Optics Mirrors, Lenses and Stuff. The Electromagnetic Spectrum.
How are things transformed? Changes and interactions Unit IV – Lesson 1 –Images made by mirrors...
-
Upload
abraham-cox -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
description
Transcript of How are things transformed? Changes and interactions Unit IV – Lesson 1 –Images made by mirrors...
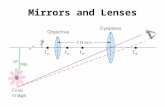
How are things transformed? Changes and interactions Unit IV Lesson 1 Images made by mirrors and lenses and their purpose Types of Mirrors Mirrors come in two basic forms: convex and concave. A convex mirror, reflects at a wider angle near its edged than its center, creating a slightly distorted image thats smaller than actual size. Concave mirrors curve inward, like a spoon (the side that holds soup). Convex vs. Concave Convex mirror Convex Mirror Convex mirrors have many uses, the smaller size of the images means that you can see more with these surfaces, hence their use in safety mirrors. Concave mirror This mirrors have the ability to create an image when their curvature bounces light to a specific area in front of them, this area is called the focal point. Non-reversing mirrors Also known as true mirrors, were created by placing two mirrors perpendicular to each other. Acoustic mirrors Huge concrete dishes built to reflect and distribute sound instead of light. Acoutic mirror Two-way mirrors These mirrors are made by coating one side of a sheet of glass with a very thi, very lightly reflective material. When the coated side faces a lighted room, some of the light reflects and some goes into a dark room behind the mirror, making it possible to see into the lighet room but not out. Two way mirror Refraction Image formation by a lens epends upon the wave property called refraction. Energys transformation, importance and uses Unit IV Lesson 2 Energy Energy is the capacity to do work. The international measurement system for energy is the International Measuring System, which from its name in french, its abreviated SI. The Joule, is the internationaly recognized unit for energy. Energy Any form of energy can be transformed into another form, the process of energy transformation is also known as energy coversion. Energy Transformation Energy doesnt disappear, it just changes forms. Energy transformation is the process of changing energy from one form to another. The main energy forms are: Radiant (light) energy Chemical energy Mechanical energy Nuclear energy Electrical energy Heat (thermal) energy Sound energy Energy Forms Energy forms can be classified in two types: Kinetic energy, which is motion energy. Potential energy, which is stored energy. Kinetic energy vs. Potential energy Sound energy Is a type of wave motion, sending molecules of air vibrating which produce sound. Electrical Energy Electrical energy is the moving electrical charges from one point to another in a conductor. Nuclear Energy Energy stored from the nucleus of an atom, that energy can be released when we combine or split the nucleus. Thermal Energy Total kinetic energy of atoms and molecules that are constantly in motion. Radiant Energy Energy made by electromagnetic waves that produce light.