Is Hepatitis B Curable? · 2020-06-06 · HBsA g subv iral partic les In tracel lu lar C o n v er...
Transcript of Is Hepatitis B Curable? · 2020-06-06 · HBsA g subv iral partic les In tracel lu lar C o n v er...

Is Hepatitis B Curable?
Marion G. Peters, MD
Professor of Medicine
Chief of Hepatology Research
University of California San Francisco
San Francisco, California
Slide 3 of 48
Learning Objectives
After attending this presentation, learners will be able to:
▪ List the limitations of current therapies for HBV
▪ Describe types of HBV cure
▪ Describe HBV latency
▪ List mechanisms of action of putative new therapies for
HBV
Slide 4 of 48
ARS 1: HBV status in 2019: which is true?
1. Acute HBV in adults leads to loss of HBsAg usually
2. HBV infection can be cured
3. Currently available drugs lead to loss of HBsAg usually
4. HBV is not a latent virus

Slide 5 of 48
ARS 2: New drugs in Phase I/II: which is false?
1. Target Hepatitis B core protein
2. Target HBV entry into hepatocyte
3. Target cccDNA in nucleus
4. Target HBV mRNA
5. Target HBV secretion
Slide 6 of 48
Prevalence of HBV/HCV Coinfection in People with HIV
» 10% of HIV persons are HBsAg positive
• About 5% to 10% of anti-HCV-antibody–positive patients are HBsAg-positive
• Hepatitis C superinfection of chronic HBsAg carriers is common in HBV endemic regions, such as Southeast Asia
Fernandez-Montero JV, Soriano V. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;26:517-530; WHO 2019.
Estimated Number of Persons Infected
Worldwide, in Millions
HBV257
HIV/HCV/HBV0.5
HIV35
HCV71 HCV/HBV
15
Not to scale.
HBV HIV4-10
HIV HCV2-3
Slide 7 of 48
HBV is a life long, dynamic disease
• Changes over time
• Risk of end stage liver disease and cancer increases with ongoing inflammation and viremia in adults
• Fibrosis can be reversible
• Drugs can decrease fibrosis progression
• HBV can be controlled but not cured
• Reactivation can occur even in those who have lost HBsAg
• HBV infection in neonates and young children leads to chronicity >90-95%
• HBV infection in adults (HIV) leads to chronicity <5% (~20%)

Slide 8 of 48
HBV Control
• Inflammatory: normalize serum ALT, biopsy
• Virologic: decrease HBV DNA
• Immune: seroconversion
–HBeAg to anti-HBe
–HBsAg to anti-HBs
• HBV as of 2019 not “cured” but controlled
Slide 9 of 48
Approved HBV treatments 2019
• Interferon alfa-2b – 1991
• Lamivudine – 1998
• Adefovir – 2002
• Entecavir – 2005
• Peginterferon alfa-2a – 2005
• Telbivudine – 2006
• Tenofovir Disoproxil– 2008
• Tenofovir alafenamide- 2017
Slide 10 of 48
Long-term Entecavir Treatment Improves Liver Histology and Fibrosis
Chang TT, et al. Hepatology. 2010;52:886-893 CCO Hepatitis.
73
96
0
20
40
60
80
Histologic improvement Fibrosis improvement
Coprimary Endpoints
Pati
en
ts (
%)
100
32
88
n = 41 55 158 50
Wk 48Long-term
biopsy >3y

Slide 11 of 48
Undetectable HBV DNA Over Time in
HBeAg Negative Patients
Lok AS, et al. Hepatology. 2009;50:661-662. Marcellin P, et al. AASLD 2008. Abstract 146. Marcellin P, et al. AASLD 2009. Abstract 481. Marcellin P, et al. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:2169-2179. Baqai S, et al. AASLD 2009. Abstract 476. Lai CL, et al. Hong Kong International Liver Congress 2006.
Extended Treatment With Nucleos(t)ide Analogues vs
1 Yr Peginterferon Treatment
Not head-to-head trials; different patient populations and trial designs
EntecavirTenofovirPeginterferon
Un
dete
cta
ble
HB
V D
NA
(%
)
90 938791
1 Yr 2 Yrs 3 Yrs
100
80
60
40
20
0
63
15 16
NA
100*
*Single center study.
96
Slide 12 of 48
HBsAg Loss Over Time in HBeAg Positive Patients
Chang TT, et al. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1001-1010. Marcellin P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2442-2455. Buster EH, et al. Gastroenterology. 2008;135;459-467. Gish R, et al. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1437-1444. Heathcote J. AASLD 2008. Abstract 158. Heathcote J, et al. AASLD 2009.
Abstract 483. Janssen HL, et al. Lancet. 2005;365:123-129; Marcellin Gastro 2016
Not head-to-head trials; different patient populations and trial designs
Extended Treatment With Nucleos(t)ide Analogues*
vs 1 Yr Peginterferon Treatment
HB
sA
g L
oss (
%)
2 3 66
100
80
60
40
20
0
5 88
NA
EntecavirTenofovirPeginterferon
*With sustained undetectable HBV DNA.
1.0 Yr 1.5-2.0 Yrs 3.0-4.0 Yrs
5
TDF +PEG 1y 9.3%37.5% geno A
Slide 13 of 48
Lai CL, et al. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1011-1020. Marcellin P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2442-2455. Marcellin P, et al. AASLD 2008. Abstract 146. Shouval D, et al. J Hepatol. 2009;50:289-295.
Marcellin P, et al. AASLD 2009. Abstract 481. Brunetto M, et al. EASL 2008. Abstract 683.Marcellin Gastro 2016
HBsAg Loss Over Time in HBeAg Negative Patients
Extended Treatment With Nucleos(t)ide Analogues*
Vs 1 Yr Peginterferon Treatment
Not head-to-head trials; different patient populations and trial designs
Pati
en
ts (
%)
< 1 04
0
100
80
60
40
20
0< 1
9
NA 07
1.0 Yr 1.5-2.0 Yrs 3.0-4.0 Yrs
*With sustained undetectable HBV DNA.
EntecavirTenofovirPeginterferon
TDF +PEG 1y 5%33% geno A

Slide 14 of 48
RT
Mature HBV
virion
Mature
Nucleocapsid
Immature
Nucleocapsid
Core + pg RNA
+ Polymerase
HBsAg proteins:
HBsAg subviral
particles
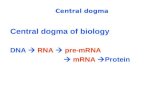
Intracellular Conversion Pathway
cccDNA
RC-DNA
Precore mRNA
Pregenomic RNA
Pre-S1 mRNA Pre-S2/S mRNA
HBx mRNA
HBx
Smc 5/6
LHBsAg
MHBsAg
SHBsAg
DNA
Repair
TR
AN
SC
RIP
TIO
N
ENCAPSIDATION
Precore Protein (p25)
HBeAg
(P14-17) spherical
NUCLEAR
TRANSPORT
ASSEMBLY AND
SECRETION
Peters and Locarnini Gastro and Hep 2017
Slide 15 of 48
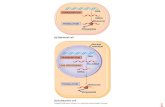
Viral Life Cycle- latent or “recovered” HBV
ER
cccDNA
Nucleus
HBsAg negAnti-HBsAnti-HBc
Immune system considers this “recovered”BUT cccDNA is template for viral replication
Slide 16 of 48
Types of HBV cure
Functional Cure- clinical resolution
Sustained, off drug:
• No inflammation: ALT and liver biopsy
• HBsAg loss
• +/- anti-HBs gain
Complete cure- virological cure
• All of above plus
• Loss of cccDNA in liver
Inactive state -an interim goal
• No inflammation: ALT and liver biopsy
• HBV DNA low or u/d
• HBsAg positive

Slide 17 of 48
RT
Mature HBV
virion
Mature
Nucleocapsid
Immature
Nucleocapsid
Core + pg RNA
+ Polymerase
HBsAg proteins:
HBsAg subviral
particles
Intracellular Conversion Pathway
cccDNA
RC-DNA
Precore mRNA
Pregenomic RNA
Pre-S1 mRNA Pre-S2/S mRNA
HBx mRNA
HBx
Smc 5/6
LHBsAg
MHBsAg
SHBsAg
DNA
Repair
TR
AN
SC
RIP
TIO
N
ENCAPSIDATION
Precore Protein (p25)
HBeAg
(P14-17) spherical
NUCLEAR
TRANSPORT
ASSEMBLY AND
SECRETION
Peters and Locarnini Gastro and Hep 2017
Slide 18 of 48
Strategies to Eradicate HBVVirologic approaches
• Entry inhibitors
• Block cccDNA
• Transcription inhibitors
• RNA interference
• HBV capsid inhibitor
• Polymerase inhibitors
• Secretion inhibitors
Host immune approaches
• Interferons
• RIG-I agonists
• TLR-7
• PD-1/ PDL-1
• IL-7
• Therapeutic vaccines
– Immune complex vaccines
– Nasal HBV (NASVAC) vaccines
– DNA vaccines
– T cell vaccines
– Adenovirus based vaccines (TG1050)
– Yeast based vaccines
Slide 19 of 48
Strategies to Eradicate HBVVirologic approaches
• Entry inhibitors
• Block cccDNA
• Transcription inhibitors
• RNA interference
• HBV capsid inhibitor
• Polymerase inhibitors
• Secretion inhibitors
Host immune approaches
• Interferons
• RIG-I agonists
• TLR-7
• PD-1/ PDL-1
• IL-7
• Therapeutic vaccines
– Immune complex vaccines
– Nasal HBV (NASVAC) vaccines
– DNA vaccines
– T cell vaccines
– Adenovirus based vaccines (TG1050)
– Yeast based vaccines

Slide 20 of 48
Figure 6
Gastroenterology 2014 147, 48-64DOI: (10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.030) Copyright © 2014 Urban Gastro review
HBV entry through NTCP receptor
Slide 21 of 48
HBV Targeting cell entry
Small molecule compounds binding to Sodium taurocholate
cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP)
• HBV pre-S1-derived lipopeptide Myrcludex-B competes with
HBV/HDV for binding to NTCP
– Prevents HBV/HDV entry
– Blocks entry at pM concentrations increased serum bile acids
– Stops new infection of hepatocytes
Zeisel Gut 2015Urban AASLD 2016; Gastro 2014
Slide 22 of 48
Mean ALT levels
Primary endpoint: <2 log HDV RNA decline or undetectable Week 24
Multicentre, open-label Phase 2b clinical trial to assess safety and efficacy of Myrcludex B + TDF in chronic HBV/HDV coinfection
Wedemeyer H, et al. ILC 2018, #GS-005
• 120 HBeAg negative HDV patients in 4 arms were treated in the MYR 202 study for 24 weeks
• Excellent safety in 239 subjects dosed so far (2, 5, 10 mg sq +TDF 24 w)
• No persistent, drug-related AEs/SAEs
• Primary endpoint was met: HDV RNA >2 log decline or undetectable
• Strong on-treatment decrease in ALT, liver stiffness, intrahepatic HDV RNA
• Relapse in most patients in the follow-up: ?? longer treatment needed
TDF MyrB/TDF TDF
150
ALT
(U
/L)
50
100
0
Weeks
30 504020–10–15 100
HD
V R
NA
de
cre
ase
by
>2 lo
g in %
5 m
g M
yrB
/TD
F
10
mg M
yrB
/TD
F
100
40
80
TD
F
0
2 m
g M
yrB
/TD
F
20
60 **
*
Median RNA log10 change to BL
Week 24 Week 48
2 mg MyrB/TDF –1.75 –0.35
5 mg MyrB/TDF –1.60 –0.12
10 mg MyrB/TDF –2.70 –0.39
TDF –0.18 +0.07
TDF TDF
10 mg MyrB /TDF5 mg MyrB /TDF2 mg MyrB /TDFTDF
Negligible effects on qHBsAg*p<0.001

Slide 23 of 48 Peters and Locarnini Gastro and Hep 2017
RT
Mature HBV
virion
Mature
Nucleocapsid
Immature
Nucleocapsid
Core + pg RNA
+ Polymerase
HBsAg proteins:
HBsAg subviral
particles
Intracellular Conversion Pathway
cccDNA
RC-DNA
Precore mRNA
Pregenomic RNA
Pre-S1 mRNA Pre-S2/S mRNA
HBx mRNA
HBx
Smc 5/6
LHBsAg
MHBsAg
SHBsAg
DNA
Repair
TR
AN
SC
RIP
TIO
N
ENCAPSIDATION
Precore Protein (p25)
HBeAg
(P14-17) spherical
NUCLEAR
TRANSPORT
ASSEMBLY AND
SECRETION
MYR
Slide 24 of 48
Strategies to Eradicate HBVVirologic approaches
• Entry inhibitors
• Block cccDNA
• Transcription inhibitors
• RNA interference
• HBV capsid inhibitor
• Polymerase inhibitors
• Secretion inhibitors
Host immune approaches
• Interferons
• RIG-I agonists
• TLR-7
• PD-1/ PDL-1
• IL-7
• Therapeutic vaccines
– Immune complex vaccines
– Nasal HBV (NASVAC) vaccines
– DNA vaccines
– T cell vaccines
– Adenovirus based vaccines (TG1050)
– Yeast based vaccines
Slide 25 of 48
cccDNA inhibitors
Drug Class Antiviral agent Trials Manufacturer
cccDNABlocking
Disubstituted sulphonamides Preclinical
cccDNADegradation
RNA guided nucleasesCRISPR/CAS9)
EBT106Anti‐HBV sgRNA
Preclinical Excision Biotherapeutics
Silencing histone acetyltransferase (HAT) inhibitors HBx targeting drugs

Slide 26 of 48 Peters and Locarnini Gastro and Hep 2017
RT
Mature HBV
virion
Mature
Nucleocapsid
Immature
Nucleocapsid
Core + pg RNA
+ Polymerase
HBsAg proteins:
HBsAg subviral
particles
Intracellular Conversion Pathway
cccDNA
RC-DNA
Precore mRNA
Pregenomic RNA
Pre-S1 mRNA Pre-S2/S mRNA
HBx mRNA
HBx
Smc 5/6
LHBsAg
MHBsAg
SHBsAg
DNA
Repair
TR
AN
SC
RIP
TIO
N
ENCAPSIDATION
Precore Protein (p25)
HBeAg
(P14-17) spherical
NUCLEAR
TRANSPORT
ASSEMBLY AND
SECRETION
MYR
Preclin
Slide 27 of 48
Strategies to Eradicate HBVVirologic approaches
• Entry inhibitors
• Block cccDNA
• Transcription inhibitors
• RNA interference
• HBV capsid inhibitor
• Polymerase inhibitors
• Secretion inhibitors
Host immune approaches
• Interferons
• RIG-I agonists
• TLR-7
• PD-1/ PDL-1
• IL-7
• Therapeutic vaccines
– Immune complex vaccines
– Nasal HBV (NASVAC) vaccines
– DNA vaccines
– T cell vaccines
– Adenovirus based vaccines (TG1050)
– Yeast based vaccines
Slide 28 of 48
RNA interference Antiviral agent Trials Manufacturer
ALN‐HBV (siRNA) Phase I‐II Alnylam
ARC‐520 (siRNA) Terminated Arrowhead pharmaceuticals
ARB‐1467 (siRNA) Phase II Arbutus Biopharma
ARB‐1740 (siRNA) Preclinial Arbutus Biopharma
RO7020322 (RG7834) (small molecule mRNA inhibitors)
Phase I Roche
IONIS-HBVRx (GSK3228836) (antisense molecule)
Phase I Ionis Pharma/GSK
IONIS‐HBVLRx (GSK33389404) (antisense molecule)
Phase I Ionis Pharma/GSK
AB‐452 (RNA destabilizer) Preclinical Arbutus Biopharma

Slide 29 of 48
Silencing HBV gene expression using RNAi-based therapy
• ARC-520 is a combination of siRNAs directed against conserved HBV RNA sequences and efficiently knocks down HBV RNA, proteins and DNA levels.
• 2 siRNAs (cover 99.6% of known HBV sequences) conjugated to cholesterol and hepatocyte-targeted ligands
• Taken up by endosomes in hepatocyte then released into cytoplasm after lysis of endosomal membrane
– Given (Arrowhead Hepdart 2015)
– Arbutus ARB-1740 decreases HBsAg, HBeAg, HDV RNA (AASLD 2016)
– ARO-HBV EASL 2018
– 1 month human dataZeisel Gut 2015
Slide 30 of 48
RNA interference therapy with ARC-520 injection –Case 1: HBeAg positive patient flared when ARC-520 stopped
Yuen M-F, et al. EASL 2018, Paris. #FRI-362
3.2 log10 HBsAg reduction from baseline to 46 IU/mL
4.7 log10 HBcrAg reduction
2.6 log10 HBeAg and 3.0 log10 HBV RNA reduction to BLOQ
HBeAg seroclearance post therapy coincides with HBV RNA drop to BLOQ
Biphasic reduction of HBV DNA by >7.5 log10 to BLOQ
ALT elevations coinciding with antigen, RNA and DNA reductions & also after ARC-520 stopped
HBsAg - ALT HBcrAg- HBV DNA- HBeAg
HBV RNA - DNAWeek
HB
sA
g[I
U/
mL
]
AL
T[I U
/L
]
0 50 100
10
100
1000
10000
100000
0
20
40
60
80
100HBsAg [IU/mL]
ALT
Single dose
Cohort 7
Multi-dose
Cohort 10
Sustained host
response
Week
HB
cr
Ag
[IU
/m
L]
HB
eA
g[
PE
IU
/m
L]
Lo
gH
BV
RN
A[
Lo
gU
/m
L]
0 50 100
10 0
10 1
10 2
10 3
10 4
10 5
10 6
10 7
2
4
6
8
LLOQ
Single dose
Cohort 7
Multi-dose
Cohort 10
HBeAg [PEIU/mL]
HBcrAg [kU/mL]
LLOQ
Log HBV RNA [Log U/mL]
Sustained host
response
Week
HB
VD
NA
[ IU
/m
L]
HB
VR
NA
[L
og
U/
mL
]
0 50 100
10 2
10 3
10 4
10 5
10 6
10 7
10 8
10 9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
HBV DNA [IU/mL]
LLOQ
Single dose
Cohort 7
Multi-dose
Cohort 10
First dose of
extension
Last dose of
extensionLLOQ
Log HBV RNA [Log U/mL]
Sustained host
response
First dose of
extension
Last dose of
extension
First dose of
extension
Last dose of
extension
HB
sAg
[IU
/mL]
ALT [IU
/L]
HB
crA
g[I
U/m
LH
BeA
g[P
EI U
/mL]
Log HB
V R
NA
[log U/m
L]
HB
V D
NA
[IU
/mL]
Log HB
V R
NA
[log U/m
L]
Slide 31 of 48
Bi-weekly Dosing of ARB-1467 LNP siRNA in HBeAg Negative, Virally
Suppressed Patients with Chronic HBV Infection Leads to Deeper Declines in
HBsAg and Potential Association with IL28b
KoshAgarwal et al. AASLD 2017
Phase 2a Single-Blind Study in HBV PatientsDuration of treatment: 3-month follow-up, 12 months after the first dose
HBeAg negativeARB-1467 0.2mg/kg monthly
N=8 (6 active, 2 placebo)
HBeAg negativeARB-1467 0.4mg/kg monthly
N=8 (6 active, 2 placebo)
HBeAg positiveARB-1467 0.4mg/kg monthly
N=8 (6 active, 2 placebo)
HBeAg negativeARB-1467 0.4mg/kg bi-weekly
N=12 (12 active)
0.4mg/kg monthlyResponders only: HBsAg
<1000IU/mL and >1log dec from bl
Wk 0 Wk 8 Wk 12 Wk 24 Wk 48
Study design
Mean changes from baseline in HBsAg (monthly vs. biweekly)
Steeper HBsAg median declines from baseline in subjects with more frequent dosing (biweekly vs. monthly)5/7 responders (71%) reached HBsAg<50IU/mLBaseline HBsAg and IL28b GT CC were significantly associated with response Most AEs mild and transient

Slide 32 of 48 Peters and Locarnini Gastro and Hep 2017
RT
Mature HBV
virion
Mature
Nucleocapsid
Immature
Nucleocapsid
Core + pg RNA
+ Polymerase
HBsAg proteins:
HBsAg subviral
particles
Intracellular Conversion Pathway
cccDNA
RC-DNA
Precore mRNA
Pregenomic RNA
Pre-S1 mRNA Pre-S2/S mRNA
HBx mRNA
HBx
Smc 5/6
LHBsAg
MHBsAg
SHBsAg
DNA
Repair
TR
AN
SC
RIP
TIO
N
ENCAPSIDATION
Precore Protein (p25)
HBeAg
(P14-17) spherical
NUCLEAR
TRANSPORT
ASSEMBLY AND
SECRETION
MYR
Preclin
siRNAs Ph1-2
Slide 33 of 48
Strategies to Eradicate HBVVirologic approaches
• Entry inhibitors
• Block cccDNA
• Transcription inhibitors
• RNA interference
• HBV capsid inhibitor
• Polymerase inhibitors
• Secretion inhibitors
Host immune approaches
• Interferons
• RIG-I agonists
• TLR-7
• PD-1/ PDL-1
• IL-7
• Therapeutic vaccines
– Immune complex vaccines
– Nasal HBV (NASVAC) vaccines
– DNA vaccines
– T cell vaccines
– Adenovirus based vaccines (TG1050)
– Yeast based vaccines
Slide 34 of 48
Core is essential for • HBV genome packaging • Reverse transcription• Intracellular trafficking• Maintenance of chronic infection as encapsidated HBV genomes
are imported into the nucleus.
pgRNA-RT
HBV core protein dimers
Class II CpAM
Heteroarylpyrimidinederivatives
Phenylpropenamideand
sulfamoylbenzamidederivatives
Aberrant core protein aggregates that are subsequently degradede.g. GLS-4, Bay-41
Functional nucleocapsids
Empty capsidse.g AT-130, AB, JNJ,
Class I CpAM
CpAM: core protein allosteric modulator- Roche, ABICAM: capsid assembly modulator - J&J, Roche

Slide 35 of 48
Antiviral agent Trials Manufacturer
GLS‐4 Phase II HEC Pharm, Sunshine
NVR 3‐778 Phase Ia NoviraPharmaceuticals/Janssen
BAY41‐4109 Phase I
JNJ56136379 Phase II JnJ Janssen
Core protein allosteric modulators (CpAMs)
Phase I (ABI‐H0731)IND enabling (ABI‐H2158)Clinical candidate (ABI‐Nx)
Assembly Biosciences
AB‐423 Phase I Arbutus Biopharma
AB‐506 IND enabling Arbutus Biopharma
Nucleocapsid assembly inhibitors/ modulators
Slide 36 of 48
Antiviral Activity of JNJ-56136379, a novel HBV
Nucleocapsid Inhibitor
Zoulim F et al. AASLD #LBO-004, 2017
Session 8JNJ-379 100mg or placebo (Day 1)25mg (D2-28) or placebo (D2-28), QD
Session 9JNJ-379 75mg or placebo, QD
Session 10 JNJ-379 150mg or placebo, QD
Session 11JNJ-379 75mg or placebo
Sessions 8 and 9n=12 per session
(8 active/4 placebo)28 days of treatment followed by 8 weeks of follow-up
56% with one AE, no SAEs, treatment d/c or deathsOne patients with Grade III elevations in ALT and AST- TDF started
HBV DNA
Baseline Day 29
Treatment Arm N Mean (SD), log10IU/mL
Mean (SD) change from baseline log10IU/mL
<LLOQ
25mg QD 8 6.90 (1.91) -2.16 (0.49) 0
75mg QD 8 5.26 (1.50) -2.89 (0.48) 3
Pooled placebo 8 5.49 (1.77) -0.01 (0.31) 0
An oral dose regimen of 250 mg daily for 28 days is being evaluated Phase 2a study is ongoing in treatment-naïve and virologically suppressed CHB patients (NCT03361956)
Slide 37 of 48 Peters and Locarnini Gastro and Hep 2017
RT
Mature HBV
virion
Mature
Nucleocapsid
Immature
Nucleocapsid
Core + pg RNA
+ Polymerase
HBsAg proteins:
HBsAg subviral
particles
Intracellular Conversion Pathway
cccDNA
RC-DNA
Precore mRNA
Pregenomic RNA
Pre-S1 mRNA Pre-S2/S mRNA
HBx mRNA
HBx
Smc 5/6
LHBsAg
MHBsAg
SHBsAg
DNA
Repair
TR
AN
SC
RIP
TIO
N
ENCAPSIDATION
Precore Protein (p25)
HBeAg
(P14-17) spherical
NUCLEAR
TRANSPORT
ASSEMBLY AND
SECRETION
MYR
Preclin
siRNAs Ph1-2CpCAM

Slide 38 of 48
Strategies to Eradicate HBVVirologic approaches
• Entry inhibitors
• Block cccDNA
• Transcription inhibitors
• RNA interference
• HBV capsid inhibitor
• Polymerase inhibitors
• Secretion inhibitors
Host immune approaches
• Interferons
• RIG-I agonists
• TLR-7
• PD-1/ PDL-1
• IL-7
• Therapeutic vaccines
– Immune complex vaccines
– Nasal HBV (NASVAC) vaccines
– DNA vaccines
– T cell vaccines
– Adenovirus based vaccines (TG1050)
– Yeast based vaccines
Slide 39 of 48
HBsAg inhibitors
Antiviral agent Trials Manufacturer
REP2139 & REP2165 Phase II Replicor
BM601 (benzimidazole derivative)
Preclinical
Slide 40 of 48
Participants entered into trialN=40
(20 with NAPs following
24 weeks of pegIFN*)
Participants currently completed treatment
and ≥ 24 weeks of follow-up34
Functional cure
(HBsAg negative, HBV DNA TND)
14/34
(41%)
Inactive chronic HBV state
(HBV DNA < 2000 IU/mL, normal ALT)
15/34
(44%)
Global summary of follow-up responses after removal of all therapy (2018)
REP 2139-Mg and REP 2165-Mg Combination Therapy in CHB (REP 401 - NCT02565719)
Personal communication, Vaillant A et al. 2018ACTG

Slide 41 of 48 Peters and Locarnini Gastro and Hep 2017
RT
Mature HBV
virion
Mature
Nucleocapsid
Immature
Nucleocapsid
Core + pg RNA
+ Polymerase
HBsAg proteins:
HBsAg subviral
particles
Intracellular Conversion Pathway
cccDNA
RC-DNA
Precore mRNA
Pregenomic RNA
Pre-S1 mRNA Pre-S2/S mRNA
HBx mRNA
HBx
Smc 5/6
LHBsAg
MHBsAg
SHBsAg
DNA
Repair
TR
AN
SC
RIP
TIO
N
ENCAPSIDATION
Precore Protein (p25)
HBeAg
(P14-17) spherical
NUCLEAR
TRANSPORT
ASSEMBLY AND
SECRETION
MYR
Preclin
siRNAs Ph1-2CpCAM
NAP
NAP
Slide 42 of 48
Strategies to Eradicate HBVVirologic approaches
• Entry inhibitors
• Block cccDNA
• Transcription inhibitors
• RNA interference
• HBV capsid inhibitor
• Polymerase inhibitors
• Secretion inhibitors
Host immune approaches
• Interferons
• Rig-I agonist- modest
• TLR-7- no effect on HBsAg but increased IFN-γ and IL-2
• PD-1/ PDL-1
• IL-7
• Birinapant selectively induces TNF mediated apoptosis (Pelligrini WEHI)
• Therapeutic vaccines
– Immune complex vaccines
– Nasal HBV (NASVAC) vaccines
– DNA vaccines
– T cell vaccines
– Adenovirus based vaccines (TG1050)
– Yeast based vaccines
Slide 43 of 48
Strategies to Eradicate HBVVirologic approaches
• Entry inhibitors
• Block cccDNA
• Transcription inhibitors
• RNA interference
• HBV capsid inhibitor
• Polymerase inhibitors
• Secretion inhibitors
Host immune approaches
• Interferons
• Rig-I agonist- modest
• TLR-7- no effect on HBsAg but increased IFN-γ and IL-2
• PD-1/ PDL-1
• IL-7
• Birinapant selectively induces TNF mediated apoptosis (Pelligrini WEHI)
• Therapeutic vaccines– Immune complex vaccines
– Nasal HBV (NASVAC) vaccines
– DNA vaccines
– T cell vaccines
– Adenovirus based vaccines (TG1050)
– Yeast based vaccines

Slide 44 of 48
qHBsAg change on anti-PD1 0.3mg/kg (Nivolumab)
19/22 decreasedqHBsAg
PD-1 receptor occupancy up to 84 d post anti PD-1: yeast vaccine Verdon et al AASLD 2017
NB:240 mg IVQ2w for RCC, SC lungMelanoma
ACTG
Slide 45 of 48
Emerging DAAs against HBV
Many currently in the pipe-line• Novel polymerase inhibitors
• Capsid inhibitors
• cccDNA inhibition or eradication
• Core protein packaging inhibitors
• Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based strategies
• Secretion inhibitors
• Immune activators
Combination therapy will likely be required for cure
• Inhibitors of polymerase, entry, core, cccDNA etc
• IFN, immune stimulant, TLR 7
• Checkpoint inhibitors PD-1/L1
BUTZeizel Gut 2015
Slide 46 of 48
Emerging DAAs against HBV
Many currently in the pipe-line• Novel polymerase inhibitors
• Capsid inhibitors
• cccDNA inhibition or eradication
• Core protein packaging inhibitors
• Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based strategies
• Immune activators
Combination therapy will likely be required for cure
• Inhibitors of polymerase, entry, core, cccDNA etc
• IFN, immune stimulant, TLR 7
• Checkpoint inhibitors PD-1/L1
BUT Selection of HBV patient will be critical
Optimization of HBV endpoints neededZeizel Gut 2015

Slide 47 of 48
ARS 2: HBV status in 2019: which is true?
1. Acute HBV in adults leads to loss of HBsAg usually
2. HBV infection can be cured
3. Currently available drugs lead to loss of HBsAg usually
4. HBV is not a latent virus
Slide 48 of 48
ARS 2: New drugs in Phase I/II: which is false?
1. Target Hepatitis B core protein2. Target HBV entry into hepatocyte3. Target cccDNA in nucleus4. Target HBV mRNA5. Target HBV secretion
Slide 49 of 48 Peters and Locarnini Gastro and Hep 2017
RT
Mature HBV
virion
Mature
Nucleocapsid
Immature
Nucleocapsid
Core + pg RNA
+ Polymerase
HBsAg proteins:
HBsAg subviral
particles
Intracellular Conversion Pathway
cccDNA
RC-DNA
Precore mRNA
Pregenomic RNA
Pre-S1 mRNA Pre-S2/S mRNA
HBx mRNA
HBx
Smc 5/6
LHBsAg
MHBsAg
SHBsAg
DNA
Repair
TR
AN
SC
RIP
TIO
N
ENCAPSIDATION
Precore Protein (p25)
HBeAg
(P14-17) spherical
NUCLEAR
TRANSPORT
ASSEMBLY AND
SECRETION
MYR Ph 2
Preclinical
siRNAs Ph1-2CpCAM Ph 1-2
NAP Ph 2

Slide 50 of 48
Question-and-Answer