Life is Cellular. Anton van Leeuwenhoek-1600’s One of the first people to use a microscope to...
-
Upload
darlene-horton -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
1
Transcript of Life is Cellular. Anton van Leeuwenhoek-1600’s One of the first people to use a microscope to...

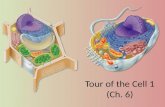
Chapter 7Cell Structure
and Function
Life is Cellular

The Cell Theory Anton van Leeuwenhoek-1600’s One of the first people to use a
microscope to study organism in pond water
Made detailed drawings of the organisms

Robert Hook -1665
Uses 1st light microscope to look at thin slices of plant tissue(cork)
Notices it was made of thousands of tiny chambers
Called them “Cells” Cells- basic units of all forms of
life

Under the microscope: drawings of the instruments used by Robert Hooke (left) and the
cellular structure of cork according to Hooke (right) (reproduced from Micrographia, 1665).

Matthais Schledian - 1838 All plants are made of cells
Rudolf Virchow – 1839 All animals are made of cells Summarized his research by saying
“Where a cell exist, there must have been a preexisting cell”

Cell Theory All living things are
composed of cells Cells are the basic units of
structure and function in all living things
New cells are produced from existing cells

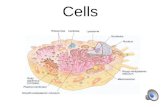
Basic Cell Structures
Despite differences in sizes and shapes, certain structures are common to most cells
All cells have a cell membrane and a cytoplasm

Plants Cells Slide Show by StudyJams
The cells of plants include several parts, such as the cell body, cytoplasm, mitochondria, nucleus, vacuole, cell wall, and cholorplasts. Only plant cells have plant cell walls and chloroplasts. Learn more about the plant cell with these detailed images from StudyJams. The pictures are set to music with information written under each photo. A short, self-checking quiz and song are also included on this link.
http://watchknowlearn.org/Video.aspx?VideoID=30845

Cell Membrane A thin, flexible barrier
around the cell Support, Protection, Interaction with environment

Cytoplasm All the material inside
the cell membrane except the nucleus
Contains many different structures known as organelles

Cytoplasm

Nucleus A large structure that contains the cells genetic material and controls the cells activities

Cell Wall A stronger, less flexible
layer around the perimeter of the cell
Found in plants Support, Protection, Interaction with environment

Prokaryotes and EukaryotesBiologist have divided cells into these 2
categories
PROKARYOTES EUKARYOTES Cell Membranes Cytoplasm No Nucleus Bacteria are
example Grow, Reproduce,
Respond to Environment
Cell Membranes/Walls
Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles-
perform important cellular functions
Some are single celled, some are multicellular
Plants, animals, fungi are examples

Cell Structures Cell Wall
Found in plants, fungi, and nearly all Eukaryotes Not found in animal cell Lies outside the cell membrane Allow H2O, O2, CO2, and other substances to pass
through them Main function is to provide support and protection for the
cell Made from fibers of carbohydrates and protein
Produced in the cell and released at the surface to build wall
Plant cell walls are made mostly of cellulose Tough carbohydrate fiber Primary component of wood and paper

Nucleus Controls cell processes and
contains hereditary information in the form of DNA
All plant and animals cell contain nucleus
Contains nearly all of the cells DNA (except Mitochondrial DNA)Coded instructions for making proteins
Main function of the cell

Nucleus

Chromatin Is the granular material
visible within the nucleus
Consist of DNA bound to proteins
Spaghetti on a plate

Chromatin

Chromosomes Are the condensed form
of chromatin Distinct, threadlike
structures containing genetic info that is passed on from one generation of cells to the next

Chromosomes

Nucleolus Small dense region of
nucleus where ribosome assembly begins
Ribosomes aid in production of protein in the cell

Nucleolus

Nuclear Envelope Double membrane layer
around the nucleus Covered with pores that
allow substances to pass into and out of the nucleus
RNA and other info carrying molecules pass through these pores

Nuclear Envelope

Cytoskeleton Network of protein
filaments, maintains cell shape, involved in cell movement, made up of microtubules and microfilaments

Cytoskeleton

Microtubules Hollow tubes of protein Maintain shape Act as tracks for organelle
movement inside the cell Help separate chromosomes in cell
division, formation of centrioles in animal cells
Bundles of microtubules in some cells form cilia and flagella to provide cellular movement

Microfiliments Long, thin fibers that function in
movement and support of cell Much narrower than microtubules Extensive networks in cells Tough, flexible support Movement of organelles Motor proteins attach to organelles and
generate force to move organelles along the cytoskeleton

Organelles in The Cytoplasm“Little Organ”
Ribosomes Produce proteins Small particles of RNA and
proteins assembled in the nucleus

Endoplasmic Reticulum Components of the cell membrane are assembled and proteins are modified
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN
ROUGH ER
LIPID SYNTHESIS IN
SMOOTH ER
Called “Rough” because of ribosome's attached to the surface
Called “ Smooth” because of lack of ribosome's on the surface

Golgi Apparatus
Enzymes attach lipids and carbohydrates to proteins here
Proteins move here from ER Proteins are sent to their
final destinations from here

Lysosomes Break down lipids,
carbohydrates, and proteins from food particles to be used by the rest of the cell
Break down organelles that have outlived their usefulness
Remove debris from cell

Vacuoles Store materials (water, carbs,
proteins) Sac-like structures Plant cells have 1 central large
vacuole filled with liquid to support heavy structures such as leaves and flowers
Sometimes called vesicles

Chloroplast• Found mostly in plants•Use sunlight to make energy rich
foodmolecules in a process known as
photosynthesis•Bound by 2 photosynthetic
membranes that contain Chlorophyll (a green pigment in plants)

Chlorophyll

Mitochondria Release stored energy from food particles
in the cell Powerhouse of the cell Use energy from food to make high
energy compounds that the cell can use to power growth, development, and movement
Has 2 membranes (Inner membrane is folded)
Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells

Organelle DNA Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain their own DNA that is
essential for their normal function and
growth

Endosymbiotic Theory Suggest that these organelles are
descendants of ancient prokaryotes They formed relationships with eukaryotic
cells that benefited them both Over time, the nuclear DNA took over cell
function and the organelle DNA became a remnant of their ancestors
In humans, we only inherit our mitochondria from our mothers!

Click on the HouseThe Cell as a Factory Read Page 182
Click icon to add picture
See Chart on page 183 – “A Comparison of Cells”

Movement through The Membrane
Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and
leaves the cell, provides protection and support
Takes in H2O and food and eliminates waste through the membrane

The Core of the Membrane is a Lipid Bylayer
Formed when certain kinds of lipids are dissolved in H2O
Each layer is composed of lipids with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
Tough, flexible barriers between the cell and its surroundings
Contain protein molecules that run through the layer
Form channels and pumps to help move materials across the membrane
Carbohydrate molecules attach to the outer surfaces of the proteins Act as chemical ID cards helping cells to
identify each other

The Core of the Membrane is a Lipid Bylayer

Diffusion One of the Most Important Functions of
the Cell Membrane is to control the movement of molecules from one side of the membrane to the other
The Concentration of a solution is the mass of the solute in a given volume of solution…mass/volumei.e 12 grams of salt dissolved in 3
liters of water is 12g/3L or 4g/L In a solution , molecules move
constantly, collide, and spread out randomly … they try to distribute evenly

Diffusion The movement of molecules from an area
of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration is known as Diffusion
When the concentration of a solute is the same throughout a solution, they system has reach Equilibrium
A solute will always try to establish a state of equilibrium
Diffusion causes substances to move across the membrane but does not require energy to do so

How Diffusion WorksThis animation shows the
Purple Molecules diffusing throughout the box.

Here the molecules move out of the liquid
and into the air by Diffusion

OsmosisIs the movement of water across a selectively
permeable membrane
Permeable Membranes allow all substances to cross
Impermeable Membranes do not allow any substances to cross
Selectively Permeable membranes only allow selected substances to cross

Osmosis

Isotonic A solution that is
equilibrium Same strength….same
concentration of solute and water

Isotonic

Hypertonic A solution that is said to
have a higher concentration of solute (less water per solute)
Above strength

Hypertonic

Hypotonic A solution that said to
have a lower concentration of solute (more water per solute)
Below Strength

Hypotonic

Osmotic Pressure A pressure exerted on the
hypertonic side of a selectively permeable membrane
Cells are filled with various molecules…salts, sugars, proteins, etc. therefore are Hypertonic to fresh water

Osmotic Pressure Water should move into the cell Cell should swell Most cells are bathed in isotonic fluids
such as blood that have concentrations of dissolved materials roughly equal to that inside the cell
Plant cells and bacteria that come into contact with fresh water have cell walls to help prevent them from expanding
Other cells use a mechanism to help pump out the excess water that is forced in by osmosis

Osmotic Pressure

The Diversity of Cellular Life
Unicellular OrganismsSingle celled organismsThey grow, respond to the
environment, and reproduce Include both prokaryotes and
eukaryotesBacteria (prokaryotes) and yeast
(eukaryotes) are examples Some live alone some live in
colonies

The Diversity of Cellular Life Multicellular Organisms
Cells do not ever live alone Cells are Interdependent; each has a function
that contributes to the fitness, or survival, of the organism
Have Cell Specialization Cells in multicellular organisms are specialized
to perform specific functions within the organism
Some created movement (muscle cells), some relay information (neurons), some produce enzymes (pancreatic cells, liver cells, gallbladder cells), etc

Levels of OrganizationA Multicellular organism from smallest to largest (most simple to most complex)
Cells
Tissue
Organs
Organ System

Cells Diversity of labor among
cellsBlood cells, nerve cells, muscle cells, etc
Specialization and Interdependence

TissuesA group of similar cells that perform a similar
function There are 4 Main types of tissue
(Muscles, Epithelial, Nervous, Connective) Epithelial Tissues cover or line body surfaces Connective Tissue include bone, blood,
cartilage and lymph Muscle Tissue controls the internal movement
of materials in the body, as well as external movement of the entire body or body parts
Nervous Tissue receives messages from the body’s external and internal environment, analyzes the data, and directs the response

Organs Many groups of tissues that
work together Each muscle in the body is and organ, although there are muscle tissue, nervous tissue (nerve endings and neurons), and connective tissue (cartilage, tendons, ligaments, blood) present in each muscle

Organ System A group of organs that works
together to perform a specific function and complete a series of specialized tasks.
There are 11 major organ systems in the human body

Chapter 7 Bellwork page 169-173
1. What does the Cell Theory State? 2. Explain the difference between Cell Wall
and Cell Membrane. 3. What is the main function of the Cell
Wall? 4. What is the main function of the
Nucleus? 5. Compare and Contrast Prokaryotes and
Eukaryotes. 6. What is the difference between
Chromatin and Chromosomes?

Chapter 7Bellwork page: 176-189
1. What are the functions of: A. Endoplasmic Reticulum B. Golgi Bodies C. Ribosomes D. Chloroplast E. Mitochondria 2. Where do we think mitochondrial DNA comes from? 3. Describe 2 main differences between Prokaryotic and
Eukaryotic Cells. 4. Describe a Lipid Bylayer. 5. Explain the process of diffusion. 6. What is Osmosis? 7. Explain the difference between isotonic, hypertonic, and
hypotonic. 8. What is facilitated diffusion? 9. Describe Active Transport.

Warm- Ups # 3 Pages 190-197
1. Explain the difference between unicellular and multicellular.
2. What is cell specialization? 3. What are the 4 levels of organization? 4. What are the 4 main types of tissue? 5. What is the difference between an
organ and an organ system?