Lesson 14 mirrors & lenses part i
-
Upload
dianegoldsberry -
Category
Business
-
view
393 -
download
3
Transcript of Lesson 14 mirrors & lenses part i

1. Working in pairs, students will match
scientific instruments to their
measurement. First two pairs to
correctly match all instruments earn the
“roller” chairs for the period.
2. Get your journal ready. Add one page of
guided notes to the next available page.
3. Time Limit: 8 minutes
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

S8P5:
Students will explore the
wave nature of sound and
electromagnetic radiation.
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

a. Identify the characteristics of electromagnetic and
mechanical waves.
b. Describe how the behavior of light waves is
manipulated causing reflection, refraction
diffraction, and absorption).
c. Explain how the human eye sees objects and colors
in terms of wavelengths.
d. Describe how the behavior of waves is affected by
medium (such as air, water, solids).
e. Relate the properties of sound to everyday
experiences.
f. Diagram the parts of the wave and explain how the
parts are affected by changes in amplitude and pitch.
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

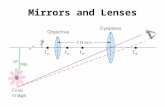
What is the difference
between a real image
and a virtual image?
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

Answer: Reflection
When a light ray hits a mirror, the light is
reflected off the shiny surface.
Which wave interaction does
a mirror demonstrate?
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

Flat surface
Produces virtual images– no
light rays pass through the image
Upright, same-sized image
http://www.geocities.com/CapeCanaveral/Hall/6645/pm-gif.htm
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

What image
is produced
by the
mirror?
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

1)To look at yourself in the mirror
2) To see around an angle – used in
periscopes
3) Overhead projectors
What uses can you think of?
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

Curves outward
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

What will the image of the plant look like in
a convex mirror?
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

Virtual image – rays never meet
Image is upright and smaller
Increase the field of view
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

1. Security in stores and factories – to
see around the corner
2.Side view mirrors on cars –
“Objects may be closer than they
appear”
What other uses can you think of for
convex mirrors?
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

Curves inward
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

D. Goldsberry 3/10/12

Has a focal point -- light rays are all
reflected to pass through one point
Has a focal length – distance from
the center of the mirror to the focal
point
D. Goldsberry 3/10/12