Chromosomes, Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosomes, Mitosis and Meiosis Chapter 10.
LESSON # 19. TWO TYPES OF CELL DIVISION 1- MITOSIS 2- MEIOSIS The number of chromosomes in the...
-
Upload
shanon-russell -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of LESSON # 19. TWO TYPES OF CELL DIVISION 1- MITOSIS 2- MEIOSIS The number of chromosomes in the...

LESSON # 19

TWO TYPES OF CELL DIVISION
1- MITOSIS
2- MEIOSIS
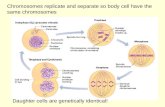
The number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is identical to that of the mother cells. It takes place in most cells (somatic cells)
The number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is the half of that of the mother cells. It takes place only in sex cells (gametes)

Somatic Cells
Reproductive Cells or Gametes
Sperm Egg
are Diploid Cells
are Haploid Cells

Somatic human cells are DIPLOID cells because they have 23 pairs of chromosomes ( 46 chromosomes ).
DIPLOID: Two sets of chromosomes.
HAPLOID: One set of chromosomes
Diploid cells: 2n cells. In this case, 2(23) cells.
Haploid cells: 1n cells. In this case, 1(23) cells.
Reproductive human cells are HAPLOID cells because they have 23 chromosomes.
(23)
(23)
Chromosomes in every pair have the same structure and function and are called homologous chromosomes.

MITOSIS
Haploid
Haploid
Haploid
(23)
(23)
(23)
During MITOSIS, the number of chromosomes does NOT change. Therefore, haploid cells will produce haploid cells.

Diploid
Diploid
Diploid
MITOSIS
During MITOSIS, the number of chromosomes does NOT change. Therefore, diploid cells will produce diploid cells.

(2n cell)
Diploid
GametogoniumDuring MEIOSIS I, a single diploid cell divides to produce two haploid repro-ductive cells. The number of chromo-somes is reduced to the half. Sister chromatids remain together.
(23)
Gamete (Haploid) Gamete (Haploid)
(23)(23)
MEIOSIS I
They are the cells that produce the gametes (oocyte and sperm).

MEIOSIS II
Haploid
Haploid
Haploid
(23)
(23)
(23)
During MEIOSIS II, the number of chromosomes does NOT change. Therefore, haploid cells will produce haploid cells.
During MEIOSIS II, each haploid gamete produces two haploid gametes. Sister chromatids separate like in mitosis.

Haploids
+
SpermEgg
1n cell 1n cell
(2n cell)
DiploidDuring FERTILIZATION, two haploid gametes combine to produce a diploid embryo.
Fe
rtilization

Somatic Cells undergo MITOSIS and cell division.
Reproductive Cells or Gametes: They are specialized cells, which come together to produce offspring.
Reproduction: It is the process by which the reproductive cells come together to produce offspring.
+chromosomes chromosomes2323
+
Haploid Haploid Diploid
chromosomes46
Gametogonia: They are cells, which undergo meiosis to produce haploid reproductive cells or gametes.

The cells that give rise to sperm and egg are diploid cells. When the cells that give rise to sperm and egg cells divide, the result is sperm or egg cells that have only half of the usual somatic number of chromosomes.
Haploid (1n) Haploid (1n)Haploid (1n) Haploid (1n)
Diploid (2n)
Spermatogonium
Diploid (2n)
Oogonium

Somatic Human Cells (diploid)
Mitosis
Diploid
Sperma-togonia
Oogonia
(Diploid)
(Diploid)Meiosis
MeiosisHaploid
Haploid
Haploid + Haploid
Diploid zygote
Sex Human Cells (haploid)

It is the process by which a single diploid cell divides to produce haploid reproductive cells.
1n 1n 1n 1n
2n
Meiosis
Homologous means same in size and function.

The Steps in Meiosis

MEIOSIS-I
MEIOSIS-II
One diploid cell gives rise two haploid cells.
Each haploid cell gives rise two haploid cells.
2n1n
1n
1n
1n
1n
1n
1n
1n
Homologous chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes
Meiosis

MetaphaseMetaphase
Paternal chromosome
Maternal chromosome
DNA
I

2n
MEIOSIS I
Homologous chromosomes
2n
MITOSIS
2n
2n
1n
1n
Homologous chromosomes

2n
1n 1n
MEIOSIS-I
MEIOSIS-II
1n 1n 1n 1n

1- Homologous chromosomes links as they condense forming tetrads.
2- Crossing over occurs.
Prophase I
MEIOSIS I
2n2n 2n
Maternal chromosomes
Paternal chromosomes

CROSSING OVER: It is the process by which non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material.
Crossing over is the first important source of genetic variation.
MEIOSIS I

Prophase I
1- Homologous chromosomes align at metaphase plate.
MEIOSIS I
or
Metaphase I
2- Independent assortment occurs.

MEIOSIS I
Green eyes & blond hair
Black eyes & black hair
Green eyes & black hair
Black eyes & blond hair
It is the random distribution of homologous chromosome pairs during the metaphase of meiosis I.
Independent Assortment:
Independent Assortment is the second important source of genetic variation.

Crossing over is the first important source of genetic variation.
Independent assortment is the second important source of genetic variation.
SOURCES OF GENETIC VARIATION
MEIOSIS I

2n2n
Microtubules separate the homologous chromosomes (sister chromatids remain together).
MEIOSIS I
1n
1n
Anaphase I

2n
1n
1n
Two haploid cells result from Cytokinesis
MEIOSIS I
Telophase I

MEIOSIS I
GENETIC VARIATION

1- Homologous chromosomes links as they condense forming tetrads.2- Crossing over occurs.
Prophase I
Crossing over is the process by which non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material Crossing over is the first important source of genetic variation.
Metaphase I1- Homologous chromosomes align at metaphase plate.
2- Independent assortment occurs. Independent assortment is the second important source of genetic variation.
Anaphase I1- Microtubules separate the homologous chromosomes (sister chromatids remain together).
Telophase I1-Two haploid cells result from Cytokinesis.
MEIOSIS I


Meiosis and Sex Outcome
DNA replication
DiploidDiploid
DiploidDiploid
HaploidHaploid
HaploidHaploid

The Y chromosome has about 50 genes.
The X chromosome has about 1500 genes.

MEIOSIS I
XX
X X
X XX X YX X Y
X Y
XY
MEIOSIS II
XX XYFemale Male
Diploid
Haploid Haploid
FERTILIZATION
MOTHER FATHERGAMETOGONIA
Meiosis and Sex Outcome
Diploid