
• High melting points
• Solids at room temperature

11
Properties of UnsaturatedFatty Acids
• Contain one or more double C=C bonds• Nonlinear chains do not allow molecules
to pack closely• Few interactions between chains• Low melting points• Liquids at room temperature

12
Fatty acids
• Common fatty acids
n = 4 butyric acid (butanoic acid)
n = 6 caproic acid (hexanoic acid)
n = 8 caprylic acid (octanoic acid)
n = 10 capric acid (decanoic acid)

13
Fatty acids
• common FA’s: n = 12: lauric acid (n-dodecanoic acid; C12:0)
n = 14: myristic acid (n-tetradecanoic acid; C14:0)
n = 16: palmitic acid (n-hexadecanoic acid; C16:0)
n = 18; stearic acid (n-octadecanoic acid; C18:0)
n = 20; arachidic (eicosanoic acid; C20:0)
n= 22; behenic acid
n = 24; lignoceric acid
n = 26; cerotic acid

14
Typical fish oil supplements

15
Learning Check L1
How would the melting point of stearic acid compare to the melting points of oleic acid and linoleic acid? Assign the melting points of –17°C, 13°C, and 69°C to the correct fatty acid. Explain.
stearic acid (18 C) saturated
oleic acid (18 C) one double bond
linoleic acid (18 C) two double bonds

16
Solution L1
Stearic acid is saturated and would have a higher melting point than the unsaturated fatty acids. Because linoleic has two double bonds, it would have a lower mp than oleic acid, which has one double bond.
stearic acid mp 69°C
oleic acid mp 13°C
linoleic acid mp -17°C

17
Fats and Oils
Formed from glycerol and fatty acids
+
HO C (CH2)14CH3
O
HO C (CH2)14CH3
O
HO C (CH2)14CH3
O
glycerol palmitic acid (a fatty acid)
CH
CH2 OH
OH
CH2 OH

18
Triglycerides (triacylglcerols)
Esters of glycerol and fatty acids
CH
CH2
CH2 O
O
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O
ester bonds
+
+
+
H2O
H2O
H2O

19
Learning Check L2
What are the fatty acids in the following triglyceride?
CH
CH2
CH2 O
O
O
C (CH2)16CH3
O
C
O
(CH2)7CH CH(CH2)7CH3
C
O
(CH2)12CH3

20
Solutions L2
What are the fatty acids in the following triglyceride?
CH
CH2
CH2 O
O
O
C (CH2)16CH3
O
C
O
(CH2)7CH CH(CH2)7CH3
C
O
(CH2)12CH3
Stearic acid
Oleic acid
Myristic acid

21
Properties of Triglycerides
Hydrogenation• Unsaturated compounds react with H2
• Ni or Pt catalyst• C=C bonds C–C bonds
Hydrolysis• Split by water and acid or enzyme catalyst• Produce glycerol and 3 fatty acids

22
Hydrogenation
CH
CH2
CH2 O
O
O
C
O
(CH2)5CH CH(CH2)7CH3
C
O
(CH2)5CH CH(CH2)7CH3
C
O
+
(CH2)5CH CH(CH2)7CH3
H23Ni

23
Hydrogenated fats
• hydrogenation leads to either saturated fats and or trans fatty acids
• the purpose of hydrogenation is to make the oil/fat more stable to oxygen and temperature variation (increase shelf life)
• example of hydrogenated fats: Crisco, margarine

24
Product of Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation converts double bonds in oils to single bonds. The solid products are used to make margarine and other hydrogenated items.
CH
CH2
CH2 O
O
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O

25
Hydrolysis
Triglycerides split into glycerol and three fatty acids (H+ or enzyme catalyst)
CH
CH2
CH2 O
O
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O
C (CH2)14CH3
O H2O+3
3+ HO C (CH2)14CH3
O
CH
CH2 OH
OH
CH2 OH
H+

26
Saponification and Soap
• Hydrolysis with a strong base• Triglycerides split into glycerol and the
salts of fatty acids • The salts of fatty acids are “soaps”• KOH gives softer soaps

27
Saponification
3+ Na+ -O C (CH2)14CH3
O
CH
CH2 OH
OH
CH2 OH
CH
CH2
CH2 O
O
O
C (CH2)16CH3
O
C
O
(CH2)16CH3
(CH2)16CH3C
O
+ 3 NaOH
salts of fatty acids (soaps)

28
Soaps• Process of formation is known as
saponification– Types of soaps:
• Sodium soap – ordinary hard soap• Potassium soap – soft soap (shaving soaps are
potassium soaps of coconut and palm oils)• Castile soap – sodium soap of olive oil• Green soap – mixture of sodium and potassium linseed
oil• Transparent soap – contains sucrose• Floating soap – contains air• Calcium and magnesium soaps are very poorly water
soluble (hard water contains calcium and magnesium salts –these insolubilize soaps)

29
Learning Check L3
What are the products obtained from the complete hydrogenation of glyceryl trioleate?
(1) Glycerol and 3 oleic acids
(2) Glyceryltristearate
(3) Glycerol and 3 stearic acids

30
Solution L3
What are the products obtained from the complete hydrogenation of glyceryl trioleate?
2. Glyceryltristearate

31
Lipids
Phospholipids
Steroids and Cholesterol
Plasma (Cell)Membranes

32
Phosphoglycerides
• Most abundant lipids in cell membranes • Control cell permeability
FATTY ACID
FATTY ACIDglycerol
PO4Amino alcohol

33
Steroids
• Steroid nucleus• 3 cyclohexane rings• 1 cyclopentane ring
steroid nucleus

34
Cholesterol
• Most abundant steroid in the body
• Add methyl CH3- groups, alkyl chain, and -OH to steroid nucleus
CH3
HO
CH3
CH3 CH3
CH3

35
Cholesterol in the Body
• Cellular membranes
• Myelin sheath, brain, and nerve tissue
• Bile salts
• Hormones
• Vitamin D

36
Bile Salts
• Synthesized in the liver from cholesterol
• Stored in the gallbladder
• Secreted into small intestine
• Mix with fats to break them part
• Emsulsify fat particles

37
Steroid Hormones
• Chemical messengers in cells• Sex hormones
Androgens in males (testosterone)
Estrogens in females (estradiol)• Adrenocorticosteroids from adrenal glands
mineralocorticoids (electrolyte balance)
glucocorticoids regulate glucose level

38
Sex Hormones
O
CH3
CH3OH
HO
CH3
CH3OH
testosterone estradiol

39
Plasma Membranes
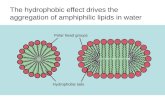
• Surround cells
• Lipid bilayer pf phospholipids
• Nonpolar hydrocarbon tails in center
• Polar (hydrophilic) sections on outside
• Some unsaturated fatty acids give flexibility
• Keep aqueous contents inside
• Allow certain biochemicals to pass through

4040
Diagram of a Plasma Membrane
Polar sections
Nonpolar tails