Lec.5,pharynx pt&rc
-
Upload
dr-kamal-motawei -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
122 -
download
8
description
Transcript of Lec.5,pharynx pt&rc


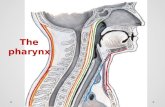
• It is a muscular tube,
deficient anteriorly,
where it lies behind
the nasal cavities, the
mouth and the larynx
• Extent: from base of
the skull to the C6
vertebra
• The wall of the
pharynx has 3 layers
1) Muscles
2) Fibrous tissue
3) Mucous
membrane

Pharynx is divided into 3 parts
1. Nasopharynx
2. Oropharynx
3. Laryngopharynx

• Lies behind the nasal cavities, above the soft palate
• Has a pure respiratory function.
• Communicates with nasal cavities.
Boundaries:
Roof: – it is formed by:
• body of sphenoid
• basilar part of occipital bone
– It shows • a collection of lymphatic tissue; pharyngeal
tonsil
Floor: – it is formed by the soft palate
– it communicates with oropharynx through the pharyngeal isthmus, which is closed during swallowing by the elevation of soft palate

Anterior wall: • formed by posterior nasal apertures
(choana)
Posterior wall: • basilar part of the occipital bone
• anterior arch of the atlas
Lateral wall:- has following features
1. Auditory tube opening: communication between nasopharynx and middle ear
2. Tubal elevation
3. Pharyngeal recess: depression behind the tubal elevation
4. Salpingopharyngeal and salpingopalatine folds
5. Collection of lymphoid tissue, tubal tonsil in submucosa of tubal elevation

• Lies behind the oral cavity
• Has a digestive & respiratory function
• Extends from the soft palate to the upper
border of epiglottis
Boundaries:
Roof: • soft palate and pharyngeal isthmus
Floor: • posterior one third of the tongue
Anterior wall: • opens into the mouth through the
oropharyngeal isthmus
Posterior wall: • supported by C2 and C3 vertibra
Lateral wall: • palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches
and palatine tonsil between them.


• Lies behind the larynx
• Below continuous with the esophagus
Boundaries:
• Anterior wall: larynx
• Posterior wall: C4– C6 vertebrae
• Lateral wall: shows
• Piriform fossa: Bounded
medially by the aryepiglottic fold and laterally by the thyroid cartilage and thyrohyoid membrane.

• 3 constrictors:
-superior
-inferior
-middle
• 3 longitudinal muscles:
-palatopharyngeus
-salpingopharyngeus
-stylopharygeus

Nerve supply
• Pharyngeal plexus: formed
by the branches from vagus
nerve, glossopharyngeal
nerve and superior cervical
ganglion.
• All pharyngeal muscles are
supplied by pharyngeal
plexus
• Exception –
stylopharyngeus, supplied
by glossopharyngeal nerve.

Blood supply
Arterial supply:
• Ascending pharyngeal
artery
• Tonsillar artery
• Facial
• Maxillary
• Lingual arteries
Venous drainage:
• Drain into the pharyngeal
plexus

WALDEYER’S RING OF LYMPHOID TISSUE
Pharyngeal tonsil
Tubal tonsil
Palatine tonsil
Lingual tonsil
Palatine tonsil
Tubal tonsil