L3 electronics pn junction
-
Upload
learninurducom-ustaadjeecom -
Category
Education
-
view
810 -
download
1
Transcript of L3 electronics pn junction

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
The pn junction diode
When a pn junction is formed, electrons in the n-material diffuse across the junction and recombine with holes in the p-material. This action continues until the voltage of the barrier repels further diffusion. Further diffusion across the barrier requires the application of a voltage.
The pn junction is basically a diode, which is a device that allows current in only one direction. A few typical diodes are shown.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Forward bias
When a pn junction is forward-biased, current is permitted. The bias voltage pushes conduction-band electrons in the n-region and holes in the p-region toward the junction where they combine.
The barrier potential in the depletion region must be overcome in order for the external source to cause current. For a silicon diode, this is about 0.7 V.
p-region n-region
p n
+
R
VBIAS
The forward-bias causes the depletion region to be narrow.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Reverse bias
When a pn junction is reverse-biased, the bias voltage moves conduction-band electrons and holes away from the junction, so current is prevented.
The diode effectively acts as an insulator. A relatively few electrons manage to diffuse across the junction, creating only a tiny reverse current.
p-region n-region
p n
+VBIAS
R
The reverse-bias causes the depletion region to widen.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
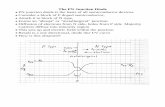
Diode characteristics
The forward and reverse characteristics are shown on a V-I characteristic curve. In the forward bias region, current increases dramatically after the barrier potential (0.7 V for Si) is reached. The voltage across the diode remains approximately equal to the barrier potential.
VR VF
IF
IR
Reverse bias
Forward bias
0.7 V
Barrier potential
The reverse-biased diode effectively acts as an insulator until breakdown is reached.
VBR (breakdown)

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Diode models
The characteristic curve for a diode can be approximated by various models of diode behavior. The model you will use depends on your requirements.
The ideal model assumes the diode is either an open or closed switch.
VR VF
IF
IR
Reverse bias
Forward bias
The complete model includes the forward resistance of the diode.
The practical model includes the barrier voltage in the approximation.
0.7 V

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Half-wave Rectifier
Rectifiers are circuits that convert ac to dc. Special diodes, called rectifier diodes, are designed to handle the higher current requirements in these circuits.
The half-wave rectifier converts ac to pulsating dc by acting as a closed switch during the positive alteration.
The diode acts as an open switch during the negative alteration.
D
D
RL
RL
+
+

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Full-wave Rectifier
The full-wave rectifier allows unidirectional current on both alterations of the input. The center-tapped full-wave rectifier uses two diodes and a center-tapped transformer.
F D1
D2RL
Vsec2
Vsec2
The ac on each side of the center-tap is ½ of the total secondary voltage. Only one diode will be biased on at a time.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Bridge Rectifier
The bridge rectifier is a type of full-wave circuit that uses four diodes. The bridge rectifier does not require a center-tapped transformer.
F
D1
D2
RL
At any instant, two of the diodes are conducting and two are off.
D3
D4

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Peak inverse voltage
Diodes must be able to withstand a reverse voltage when they are reverse biased. This is called the peak inverse voltage (PIV). The PIV depends on the type of rectifier circuit and the maximum secondary voltage.For example, in a full-wave circuit, if one diode is conducting (assuming 0 V drop), the other diode has the secondary voltage across it as you can see from applying KVL around the green path.
0 V
Vsec
Notice that Vp(sec) = 2Vp(out) for the full-wave circuit because the output is referenced to the center tap.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Peak inverse voltage
For the bridge rectifier, KVL can be applied to a loop that includes two of the diodes. Assume the top diode is conducting (ideally, 0 V) and the lower diode is off. The secondary voltage will appear across the non-conducting diode in the loop.
0 V
Notice that Vp(sec) = Vp(out) for the bridge because the output is across the entire secondary.
Vsec

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Power supplies
By adding a filter and regulator to the basic rectifier, a basic power supply is formed.
7805
FD1
D2C1
D3
D4C2
Typically, a large electrolytic capacitor is used as a filter before the regulator, with a smaller one following the regulator to complete filtering action.
1000 F 1 F
IC regulator

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Special-purpose diodes
Special purpose diodes include Zener diodes – used for establishing a reference voltage
Varactor diodes – used as variable capacitors
Light-emitting diodes – used in displays
Photodiodes – used as light sensors

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Troubleshooting power supplies
Begin troubleshooting by analyzing the symptoms and how it failed. Try to focus on the most likely causes of failure.
7805
FD1
D2C1
D3
D4C2
1000 F 1 F
IC regulator
A power supply has no output, but was working until a newly manufactured PC board was connected to it. (a) Analyze possible failures. (b) Form a plan for troubleshooting.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Troubleshooting power supplies
7805
FD1
D2C1
D3
D4C2
1000 F 1 F
IC regulator
The supply had been working, so the problem is not likely to be an incorrect part or wiring problem. The failure was linked to the fact that a new PC board was connected to it, which points to a possible overloading problem. If the load was too much for the supply, it is likely a fuse would have blown, or a part would likely have overheated, accounting for the lack of output.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Troubleshooting power supplies
1. Disconnect power and check the fuse. If it is bad, replace it. Before reapplying power, remove the load, open the power supply case, and look for evidence of overheating (such as discolored parts or boards). If no evidence of overheating proceed.2. Check the new pc board (the load) for a short or overloading of the power supply that would cause the fuse to blow. Look for evidence of overheating.
3. Verify operation of the supply with measurements (see next slide).
Based on the analysis, a sample plan is as follows. (It can be modified as circumstances warrant.)

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Troubleshooting power supplies
Reapply power to the supply but with no load. If the output is okay, put a resistive test load on the power supply and measure the output to verify it is operational. If the output is correct, the problem is probably with the new pc board. If not, you will need to further refine the analysis and plan, looking for an internal problem.
The analysis showed that a likely cause of failure was due to an overload. For the measurement step, it may be as simple as replacing the fuse and confirming that the supply works. After replacing the fuse:

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Majority carrier
Minority carrier
PN junction
Diode
The most numerous charge carrier in a doped semiconductor material (either free electrons or holes.
Selected Key Terms
The boundary between n-type and p-type semiconductive materials.
An electronic device that permits current in only one direction.
The least numerous charge carrier in a doped semiconductor material (either free electrons or holes.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Barrier potential
Forward bias
Reverse bias
Full-wave rectifier
A circuit that converts an alternating sine-wave into a pulsating dc consisting of both halves of a sine wave for each input cycle.
The condition in which a diode conducts current.
The inherent voltage across the depletion region of a pn junction diode.
Selected Key Terms
The condition in which a diode prevents current.

© 2010 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458. All Rights Reserved.
Instructor: Muhammad Bilal
Bridge rectifier
Zener diode
Varactor
Photodiode A diode whose reverse resistance changes with incident light.
A type of diode that operates in reverse breakdown (called zener breakdown) to provide a voltage reference.
A type of full-wave rectifier consisting of diodes arranged in a four corner configuration.
Selected Key Terms
A diode used as a voltage-variable capacitor.