Institute of Dentistry, CMH Lahore Medical College ...
Transcript of Institute of Dentistry, CMH Lahore Medical College ...

Institute of Dentistry,
CMH Lahore Medical College
Curriculum and study Guide
Third Year BDS

Table of contents
1. Introduction to study guide---------------------------------------------------- 1
2. Mission and vision statement-------------------------------------------------- 2
3. Rationale of curriculum-------------------------------------------------------- 3
4. Introduction to curricular framework-------------------------------------- 3
5. 4 years curricular framework-------------------------------------------------4
6. Curricular map of BDS---------------------------------------------------------5
7. BDS program outcomes-------------------------------------------------------- 6
8. Undergraduate competencies--------------------------------------------------7
9. Coordinator for 3rd year BDS 2019--------------------------------------- 8
10. Student representative----------------------------------------------------------9
11. Clerkship Subjects--------------------------------------------------------------- 10
12. Hours of teaching---------------------------------------------------------------- 10
13. Introduction to Periodontology----------------------------------------- 11
a. Curricular Map of Periodontology -------------------------------------------------- 11
b. Resources -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ---- 12
• Teaching resources -------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
• Infrastructure resources --------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
• Supporting Staff --------------------------------------------------------------------- 13
c. Teaching and learning strategies----------------------------------------------------------- 13
d. Learning methodologies--------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
e. Curriculum implementation----------------------------------------------------------------- 15
f. Course outline--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 17
g. Topic and Exam weightage ----------------------------------------------------------------- 18
h. Table of specification for teaching, learning objectives and assessment-------------- 19
i. Learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 35
j. Other learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------- 37
k. Summative assessment methods and policies---------------------------------------------- 37
l. Table of specifications for annual examination------------------------------------------- 40
m. Sample MCQs and SEQs--------------------------------------------------------------------- 41
14. Introduction to Oral Pathology ------------------- 45
a. Curricular Map of Orthodontics and Oral pathology---------------------------------- 45
b. Resources ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 46
• Teaching resources --------------------------------------------------------------------- 46
• Supporting Staff------------------------------------------------------------------------- 46
• Infrastructure resources --------------------------------------------------------------- 46
c. Teaching and learning strategies----------------------------------------------------------- 47
d. Learning methodologies--------------------------------------------------------------------- 47
e. Curriculum implementation----------------------------------------------------------------- 49
f. Course outline -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 50

g. Table of specification for teaching, learning objectives and assessment-------------- 53
h. Learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 61
i. Other learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------- 62
j. Summative assessment methods and policies---------------------------------------------- 63
k. Table of specifications for annual examination-------------------------------------------- 66
l. Sample MCQs and SEQs-------------------------------------------------------------------- 68
15. Introduction to Oral Medicine 70
a. Curricular Map of Oral Medicine ------------------------------------ 70
b. Resources ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 71
• Teaching resources --------------------------------------------------------------------- 71
• Infrastructure resources ---------------------------------------------------------------- 71
c. Teaching and learning strategies----------------------------------------------------------- 72
d. Learning methodologies--------------------------------------------------------------------- 72
e. Curriculum implementation----------------------------------------------------------------- 74
f. Course Outline -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 75
g. Table of specification for teaching, learning objectives and assessment-------------- 78
h. Learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 92
i. Other learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------- 96
j. Summative assessment methods and policies---------------------------------------------- 97
k. Table of specifications for annual examination-------------------------------------------- 98
l. Sample MCQs and SEQs--------------------------------------------------------------------- 101
16. Introduction to General Medicine------------------------------------ 103
a. Resources --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 103
• Teaching resources ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 103
• Infrastructure resources ---------------------------------------------------------------- 103
b. Teaching methodologies---------------------------------------------------------------- 104
c. Learning methodologies-------------------------------------------------------------------- 104
d. Curriculum implementation----------------------------------------------------------------- 106
e. Course Outline ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 107
f. Table of specification for teaching, learning objectives and assessment ------------- 109
g. Learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 121
h. Other learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------- 121
i. Summative assessment methods and policies---------------------------------------------- 122
j. Table of specifications for annual examination-------------------------------------------- 123
k. Sample MCQ and SEQ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 126

17. Introduction to General Surgery------------------------------------ 127
a. Teaching and learning strategies----------------------------------------------------------- 127
b. Learning methodologies-------------- ----------------------------------------------------- 128
c. Curriculum implementation----------------------------------------------------------------- 130
d. Outcomes of the BDS Gen Surgery course------------------------------------------------ 125
e. General Surgery Course Organisation ----------------------------------------------------- 132
f. General Surgery Curriculum Annexures--------------------------------------------- 134
g. Other learning resources---------------------------------------------------------------------- 139
h. Summative assessment methods and policies---------------------------------------------- 140
i. Table of specifications for annual examination-------------------------------------------- 143

1
Introduction to study guide
This study guide book is designed for Dental undergraduates by consolidated effort of all subjects across
the year to provide Dental students of IOD CMH Lahore Medical College a resource material which
would highlight important aspects of curriculum. The study guide aims to promote self-regulated
lifelong learning among students by giving them the control over their learning.
The pervasive curriculum aspects of undergraduates’ competencies, assessment policies and curriculum
coordinators are mapped in his guide book. Horizontal integration across the year better conceptual
understanding while vertical integration promotes clinically relevant understanding. IOD CMH aims
to improve health indicates of society by improvement of students and doctors in preventive health
service provision and health education provision to society through community programs.
The study guide gives an overview of intended course outcomes and objectives in relation to the course
content. The assessment methodology tailored to intuitional strategy is provided.
This study guide has been carefully designed keeping in view PMDC and NUMS curriculum and guide
lining dedicated effort by faculty is done to make this guide tailored to student’s needs. Students
feedback has been seeded and incorporated at all stages during study guide development. Curriculum
is a living dynamic entity. Our aim to improve it by every passing day. This humble effort of all faculty
acts as a guiding light for our dear students.

2
Mission Statement
To provide an excellent learning and teaching environment, inculcating
ethical values and social responsibilities in undergraduate and
postgraduate medical &dental students and nursing and allied health
sciences students to enhance the level of comprehension healthcare in
the Army/Country
Vision Statement
To ensure the development of internationally acclaimed quality
standards and practices for the NUMS Higher Education that benefits
and lives upto the stakeholder’s needs and expectations

3
Rationale of Curriculum The curriculum is designed to address both local and international needs. The curriculum is
focused to prepare students for the international licencing exams and training abroad as well as
empowering them to treat local patients with safety and efficiency. Dentists work as a healer in the
community. A dentist should have evidence based and update knowledge about the epidemiology of
the practicing area. The curriculum of IOD CMH LMC is planned with a collaboration of clinical and
basic sciences faculty in addition to students and family medicine department to ensure that the
prevailing health conditions of the society are treated and dealt with effectively. The emergence of new
techniques in preservation of existing dentition and restoration of the lost dentition and oral structures
has led to changes in the curriculum with more emphasis on new and advanced techniques, procedures
and evolution of new and advanced technology (e.g. CADCAM & Implants).
Introduction to Curricular Framework
This study guide is developed as resource assistance to the students and faculty. The study guide
development process included representation from teaching faculty, management, leadership of college
and students. The study guide is made to achieve and alignment between societies’ needs, institutional
needs, patient needs & student’s needs.
The curriculum implemented is a hybrid type of curriculum which has both horizontal and
vertical integration. Spiral integration is introduced as an adjunct to horizontal and vertical integration.
The curriculum spans over 2 phases
PHASE 1 (Year 1&2): Includes basic sciences Anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, Oral biology and
tooth morphology, Science of dental Materials, Pharmacology and Community Dentistry, Behavioral
Sciences, general pathology, Islamiyat and Pakistan studies. It also includes preclinical Prosthodontics
and operative dentistry.
PHASE 2 (Year 3rd
& Final Year): includes Periodontology, Oral Pathology, Oral Medicine, General
Medicine, General Surgery, Oral Surgery, Prosthodontics, Orthodontics and dental radiology, Operative
Dentistry.

4
4 Years Curricular Framework
BDS SCHEME OF STUDIES
BASIC DENTAL SCIENCES / PRE-
CLINICAL YEAR
CLINICAL YEARS
1st YEAR 2
nd Year 3
rd Year Final Year
Anatomy Science of Dental
Material
Periodontology Prosthodontics
Physiology Gen. Pathology Oral pathology Operative Dentistry
Biochemistry Pharmacology Oral Medicine Oral Surgery
Pak studies & Islamic
Studies
Gen. Medicine Orthodontics and Dental
radiology
Oral Biology Community Dentistry Gen. Surgery
Pre-Prosthodontics Oral Surgery
Pre-Operative Dentistry Prosthodontics
Self-Directed Learning Sessions

5
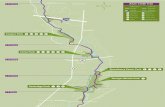
Curricular Map Of BDS

6
BDS Program Outcomes
At the end of four years dental undergraduate program, the graduates should be able to:
1. Independently assess the patients, order relevant investigations and formulate a treatment plan.
2. Render treatments in the domain of general dental practitioners to their parents in time efficient
and quality-controlled manner.
3. Practice evidence-based dentistry.
4. Modify dental treatments according to patient’s special needs, if any, in the form of medical
conditions, physical or mental disabilities etc
5. Assess and refer the patients with case difficulty indices requiring consultation or treatment by
specialists.
6. Show empathy and respect in their attitude and behavior towards their patients.
7. Maintain high ethical and professional standards in their pursuit of clinical excellence.
8. Draw upon their existing knowledge and update it through continuing education programs.
9. Exercise infection control protocol guidelines laid out by their local health councils.
10. Exercise management qualities to maintain single or multiple unit private practices where
applicable.
11. Work in a team of other health care professionals including dentists, dental assistants, dental
hygienists, laboratory technicians, ceramists and dental nurses etc.
12. Maintain patient records with emphasis on legal and patient confidentiality aspects.
13. Provide basic life support to patients requiring critical care in or outside dental set up.
14. Manage dental emergencies in a dental set up.
15. Demonstrate clear verbal and written communication skills.

7
Undergraduate Competencies
IOD CMH Lahore medical College envisions to produce graduates who are proficient in
following competencies at the end of 4th year
Dental Expertise
Communication
Critical thinking
Management
Scholar
Professionalism
Evidence based practice providing holistic care
Empathetic
Providing Community service

8
Co-ordinators Third Year BDS 2019
Coordinator Name Department Extension
Prof. Dr. Muhammad
Nasir Saleem
Professor
Periodontology 314
Prof. Dr. Sabahat
Javaid
Professor
Oral Pathology 345
Assist Prof.
Dr. Fareed Ahmed
Assistant Professor
Oral Medicine 350
Associate Prof.
Dr Javaid Iqbal
Associate professor
General Medicine 470
Prof. Dr.Imran Daula
Professor
General Surgery 453

9
Class representatives
Name Designation
Saad Khakwani CR 1st Year BDS
Hafiza Eman GR 1st Year BDS
Muhammad Ahsan Fayyaz CR 2nd Year BDS
Alizay Fatima GR 2nd Year BDS
Rehan CR 3rd Year BDS
Arzoo Zulfiqar GR 3rd Year BDS
Ahmad Waheed CR Final Year BDS
Noor Fatima GR Final Year BDS

10
Clerkship Subjects
Following are the core subjects for Third year BDS for which professional examination will be held at
the end of the academic year:
1. Periodontology
2. Oral Pathology
3. Oral Medicine 4. General Medicine
5. General Surgery
Hours of teaching
Subject PMDC
2019
Lecture
hours
Clinical
hours
Self-
Study
hours
Total Teaching
Hours
CMH
Periodontology 175 60 126 0 186
Oral Pathology 150 120 31 0 151
Oral Medicine 125 50 84 0 134
General Medicine 200 72 180 0 252
General Surgery 200 58 175 0
233
Operative Dentistry 100 30 140 70
170

11
INTRODUCTION TO PERIODONTOLOGY
Periodontology is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as
diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which
includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament.
Curricular Map of Periodontology

12
Resources
a. Teaching resources
b. Infrastructure resources
Teaching resources
Sr. #. Faculty Name Department as per PM
& DC certificate
Qualification
1 Prof. Dr. Nasir Saleem Professor BDS, FCPS, MSc
2 Dr. Farhan Javed Assistant Professor BDS, MDS
3 Dr. Yousaf Athar Assistant professor BDS, MSc
4 Dr. Daniyal Naeem Dar Registrar BDS
5 Dr. Awrisha Tariq Registrar BDS
6 Dr. Aimen Malik Registrar BDS
7 Dr. Ayesha Tariq Registrar BDS
Infrastructure resources
Sr. #. Infrastructure Resources Quantity
1 Operating Halls 1
2 Dental Units
• Periodontology clinic
20
3 Dental Stools
• Periodontology
20
5 Reception 1
6 Mini Library 1
7 Staff Room 1
8 Dental stores 1

13
Supporting staff
Serial No. Name Designation
1 Najam Ejaz Dental Hygienist
2 Umber Chohan Dental Hygienist
3 Akif Sajid Dental Hygienist
4 Maria Rasheed Dental Hygienist
5 Farooq Ali Dental Assistant
Teaching and Learning Strategies
Multiple educational methods will be used comprising of self-study, interactive lectures, group
discussions, practical, and manual dexterity skill sessions.
(i) Methods for achieving cognitive objectives
• Interactive lectures using audio visual aids on power point presentation
• Group discussions in form of large group and small group
• Collaborative learning
• Self-study and reading from learning resources
(ii) Methods for achieving psychomotor objectives
• Theoretical information provided in lectures
• Clinical demonstrations provided by teaching faculty on models and patients
• Supervised practice on patients
(iii) Methods for achieving affective objectives
• Interaction with peers, group members, teachers, support staff etc.
• Group discussions (small and large)
• Oral presentations by students

14
Learning Methodologies
The following teaching /learning methods are used to promote better understanding:
• Interactive lectures
• Small group discussions
• Practical
• Skill sessions
• Self-directed learning
• Assignments
• Oral presentations by students
Interactive lectures
In large group, the lecturer introduces a topic which explains the underlying phenomena through
questions, pictures, exercise, etc. Students are actively involved in the learning process.
Small group discussions
This format helps students to clarify concepts and acquire skills and attitudes. Students exchange
opinions and apply knowledge gained from lectures and self-study. The facilitator role is to ask probing
questions, summarize, or rephrase to help clarify concepts.
Practical
In practical sessions students observe demonstrations from faculty members on proper instrument use
and handling both inside and outside the patients mouth. The students are trained in diagnosing and
treating a periodontal disease as per protocols set by the department.
Skill session
Students are required to practice suturing techniques on inanimate materials.
Self- directed learning
Students' take responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing
with peers, seeking information from Learning Resource Center, teachers and resource persons within
and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hours or afterwards
for self-study.
Assignments
Students are given written formative assignments on designated topics. Revision of the topics already
covered by anatomy and physiology departments are given to students as oral presentations.
Oral presentations by students
Students are assigned topics during revision session to enhance their communication skills and group
learning.

15
Curriculum Implementation
Curriculum implementation refers to putting into practice the official document including course
content, objectives, learning and teaching strategies. Implementation process helps the learner to
achieve knowledge, skills and attitudes required of the learning tasks. Learners are a pertinent
component of the implementation process. Implementation occurs when the learner achieves the
intended learning experiences, knowledge, ideas, skills and attitudes which are aimed to make the
learner an effective part of the society. Curriculum implementation also refers to the stage at which
curriculum is put into effect. There has to be an implementing agent as well. Teacher is an important
part of this process and implementation of the curriculum is the way the teacher selects and utilizes
various components of the curriculum. Implementation occurs when the teacher’s formulated course
content, teacher’s personality and teaching and learning environment interact with the learners.
Therefore, curriculum implementation is how the officially planned course of study is translated and
reflected by the teacher into schemes of work, lesson plans, syllabus and resources are effectively
transferred to the learners. Curriculum implementation can be affected by certain factors such as
teachers, learners, learning environment, resource materials and facilities, culture and ideology,
instructional supervision and assessments.
Personnel involved in teaching and facilitation
(i) Lectures delivery by:
Dr Nasir Saleem (Professor)
Dr Farhan Javed (Assistant Professor)
Dr Yousaf Athar (Assistant Professor)
(ii) Demonstrators for practical and small group discussion sessions:
Dr Daniyal Naeem Dar
Dr Awrisha Tariq
Dr Aimen Malik
Dr Ayesha Tariq
(iii) Support staff: 5 (4 Dental hygienists, 1 Dental Assistant)
(iv) Computer assistant: 1 as nominated by the college

16
Time frame
Course duration:
• Lectures: 36 weeks
• Clinical rotations: 9 weeks per rotation
Lectures:
• Monday (8:00 to 8:50am)
• Wednesday: (8:50 to 9:40 am)
Practical/ clinical visits:
• Tuesday and Thursday (10:00 to 3:00 pm)
• Friday (10:00 to 3:00 pm) with 1 pm to 2 pm Prayer break

17
Course Outline
Section - 1 The Normal Periodontium, Classification and Epidemiology of periodontal disease.
This section deals with the basic anatomy and physiology of the periodontium and gives an overview
of how to classify patients into different categories of periodontal disease. The incidence, distribution,
and possible control of periodontal diseases and other factors relating to health are also included in this
topic.
Section – 2 Etiology of periodontal disease
This subject includes the role of microbiology in periodontal disease and its interaction with the host
and its response in return. The influence of iatrogenic and systemic factors an dental deposits and how
they contribute towards periodontal disease is also covered here.
Section – 3 Periodontal pathogenesis.
This area deals with the pathogenesis of periodontal pocket, bone loss and explains the detail of the
phases of gingival inflammation.
Section – 4 Periodontal diseases.
This domain discusses in detail the diagnosis, pathogenesis, management and complications of various
periodontal diseases including autoimmune and acute periodontal conditions.
Section – 5 Periodontal Examination, Diagnosis and Therapy
This subject deals with the details of history taking, periodontal investigations and diagnosis. The
instruments, procedures and chemotherapeutic agents used to manage the periodontal diseases non
surgically are also covered under this topic.
Section – 6 Surgical Periodontology
This subject deals with the details of periodontal surgery, which includes the armamentarium,
preparation, techniques, and postoperative healing of curettage, gingivectomy, gingivoplasty and
various flap and bone surgeries. It also includes regenerative and periodontal plastic and esthetic
surgeries.
Section – 7 Dental Implants
This topic involves the basic knowledge of dental implants for students at an undergraduate level
teaching then the basic introduction, rationale, treatment planning and complications of implants.
Section – 8 Supportive Periodontal Care
This subject deals with the explaining management of patient with periodontal disease post-surgical
and non-surgical treatment and maintaining their oral hygiene. Details of patient referral are also
discussed is also covered under this domain.

18
Topic and Exam Weightage
Topic Weightage (%age)
The Normal Peridontium and Classification
and Epidemiology of Periodontal diseases
11
Etiology of Periodontal Disease 11
Periodontal Pathogenesis 11
Periodontal Disease 21
Periodontal Examination, Diagnosis and
Therapy
11
Surgical Periodontology 11
Dental Implants 11
Supportive Periodontal Care 13
Topic
Lecture
Hour
Weightage
(hrs)
Clinical
Hour
Weightage
(hrs)
The Normal Periodontium and Classification
and Epidemiology of Periodontal diseases
6.6 14
Etiology of Periodontal Disease 6.6 14
Periodontal Pathogenesis 6.6 14
Periodontal Disease 12.6 26.5
Periodontal Examination, Diagnosis and
Therapy
6.6 14
Surgical Periodontology 6.6 14
Dental Implants 6.6 14
Supportive Periodontal Care 7.8 16.5
Total 60 127

19
TOPICS AND
OBJECTIVES
FACULTY
LEARNING
DOMAIN
(CPA)
LEARNING
STRATEGY
ASSESSMENT
Periodontology
Clinical
Viva
OSPE
NUMS
MCQs
NUMS
SEQs
THE NORMAL PERIDONTIUM, CLASSIFICATION AND
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES
X
3
1
• Explain
development of the
tooth supporting
apparatus
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Explain anatomy
of Periodontium C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Correlate the
microscopic
features and
clinical features of
the periodontium
C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Understand the
nerve and vascular
supply of the
periodontium
C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Explain effects of
Aging on the
normal
peri0dontium
C Interactive
lecture
• Explain gingival
diseases (plaque
and non-plaque
induced gingivitis
and periodontitis
along with
classification
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Discuss
developmental and
acquired
deformities along
with mucogingival
C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion

20
deformities around
teeth
• Discuss the
definition of
epidemiology.
C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Explain how to
diagnose
periodontal
diseases and
difference between
chronic and
aggressive
periodontitis
C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
ETIOLOGY OF PERIODONTAL DISEASE X 3 1
PERIODONTAL MICROBIOLOGY
• Discuss diversity
of intraoral
surfaces for
bacterial adhesion
and structure and
composition of
dental plaque
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Discuss plaque
formation at
ultrastructural level
and growth
dynamics of plaque
C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Discuss different
properties of dental
plaque and
association of
plaque micro-
organisms with
periodontal
diseases
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Explain the role of
calculus and other
predisposing
factors
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion

21
HOST RESPONSE AND HOST BACTERIAL INTERACTIONS
• Identification of
cells of immunity
and inflammation.
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Discuss
mechanism of
migration and
functioning of
leucocytes
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Discuss different
microbial aspects
of microbial host
interaction and
microbiology and
immunology in
periodontal
diseases
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Discuss toll like
receptors and
innate immunity
response
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Discuss similarities
between
periodontal
diseases and other
chronic
inflammatory
diseases
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Discuss host
response and
potential targets for
host modulation
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Explain host
modulatory therapy
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
SYSTEMIC FACTORS

22
• Treatment of
medically
compromised
patients
Dr. Farhan
Javed CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Influence of
systemic disorders
and stress on
periodontium
Dr. Farhan
Javed CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
IATROGENIC AND OTHER FACTORS
• Overview of factors
predisposing to
periodontal disease
(local and systemic)
Dr. Farhan
Javed CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
DENTAL DEPOSITS
• Explain origin,
composition,
formation and
mode of
attachment of
calculus
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Classify and
differentiate supra
and sub-gingival
calculus
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Explain theories of
mineralization C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Clinical
significance of
calculus CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics

23
• Dental Stains,
Materia Alba,
Dental pellicle
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
PERIODONTAL PATHOGENESIS X 3 1
GINGIVAL INFLAMMATION
• Explain in detail
the 4 stages of
gingival
Inflammation
Dr. Yousaf
Athar CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
PERIODONTAL POCKET
• Define and Classify
Periodontal Pocket
Dr. Farhan
Javed
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Explain the clinical
features,
pathogenesis and
pocket contents CPA
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion/
clinics
• Histopathology of
Soft and hard tissue
wall of the
periodontal pocket C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion/
clinics
• Treatment options
for periodontal
pocket CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
BONE LOSS AND PATTERNS OF BONE LOSS
• Bone destruction
patterns in
periodontal disease
Dr. Farhan
Javed CPA
Interactive
lecture/ small
group

24
discussion /
Clinics
• Bone destruction
caused by trauma
from occlusion
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion /
Clinics
• Bone destruction
caused by systemic
disorders C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion /
Clinics
• Factors determining
bone morphology
in periodontal
disease
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion /
Clinics
PERIODONTAL DISEASES X 4 2
GINGIVITIS
• Explain clinical
findings of
gingivitis including
gingival bleeding on
probing, color
changes, changes in
consistency and
surface texture
Dr. Farhan
Javed
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Explain changes in
position of gingiva
and changes in
gingival contour
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Role of Saliva
CPA
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion /
Clinics
• Explain the
composition,
formation and
methods of
collection of GCF
CPA
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion

25
• Clinical significance
of Sulcular fluid
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
ACUTE PERIODONTAL CONDITIONS
• Explain the
clinical features,
microbiology
involved,
diagnosis,
treatment and
complications of
peri-coronitis
Dr. Farhan
Javed
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Explain the
clinical features,
microbiology
involved,
diagnosis and
treatment of
Primary Herpetic
Gingivostomatitis
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Explain the
etiology, clinical
features,
microbiology
involved,
diagnosis and
treatment of
Necrotizing
ulcerative
Gingivitis
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
DESQUAMATIVE GINGIVITIS
• Diagnosis of
Desquamative
gingivitis
Dr. Farhan
Javed
C Interactive
lecture/case-

26
• Diagnose,
differentiate and
treat Lichen
Planus,
Pemphigoid,
Pemphigus
Vulgaris, Chronic
Ulcerative
Gingivitis, Linear
IgA disease,
Lupus
erythematosus,
Dermatitis
Herpetiformis and
Erythema
Multiforme.
C
C
C
based
discussion
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Drug Eruptions
• Conditions
mimicking
Desquamative
Gingivitis
GINGIVAL ENLARGEMENTS
• Classify Gingival
Enlargements.
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Explain the
pathophysiology
of different types
of gingival
enlargements
C
Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion
• Explain the
microscopic and
histopathological
features.

27
• Determine a
treatment plan for
all types of
Gingival
Enlargements
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Management
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS
• Explain and
Correlate Clinical
and
histopathological
features of
Chronic
Periodontitis
Dr. Farhan
Javed
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Explain the
disease
distribution CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Management of
Chronic
Periodontitis CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Risk factors for
disease
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
AGGRESSIVE PERIODONTITIS
• Clinical features,
general
characteristics,
disease
distribution,
background and
management of
aggressive
periodontitis
Dr. Farhan
Javed CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics

28
• Risk factors for
disease
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
NECROTISING ULCERATIVE GINGIVTIS AND PERIODONTITIS
• Etiology, clinical
features,
microbiology
involved,
diagnosis and
treatment of
Necrotizing
Ulcerative
Gingivitis Dr. Farhan
Javed C
Interactive
lecture/case
-based
discussion
Interactive
lecture/case
-based
discussion
• Etiology, clinical
features,
microbiology
involved,
diagnosis and
treatment of
Necrotizing
Ulcerative
Periodontitis
TRAUMA FROM OCCLUSION
• Acute and Chronic
Trauma
Dr. Farhan
Javed
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Primary and
Secondary Trauma
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Consequences of
trauma
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Tissue Response
of trauma Interactive
lecture/ small
group
discussion

29
• Diagnosis of
Occlusal trauma C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Occlusal
adjustment C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Splinting
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
PERIODONTAL MANIFESTATION OF SYSTEMIC DISEASES
• Different systemic
diseases are
discussed with
reference to their
periodontal
manifestations
Dr. Farhan
Javed CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
PERIODONTAL EXAMINATION DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY X 3 1
PERIODONTAL EXAMINATION
• History taking
and Diagnosis
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Periodontal
screening and
complete
examination of
oral cavity.
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
PERIODONTAL DIAGNOSIS
• First and second
visit of patient
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Differential
diagnosis along
with laboratory
CPA Interactive
lecture/case-
based

30
aids to clinical
diagnosis
discussion/
Clinics
TREATMENT PLANNING AND PLAQUE CONTROL
• Phases of
periodontal
treatment,
retreatment of
patient in case of
reoccurrence Dr. Yousaf
Athar
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Mechanical
control of dental
plaque CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Motivation,
education and
instruction
Dr. Farhan
Javed
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Interdental
cleaning
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Scaling and root
planning with
advantages and
disadvantages CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics/
Skills
session
• Chemical control
of dental plaque
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Chemotherapeuti
c agents for
topical and
systemic
administration
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
INSTRUMENTATION

31
• Manual scaling
instruments
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics/
Skills
session
• Ultrasonic scalers
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Surgical
instruments
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
CHEMOTHEURAPEUTIC AGENTS
• Definitions
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Antibiotics in
Periodontal
Diseases CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Local Drug
Delivery
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
PERIODONTAL THERAPY (NON-SURGICAL)
• Proper history
diagnosis and
examination of
patient Dr. Farhan
Javed
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Complete
periodontal
charting CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/

32
Clinics/
Skills
session
• Scaling and Root
planning
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics/
Skills
session
• Follow up
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
SURGICAL PERIODONTOLOGY X 3 1
GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF PERIODONTAL SURGERY
• Equipment, Pre op
management,
Anesthesia
Dr. Farhan
Javed
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Periodontal
dressings C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Post op
instructions,
complications and
Management
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Indications and
Contraindications C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
SURGICAL PROCEDURES
• Curettage –
Rationale,
indication,
procedure, post
treatment healing
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics/

33
Dr Farhan
Javed
Dr. Nasir
Saleem
Skills
session
• Gingivectomy –
indication,
contraindications,
procedure, types
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Gingivoplasty -
indication,
contraindications,
procedure
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Flap surgery –
Classification,
designs, incisions,
suturing, post
treatment healing,
flap techniques,
sutures
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Osseous surgery –
Rationale, Factors,
Technique, steps
involved,
armamentarium,
post op
maintenance
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Regenerative
Periodontal
Therapy- GTR,
GBR, grafts
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Furcation
Involvement –
Anatomy,
Diagnosis, Factors
affecting,
Classification,
Treatment Options,
prognosis
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics/
Skills
session
• Esthetic and Plastic
Periodontal
Surgery –
objectives, factors
affecting outcome,
techniques to
remove frenum,
deepen vestibule,
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion

34
increase attached
gingiva.
DENTAL IMPLANTS X 3 1
• Basic Introduction
and Rationale of
Dental implants
Dr. Farhan
Javed
C
Interactive
lecture/
small group
discussion
• Treatment
Planning C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Complications
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
SUPPORTIVE PERIODONTAL CARE X 3 1
• Rationale for
supportive
periodontal
treatment
Dr. Yousaf
Athar
C
Interactive
lecture/case
-based
discussion
• Maintenance
Program
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case
-based
discussion/
Clinics
• Classification of
post treatment
patients C
Interactive
lecture/case
-based
discussion
• Referral of patient
to the periodontist
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case
-based
discussion/
Clinics
• Splinting of the
teeth C
Interactive
lecture/case

35
Learning resources
Topics Resources
The Normal Peridontium
Classification of Periodontal Disease and
Epidemiology
• Clinical periodontology by Glickman
• Clinical Periodontology by Manson
• Color Atlas of Clinical Surgical
Periodontology by Strahan & White
• A textbook of clinical periodontology by Jan
Lindhe
• Fundamentals of Periodontics by Thomas G
Wilson, Kenneths Komman
• Periodontology and Periodontics, Modern
Theory and Practice by Sigurd P. Ramford
Major M. Ash
Etiology of Periodontal disease
• Clinical periodontology by Glickman
• Clinical Periodontology by Manson
• Color Atlas of Clinical Surgical
Periodontology by Strahan & White
• A textbook of clinical periodontology by Jan
Lindhe
• Fundamentals of Periodontics by Thomas G
Wilson, Kenneths Komman
• Periodontology and Periodontics, Modern
Theory and Practice by Sigurd P. Ramford
Major M. Ash
Periodontal Pathogenesis
• Clinical periodontology by Glickman
• Clinical Periodontology by Manson
• Color Atlas of Clinical Surgical
Periodontology by Strahan & White
• A textbook of clinical periodontology by Jan
Lindhe
• Fundamentals of Periodontics by Thomas G
Wilson, Kenneths Komman
• Periodontology and Periodontics, Modern
Theory and Practice by Sigurd P. Ramford
Major M. Ash
Periodontal Disease • Clinical periodontology by Glickman
• Clinical Periodontology by Manson
• Color Atlas of Clinical Surgical
Periodontology by Strahan & White
• A textbook of clinical periodontology by Jan
Lindhe

36
• Fundamentals of Periodontics by Thomas G
Wilson, Kenneths Komman
• Periodontology and Periodontics, Modern
Theory and Practice by Sigurd P. Ramford
Major M. Ash
Periodontal Examination, Diagnosis and
Therapy
• Clinical periodontology by Glickman
• Clinical Periodontology by Manson
• Color Atlas of Clinical Surgical
Periodontology by Strahan & White
• A textbook of clinical periodontology by Jan
Lindhe
• Fundamentals of Periodontics by Thomas G
Wilson, Kenneths Komman
• Periodontology and Periodontics, Modern
Theory and Practice by Sigurd P. Ramford
Major M. Ash
Surgical Periodontology
• Clinical periodontology by Glickman
• Clinical Periodontology by Manson
• Color Atlas of Clinical Surgical
Periodontology by Strahan & White
• A textbook of clinical periodontology by Jan
Lindhe
• Fundamentals of Periodontics by Thomas G
Wilson, Kenneths Komman
• Periodontology and Periodontics, Modern
Theory and Practice by Sigurd P. Ramford
Major M. Ash
Dental Implantology
• Clinical periodontology by Glickman
• Clinical Periodontology by Manson
• Color Atlas of Clinical Surgical
Periodontology by Strahan & White
• A textbook of clinical periodontology by Jan
Lindhe
• Fundamentals of Periodontics by Thomas G
Wilson, Kenneths Komman
• Periodontology and Periodontics, Modern
Theory and Practice by Sigurd P. Ramford
Major M. Ash
Supportive Periodontal Care
• Clinical periodontology by Glickman
• Clinical Periodontology by Manson
• Colour Atlas of Clinical Surgical
Periodontology by Strahan & White
• A textbook of clinical periodontology by Jan
Lindhe
• Fundamentals of Periodontics by Thomas G
Wilson, Kenneths Komman

37
• Periodontology and Periodontics, Modern
Theory and Practice by Sigurd P. Ramford
Major M. Ash
Other Learning Resources
Clinics / Practical Students will be involved in clinical work in the periodontology clinic
Videos Video familiarize the student with the procedures and protocols to assist
patients
Computer
Lab/CSs/DVDs/ Internet
Resources:
To increase the knowledge, students should utilize the available internet
resources and CDs/ DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase
learning.
Self-Learning
Self-Learning is scheduled to search for information to solve cases, read
through different resources and discuss among the peers and with the faculty
to clarify the concepts.
Assessment Methods
Internal Assessment
a. Weightage of internal assessment shall be 10 %, each for theory and practical, in BDS
Professional Examination.
b. The Internal Assessment shall comprise of monthly test / PBL / assignments / Clinical tests /
clinical Vivas,etc.
c. The Internal Assessment record shall be kept in the respective department of the College /
Institute and after approval of Principal, a summary as per University registration number shall
be furnished to the Controller of Examinations, at least two weeks before the commencement
of final examination.
d. The result of all the class tests / tools which contribute towards IA will be displayed to the
students during an academic year.
e. The same internal assessment shall be counted both for annual and supplementary
examinations. The students who are relegated, however, can improve the internal assessment
during subsequent year
f. Internal assessment tools of any subject may be changed after the approval of
respective FBS
Annual Examination
a. The weightage of Annual Examination shall be 90%, each for theory and practical, in BDS.

38
Sr.
No
Topic No of MCQs
(25)
(C1=10, C2=7,
C3=8) 01 mark
each
• No. of SAQs/SEQs (09)
05xSAQs/SEQs (C1 &
C2) =7 marks each
• 03xSAQ/SEQs(C3) =7
marks each
• 01xSAQs/SEQs(C3) =9
marks each
1 The Normal Periodontium 03 01
2 Classification of periodontal
disease and epidemiology
3 Etiology of periodontal disease
• Periodontal microbiology
• Host response and host
bacterial interactions
• Iatrogenic and other local
factors
• Systemic factors
• Dental deposits
03
4 Periodontal pathogenesis
• Gingival inflammation
• Periodontal pocket
• Bone loss and patterns of
bone loss
03
01
5 Periodontal diseases
• Gingivitis
• Acute periodontal
conditions
• Desquamative gingivitis
• Chronic enlargement
• Gingival growth
• Chronic periodontitis
• Aggressive periodontitis
• NUP, NUP
• Trauma from occlusion
• Systemic disease with
periodontal manifestation
04
02
6 Periodontal examination, diagnosis
and therapy
• Periodontal examination
• Periodontal diagnosis
• Treatment planning
• Plaque control
• Instrumentation
• Chemotherapeutic agents
• Periodontal therapy (non-
surgical)
03
01

39
b. The examination comprises of a theory paper and practical/clinical examinations as per
PM&DC regulations and the Table of Specifications (TOS) of the University.
c. The gap between two consecutive theory papers shall not be more than two days.
d. The Theory Paper shall be of 3-hours duration, held under the arrangements of the university.
It shall have two parts; MCQs (30%) and SAQs/SEQs (70 %) for the year 2018. It may be
changed after the approval of Academic Council.
e. Allocated time for MCQs for 2019 shall be as under:
25 MCQs - 30 Minutes
30 MCQs - 40 Minutes
40 MCQs - 50 Minutes
45 MCQs - 60 Minutes
f. Each MCQs shall have four distractors
g. The distribution of SAQs/SEQs as well as MCQ difficulty levels for BDS annual examinations
is as under: -
7 Surgical periodontology
• Surgical curettage
• Gingivectomy ,
gingiveoplasty
• Flap surgery
• Osseous surgery ,
regenerative periodontal
therapy , GTR
• Furcation involvement
• Esthetic and plastic
periodontal surgery
03
01
8 Dental implants-basic intro ,
rationale , treatment planning ,
complications
03
01
9 Supportive periodontal care
• Rationale for supportive
periodontal treatment
• Maintenance program
• Classification of post
treatment patients
• Referral of patient to the
periodontist
• Splinting of teeth
03
01
Total 25 (25 marks) 09 (65 marks)
Grand Total 90 Marks

40
Internal assessment calculation (Theory/ Annual)
A B C D F G
Roll No.
Name
All modules/ Pre-Annual Exams or any other exam
Total Marks of internal
assessment out of 10
Total Marks Sum of Marks obtained x 10 / sum of total marks
in all exams
Table of specifications for Annual Professional Exam:
Practical
VIVA
50 marks
Practical / Clinical
40 marks
Total
Examiner 1
Examiner 2
Oral Examination
and Diagnosis
History
Taking
Scaling of teeth
Identification
of Slides and
Instruments
90 Marks
25 Marks
25 Marks
10 Marks
5 Marks
15 Marks
10 Marks
Internal assessment calculation (Practical)
A B C D F G
Roll No.
Name
OSPE/ Practical Class tests throughout the year / Pre
annual Practical Exams or any other exam
Total Marks of internal
assessment out of 10
Total Marks
Sum of Marks obtained x 10 / sum of total marks
in all exams

41
Multiple Choice Question (MCQs)
• A multiple-choice question (MCQ) consist of a stem that states the question or problem
followed by a set of possible answers that contain an option that is best answer to the
question.
• After reading the questions students should select the appropriate option from the given
possible answers.
• The correct answer carries one mark and incorrect carries zero. There is no negative marking.
Sample MCQ
The tooth supporting tissues are derived from
a) Dental papilla
b) Dental follicle
c) Dental lamina
d) Hertwigs epithelial root sheath e) Enamel knot key: b
Short essay question (SEQs)
• Short essay questions require students to present written answers that are used to asses basic
knowledge of key facts and provide students with an opportunity to demonstrate reasoning and
explain their understanding of the subject.
Sample SEQ
A 29-year-old woman, medically fit and healthy, presented to your clinic with the complaint of food
impaction in upper right jaw. On probing, you find a deep periodontal pocket between tooth # 14 and
15.
a) Classify Periodontal Pockets. (2)
b) Correlate the Clinical and Histo-pathological features of periodontal pocket. (5)
Key: a)
True and false/pseudo pocket
Supra and infra bony pockets
Gingival and periodontal pockets
Simple, compound and complex pockets
b)

42
1 Gingival wall of pocket presents
various degrees of bluish red
discoloration; flaccidity; a smooth,
shiny surface; and pitting on pressure.
The discoloration is caused by circulatory
stagnation; the flaccidity, by destruction of
gingival fibres and surrounding tissues; the
smooth, shiny surface. By atrophy or
epithelium and edema; and the pitting on
pressure, by edema and degeneration
2 Less frequently, gingival wall may be
pink and firm.
In such cases, fibrotic changes predominate
over exudation and degeneration,
particularly in relation to outer surface of
pocket wall. However, despite external
appearance of health, inner wall of pocket
invariably presents some degeneration and is
often ulcerated (see figure 27-15)
3 Bleeding is elicited by gently probing
soft tissue wall of pocket
Ease of bleeding results from increased
vascularity, thinning and degeneration of
epithelium and proximity of engorged
vessels to inner surface
4 When explored with a probe, inner
aspect of pocket is generally painful
Pain on tactile stimulation is caused by
ulceration of inner aspect of pocket wall
5 In many cases, pus may be expressed
by applying digital pressure
Pus occurs in pockets with supportive
inflammation of inner wall
Internal Examiner
He/she shall be Professor and Head of Department who has been involved in teaching of the class being
examined for at least six months. Second preference shall be Associate/Assistant Professor who is
involved in teaching of the class and posted there for one year. Third preference shall be a recognized
Professor of the subject.
External Examiner
He/she shall be a Professor/Associate Professor of a recognized Medical/Dental College or at least an
Assistant Professor with three years teaching experience in the relevant subject.
Conflict of Interest
No person shall serve as an examiner whose close relative (wife, husband, son, daughter, adopted son,
adopted daughter, grand-son, grand-daughter, brother, sister, niece /nephew, son and daughter- in-law
brother and sister- in-law, parental and maternal uncle and aunt etc) is appearing in the examination.
All examiners likely to serve as an examiner shall render a certificate in compliance to this para.
Paper Setting
a. Each College / Institute shall forward a set of two question papers as per TOS along with the
key for each subject to the Controller of Examinations, at least three months in advance of the
annual examination. The question paper as a whole / a question without a comprehensive key
shall not be considered towards final paper setting.
b. The set of question papers shall be prepared by the respective Head of Department (HoD) and
furnished to Controller of Examinations through Head of Institution (HoI)
c. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the final paper setting having fair
representation of each college / institute.

43
Paper Assessment
a. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the theory paper marking, to be
undertaken in the manner as deemed appropriate.
b. The Examination Directorate shall coordinate directly with the faculty, earmarked for the paper
marking
c. A student who scores 85% and above marks in any subject shall qualify for distinction in that
particular subject.
d. A fraction in aggregate marks of a subject shall be rounded off to whole number. If it is less
than 0.5 then it will be rounded off to the previous whole number while 0.5 or more will be
rounded off to the next whole number.
Practical / Clinical Examinations
a. The Controller of Examiners shall approve the faculty to serve as the internal & external
examiners.
b. The number of external and internal examiners shall be equal.
c. One external & internal examiner each shall be marked for a group of 100 students.
d. Candidates may be divided into groups in the clinical and practical examinations and be
standardized by incorporating clinical exam
e. Practical/clinical examination shall be held after the theory examination of the subject
but in special cases, it may be held before the theory examination with the approval of the
Controller of Examinations. For the purpose of practical/clinical examination, the candidates
may be divided into sub groups by the examiners.
f. The assessment of the practical / clinical examination duly signed by internal & external
examiner shall be furnished to the Controller of Examinations within one week of the
conclusion of examination
Pass Marks
a. Pass marks for all subjects less Islamic / Pakistan Studies, shall be 50 % in theory and practical,
separately.
b. Pass marks for Islamic / Pakistan Studies shall be 33 % which, however, shall not be counted
towards final scoring of the professional examination.
c. No grace marks shall be allowed to any student in any examination.
Declaration of Result.
Every effort shall be made to declare the result of each examination within one month of the last
practical examination or earlier.
Promotion.
No student shall be promoted to the higher classes unless he/she passes all the subjects of the previous
class
Re-Totaling.
Any student may apply to the Controller of Examinations on a prescribed form along with the specified
fee.

44
Supplementary Examination.
The interval between a supplementary examination and the previous professional examination shall not
be more than two months. There shall be no special supplementary examination.

45
INTRODUCTION TO ORAL PATHOLOGY
Oral Pathology is the specialty of dentistry and pathology which deals with the
nature, identification, and management of diseases affecting the oral and
maxillofacial regions. It deals with diagnosis and study of the causes, processes
and effects of diseases affecting the oral and maxillofacial region. The main
method of examination of specimens is by light microscopy.
Curricular Map of Oral Pathology

46
Resources
a. Teaching resources
b. Infrastructure resources
c. Supporting staff
Teaching resources
Sr. #. Faculty Name Department as per PM
& DC certificate Qualification
1 Prof. Dr. Shabahat Javaid Butt Professor MBBS, MPhil
3 Dr. Faiqua Yasser Associate professor BDS, MPhil
4 Dr. Bismah Ahmad Senior Registrar BDS, Mphil
5 Dr. Ayesha Mohammad Rana Registrar BDS
6 Dr. Eesha Najam Registrar BDS
7 Dr. Shan Nafees Registrar BDS
8 Dr Khursand binte Azam Registrar BDS
Infrastructure resources
Sr. #. Infrastructure Resources Quantity
1
Lecture hall
• Seating Capacity
• Multimedia
• Microphone
• Computer system
1
2
Oral Pathology lab
• Gross Specimens
• Microscope
• Slides
3 Mini library
1
Supporting staff a) Lab assistant
b) Computer operator/lecture hall attendant

47
Teaching and Learning Strategies
Multiple educational methods will be used comprising of self-study, interactive lectures, group
discussions, practical, and manual dexterity skill sessions.
(i) Methods for achieving cognitive objectives
• Interactive lectures using audio visual aids on power point presentation
• Group discussions in form of large group and small group
• Collaborative learning
• Self-study and reading from learning resources
(ii) Methods for achieving psychomotor objectives
• Focusing the histological slides on microscope
• Identification of normal histological structures on slides under different magnification
• Drawing and labeling the histological slides on practical notebooks
(iii) Methods for achieving affective objectives
• Interaction with peers, group members, teachers, support staff etc.
• Group discussions (small and large)
• Oral presentations by students
Learning Methodologies
The following teaching /learning methods are used to promote better understanding:
• Interactive lectures
• Small group discussions
• Practical
• Skill sessions
• Self-directed learning
• Assignments
• Oral presentations by students

48
Interactive lectures
In large group, the lecturer introduces a topic which explains the underlying phenomena
through questions, pictures, exercise, etc. Students are actively involved in the learning process.
Small group discussions
This format helps students to clarify concepts and acquire skills and attitudes. Students
exchange opinions and apply knowledge gained from lectures and self-study. The facilitator
role is to ask probing questions, summarize, or rephrase to help clarify concepts.
Practical
In practical sessions students observe histological slides under microscope or on multimedia
for better understanding of the subject. They are also required to maintain practical manuals in
which they draw and label histological diagrams and different aspects/views of teeth for better
understanding.
Skill session
Students are taught to accurately carve out tooth models from soap for better understanding of
tooth morphology.
Self- directed learning
Students' take responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and
discussing with peers, seeking information from Learning Resource Center, teachers and
resource persons within and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college
scheduled hours or afterwards for self-study.
Assignments
Students are given written formative assignments on designated topics.
Oral presentations by students
Students are assigned topics during revision session to enhance their communication skills and
group learning.

49
Curriculum Implementation
Curriculum implementation refers to putting into practice the official document including course
content, objectives, learning and teaching strategies. Implementation process helps the learner to
achieve knowledge, skills and attitudes required of the learning tasks. Learners are a pertinent
component of the implementation process. Implementation occurs when the learner achieves the
intended learning experiences, knowledge, ideas, skills and attitudes which are aimed to make the
learner an effective part of the society. Curriculum implementation also refers to the stage at which
curriculum is put into effect. There has to be an implementing agent as well. Teacher is an important
part of this process and implementation of the curriculum is the way the teacher selects and utilizes
various components of the curriculum. Implementation occurs when the teacher’s formulated course
content, teacher’s personality and teaching and learning environment interact with the learners.
Therefore, curriculum implementation is how the officially planned course of study is translated and
reflected by the teacher into schemes of work, lesson plans, syllabus and resources are effectively
transferred to the learners. Curriculum implementation can be affected by certain factors such as
teachers, learners, learning environment, resource materials and facilities, culture and ideology,
instructional supervision and assessments.
Personnel involved in teaching and facilitation
(i) Lectures delivery by: Prof. Dr. Sahbahat Javaid Butt (Professor)
Dr. Faiqa Yassir (Associate professor)
(ii) Registrar for clinics/practical and small group discussion sessions:
• Dr. Bismah Ahmad (Senior Registrar)
• Dr. Ayesha Mohammad Rana
• Dr. Eesha Najam
• Dr. Shan Nafees
• Dr Khursand binte Azam
(iii) Support staff: 2 as nominated by the medical education department
(iv) Computer assistant: 1 as nominated by the college
Time frame
Course duration: 36 weeks
Lectures: Monday (8:50 to 9:40am) (11:40 to 12:00 pm)
Wednesday: (10:00 to 10:50 am) (11:40 to 12:00 pm)
Friday: (8:50 to 9:40 am)
Practical/ clinical visits:
Wednesday: (8:00 to 8:50 am)
Self-study: 5-6 hours per week

50
Course Outline
SECTION I- WHITE LESIONS
Topic weightage: 2.2 %, Time allocation: 3 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 2 MCQS, 0 SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
This section introduces students to diagnose the white lesions by correlating the clinical and
histopathological features. By the end of this unit, students will be able to distinguish white
lesions from one another on the basis of etiology, location and keratosis. e.g Candidiasis,
Leukoderma
SECTION II - EPITHELIAL PATHOLOGY
Topic weightage: 10 %, Time allocation: 5 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 2 MCQS, 1 SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
This section familiarizes students with several key themes and subjects regarding
different types of lesions involving the squamous epithelium. It will include the concepts of
the lesions based on etiology, pathogenesis, clinical features and final diagnosis on
microscopic examination of the biopsy specimens. The aim of this section is to allow students
to develop scientific knowledge, understanding and competence in the area of e.g. Hyperplastic
Epithelial lesions, Benign epithelial lesions, Squamous cell carcinoma and variants
SECTION III - INFECTIONS
Topic weightage: 12.2 %, Time allocation: 10 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 4 MCQS, 1 SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
The aim of this section is to allow students to develop understanding of infectious diseases.
Students of 3rd year BDS should be able to distinguish between different types of infections
and diagnose bacterial, fungal & viral infections. The students also learn the treatment
modalities of these diseases. e.g. Noma, Tuberculosis, Herpes simplex virus, Varicella Zoster
virus, Candidiasis, Histoplasmosis
SECTION IV - BONE PATHOLOGY
Topic weightage: 9 % , Time allocation : 4 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 1 MCQS, 01SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
The section helps the students to develop understanding regarding bone diseases. By the end
of this section, candidates will be able to distinguish different diseases and diagnose them using
clinical, radiographic & microscopic correlation. The students also learn the treatment
modalities of these diseases e.g Fibrous dysplasia, Cemento osseous dysplasia etc.

51
SECTION V - CONNECTIVE TISSUE LESIONS
Topic weightage: 2.2 %, Time allocation : 3 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 2 MCQS, 0 SEQ/SAQ, 2-OSPE Station
This sections helps students to understand the classification and types of the oral connective
tissue lesions, clinical presentation of connective tissue lesions and diagnosis of lesions with
clinical and microscopic features.
SECTION VI - HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES
Topic weightage: 11 %, Time allocation : 8 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 1 MCQS, 01 SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
By the end of this section, candidates will be able to distinguish different diseases and diagnose
them using clinical, radiographic & microscopic correlation. The students also learn the
treatment modalities of these malignancies. e.g Hodgkins lymphoma Non Hodgkin lymphoma
SECTION VII - ODONTOGENIC AND NON ODONTOGENIC CYSTS
Topic weightage: 10 %, Time allocation : 5 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 2 MCQS, 01 SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
By the end of this section, students will be able to distinguish different cysts from one
another on the basis of their tissue of origin, nature, expansion and radiographic presentation.
Using the core knowledge will enable them to diagnose cysts using clinical, radiographic &
microscopic evaluation.
SECTION VIII - ODONTOGENIC TUMORS
Topic weightage: 9%, Time allocation : 4 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 1 MCQS, 1 SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
By the end of this section, students will be able to distinguish different tumors from one
another on the basis of their tissue of origin, nature and radiographic presentation. Using the
core knowledge will enable them to diagnose odontogenic tumors using clinical, radiographic
& microscopic evaluation e.g. Ameloblastoma, Keratocystic odontogenic tumour.
SECTION IX - SALIVARY GLAND PATHOLOGY
Topic weightage: 10 %, Time allocation : 5 weeks

52
Assessment items in Final Exams: 2 MCQS, 1 SEQ/SAQ, 2-OSPE Station
In this section students will understand basic classification of salivary gland pathology describe
clinical presentation of salivary gland lesions Diagnosis of salivary gland lesions by correlating
clinical and microscopic features.
SECTION X - DENTAL CARIES AND PERIAPICAL DISORDERS
Topic weightage: 2.2 %, Time allocation : 3 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 2 MCQS, 0 SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
In this section students are taught about the Etiology, Clinical Types, Role of Plaque,
Carbohydrates , Enamel Caries , Dentine Caries , Cementum Caries
SECTION XI - IMMUNE-MEDIATED DISORDERS:
Topic weightage: 10 %, Time allocation : 5 Weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 2 MCQS, 1SEQ/SAQ, 2-OSPE Station
In this section students are taught about different immune mediated disorders e.g. Pemphigus
vulgaris, Mucous membrane pemphigoid, Epidermolysis bullosa etc.
SECTION XII - DEVELOPMENTAL DISTURBANCES OF THE ORAL REGION
Topic weightage: 10 %, Time allocation : 5 weeks
Assessment items in Final Exams: 2 MCQS, 1 SEQ/SAQ, 1-OSPE Station
By the end of this section, candidates will be able to understand the basic classifications and
types of developmental anomalies, understand the congenital defects related to disturbances in
development of oral structures like lips, teeth, palate (hard and soft), tongue, understand the
developmental defects of oral cavity present in different types of syndromes related to genetic
defects in chromosomes

53
Table of specification for teaching, learning objectives and
assessment
At the end of the year students will be able to know:
TOPICS AND OBJECTIVES FACULT
Y
Learning
Domain
(CPA)
LEARNING
STRATEGY ASSESSMENT
Operative Dentistry Clinical viva OSPE NUMS
MCQs
NUM
S
SEQs
1. WHITE LESIONS X 2 0
• Enlist Candidiasis in
Dentistry
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C1
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Explain the clinical and
histopathological
features of Leukodema,
White Sponge Nevus
Tobacco Pouch
Keratosis
Nicotine Stomatitis,
Actinic Cheilitis
C2
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Describe the clinical
and histopathological
features of Submucous
Fibrosis, Hairy
Leukoplakia,
Hairy Tongue,
Geographic Tongue
C2
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Discuss Dysplasia in
detail (mild, moderate,
severe, ca-in-situ)
C2
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Overview of Lichen
Planus, Leukoplakia,
Speckled Leukoplakia,
PVL, Erythroplakia (red
lesion)
C3
Interactive
lecture/small
practical
• Enlist the recommended
guidelines for
sterilization of dental
operatories and dental
instruments
C2 Interactive
lecture

54
2.EPITHELIAL PATH X 2 1
• Understand basic
classification and types
of oral epithelial lesions
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C2
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Describe clinical
presentation of
epithelial lesions C2
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion
• Diagnosis of epithelial
lesions by correlating
clinical and microscopic
features of the
following diseases:
• Squamous Cell
Carcinoma ( definition,
risk factors,
pathogenesis)
• SCC Clinical
Presentation, TNM
Classification
• SCC Histopathological
Grading, treatment,
prognosis
• Variants of SCC
(Verrucous, spindle,
basaloid, adenoid,
adenosquamous,
nasopharyngeal)
• Squamous papilloma
• Keratoacanthoma
• Smokers melanosis
• Melanoma
(ABCD,clinical types
only)
C3
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
2. INFECTIONS X 4 1
• Discuss Different Viral
Infections:
• Herpes simplex virus
• Varicella Zoster virus
• Epstein- barr virus
• Cytomegalovirus
• Human Herpesvirus 8
• Human papilloma
viruses
• Retrovirus (HIV)
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C2
Interactive
lecture/practic
al
1

55
• Discuss Different
Bacterial infections and
Granulomatous
disorders
• Noma
• Tuberculosis
• Syphilis
• Actinomycosis
C3
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
2
• Discuss Different
Fungal Infections
• SUPERFACIAL
FUNGAL
INFECTIONS e.g
Candidiasis
• DEEP FUNGAL
INFECTIONS e.g
Histoplasmosis,
Paracoccidiodomycosi,
Blastomycosis,
Aspergillosis
C2 Interactive
lecture 1
3. BONE PATHOLOGY X 1 1
• Distinguish different
diseases and diagnose
them using clinical,
radiographic &
microscopic correlation.
1. Fibrous dysplasia
2. Cemento osseous
dysplasia
3. Ossifying Fibroma
4. Paget’s disease
5. Hyperparathyroidism
6. Osteopetrosis
7. Osteogenesis
imperfecta
8. Cherubism
9. Cleidocranial
dysplasia
10. BENIGN
TUMOURS:
• Tori
• Osteoblastoma&
osteoid osteoma
• Giant cell lesions
11. MALIGNANT
TUMOURS:
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C1
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion

56
• Osteogenic sarcoma
• Chondrosarcoma
• Ewing’s sarcoma
4. CONNECTIVE
TISSUE LESIONS X 2 0
• Understand basic
classification and types
of oral connective tissue
lesions
Prof.Dr.
Shabahat
Javaid Butt
C2
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Describe clinical
presentation of
connective tissue
lesions
C3
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Diagnosis of these
lesions by correlating
clinical and microscopic
features of the
following diseases:
• 1- Fibrous tissue lesions
2- Neural tissue
neoplasms
• 3- Muscle tissue
neoplasms
• 4- Adipose and
Vascular tissue
neoplasms
• 5- Osseous and
cartilaginous tissue
neoplasms
C3
Interactive
lecture/practic
al
5. HAEMATOLOGICA-
L MALIGNANCIES X 1 1
• Distinguish different
diseases and diagnose
• them using clinical,
radiographic &
microscopic correlation.
The treatment
modalities of these
malignancies.
1- Hodgkins lymphoma
2- Non Hodgkin
lymphoma
3- Burkitt Lymphoma
4- Multiple Myeloma
5- Plasmacytoma
Prof.Dr.
Shabahat
Javaid Butt
C2
Interactive
lecture/case
based
discussion

57
6- Langerhan cell
histiocytosis
7- Anaemia and
Leukaemia (Oal
presentation only)
6. ODONTOGENIC
AND NON
ODONTOGENIC
CYSTS
X 2 1
• Diagnose cysts using
clinical, radiographic &
microscopic evaluation.
• ODONTOGENIC
CYSTS:
1. Periapical cysts
2. Dentigerous cysts
3. Eruption cysts
4. Paradental cysts
5. Lateral periodontal
cysts
6. Gingival cysts of
adult & newborn
7. Glandular
odontogenic cyst
• NON-
ODONTOGENIC
CYSTS:
1. Nasopalatine duct
cysts
2. Nasolabial cysts
3. Globulomaxillary
cyst
4. Median palatal cyst
5. Median mandibular
cyst
6. Palatal cysts of
newborn
7. Dermoid cyst
8. Epidermoid cys
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C1
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
1
1
7. ODONTOGENIC
TUMOURS: X 1 1
• Diagnose odontogenic
tumours using clinical,
radiographic &
microscopic evaluation.
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C2
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion

58
• EPITHELIAL
ODONTOGENIC
TUMORS:
1. Ameloblastoma
2. Keratocystic
odontogenic tumour
3. Calcifying epithelial
odontogenic tumour
4. Adenomatoid
odontogenic tumou
5. Squamous
odontogenic tumourr
• CONNECTIVE
TISSUE
ODONTOGENIC
TUMOURS
1. Odontogenic fibroma
2. Odontogenic
myxoma
3. Cementoblastoma
4. Ameloblastic
fibroma& fibrodontoma
5. Odontogenic
carcinoma
6. Primary intra osseous
carcinoma
C2
8. SALIVARY GLAND
PATHOLOGY X 2 1
• Understand basic
classification of salivary
gland pathology
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C2
Interactive
lecture/practic
al
• Describe clinical
presentation of salivary
gland lesions
1. Reactive Lesions
(mucocele, mucous
retention cyst,
sialolithiasis,
necrotizing
sialometaplasia)
2. Infections (bacterial
sialadenitis)
3. Immune-mediated
diseases
(lymphoepithelial
sialadenitis, Sjogren
syndrome)
C2
Interactive
lecture/practic
al

59
4. Benign tumours
(pleomorphic adenoma,
warthin tumour,
monomorphic adenoma)
5. Malignant tumours
(mucoepidermoid
carcinoma, adenoid
cystic carcinoma, acinic
cell carcinoma,
polymorphous low-
grade adenocarcinoma)
C3
9. DENTAL CARIES
AND PERIAPICAL
DISORDER
X 4 0
• DENTAL CARIES:
1 Aetiology
2 Clinical Types
3 Role of Plaque,
Carbohydrates
4 Enamel Caries
5 Dentine Caries
6 Cementum Caries
• PERIAPICAL
PATHOLOGY:
1. Acute and chronic
periodontitis
2. Chronic apical
periodontitis
3. Periapical abscess
4. Periapical granuloma
5. Acute and chronic
osteomyelitis
6. Cellulitis
Dr.Faiqua
Yasser C2
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
2
2
10. IMMUNE-
MEDIATED
DISORDERS
X 2 1
• Describe
1.Pemphigus vulgaris
2 Mucous membrane
pemphigoid
3 Epidermolysis bullosa
4 Erythema Multiforme
5 Lichenoid Reactions
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser C3
Interactive
lecture
11. DEVELOPMENTAL
DISTURBANCES OF
ORAL LESIONS
X 2 1

60
• Understand basic
classifications and types
of developmental
anomalies
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C1
Interactive
lecture/practic
al
• Understand the
congenital defects
related to disturbances
in development of oral
structures like lips,
teeth, palate (hard and
soft), tongue
C2
Interactive
lecture/practic
al
• Understand the
developmental defects
of oral cavity present in
different types of
syndromes related to
genetic defects in
chromosomes
Dr. Faiqua
Yasser
C3
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Developmental
disturbances of oral
region are discussed
under three broad
categories
1- Developmental
disturbances in Teeth
2- Developmental
disturbances in soft
tissue
3- Developmental
disturbances in bone
C1
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion

61
Learning Resources
Topics Resources
Oral Pathology
WHITE LESIONS Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology.
EPITHELIAL PATHOLOGY Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
DENTAL CARIES
Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
DEVELOPMENTAL DISTURBANCES OF
THE ORAL REGION Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
PERIAPICAL DISORDERS Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
IMMUNE-MEDIATED DISORDERS Cawson's essentials of oral pathology and oral medicine.
SALIVARY GLAND PATHOLOGY Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
VIRAL INFECTIONS
1. Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
2. Cawson's essentials of oral pathology and oral medicine
3. Neville Oral and maxillofacial pathology
FUNGAL INFECTIONS Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS +
GRANULOMATOUS DISEASES
Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 6th Edition Clinical
Pathologic Correlations Authors:
Joseph Regezi ,James Sciubba ,Richard Jordan
ODONTOGENIC TUMOURS
1. Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
2. Cawson's essentials of oral pathology and oral medicine
ODONTOGENIC CYSTS
1. Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
2. Cawson's essentials of oral pathology and oral medicine
Non-ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
BONE PATHOLOGY
Neville Oral and maxillofacial pathology
CONNECTIVE TISSUE LESIONS Neville Oral and maxillofacial pathology

62
HAEMATOLOGICAL Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
MALIGNANCIES (Lymphomas) Contemporary oral and maxillofacial pathology
Other Learning Resources
Hands- on Activities / Practical
Students will be involved in Practical sessions and hands-on activities that
link with the blood module to enhance the learning
Labs
Utilize the lab provides the simulated learning to the specimens and models
available.
Skills Lab
A skills lab provides the simulated learning experience to learn the basic
skills and procedures. This helps patients
Computer
Lab/CSs/DVDs/ Internet
Resources:
To increase the knowledge, students should utilize the available internet
resources and CDs/ DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase
learning.

63
Summative Assessment Methods and Policies
Internal Assessment
a. Weightage of internal assessment shall be 10 %, each for theory and practical, in BDS
Professional Examination.
b. The Internal Assessment shall comprise of monthly test / assignments / class presentation
/ send-ups /class tests / OSPE etc.
c. The Internal Assessment record shall be kept in the respective department of the College /
Institute and after approval of Principal, a summary as per University registration number
shall be furnished to the Controller of Examinations, at least two weeks before the
commencement of final examination.
d. The result of all the class tests / tools which contribute towards IA will be displayed to the
students during an academic year.
e. The same internal assessment shall be counted both for annual and supplementary
examinations. The students who are relegated, however, can improve the internal
assessment during subsequent year
f. Internal assessment tools of any subject may be changed after the approval of respective
FBS
Annual Examination
a. The weightage of Annual Examination shall be 90%, each for theory and practical, in BDS.
b. The examination comprises of a theory paper and practical/clinical examinations as per
PM&DC regulations and the Table of Specifications (TOS) of the University.
c. The gap between two consecutive theory papers shall not be more than two days.
d. The Theory Paper shall be of 3-hours duration, held under the arrangements of the
university. It shall have two parts; MCQs and SEQs for the year 2019. It may be changed
after the approval of Academic Council.
• Internal Examiner
He/she shall be Professor and Head of Department who has been involved in teaching
of the class being examined for at least six months. Second preference shall be
Associate/Assistant Professor who is involved in teaching of the class and posted there
for one year. Third preference shall be a recognized Professor of the subject.
• External Examiner
He/she shall be a Professor/Associate Professor of a recognized Medical/Dental
College or at least an Assistant Professor with three years teaching experience in the
relevant subject.
• Conflict of Interest
No person shall serve as an examiner whose close relative (wife, husband, son,
daughter, adopted son, adopted daughter, grand-son, grand-daughter, brother, sister,

64
niece /nephew, son and daughter- in-law brother and sister- in-law, parental and
maternal uncle and aunt etc) is appearing in the examination. All examiners likely to
serve as an examiner shall render a certificate in compliance to this para.
• Paper Setting
a. Each College / Institute shall forward a set of two question papers as per TOS along
with the key for each subject to the Controller of Examinations, at least three months
in advance of the annual examination. The question paper as a whole / a question
without a comprehensive key shall not be considered towards final paper setting.
b. The set of question papers shall be prepared by the respective Head of Department
(HoD) and furnished to Controller of Examinations through Head of Institution (HoI)
c. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the final paper
settinghaving fair representation of each college / institute
• Paper Assessment
a. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the theory paper marking,
to be undertaken in the manner as deemed appropriate.
b. The Examination Directorate shall coordinate directly with the faculty,earmarked for
the paper marking
c. A student who scores 85% and above marks in any subject shall qualify for distinction
in that particular subject.
d. A fraction in aggregate marks of a subject shall be rounded off to whole number. If it
is less than 0.5 then it will be rounded off to the previous whole number while 0.5 or
more will be rounded off to the next whole number.
• Practical Examinations
a. The Controller of Examiners shall approve the faculty to serve as the internal & external
examiners.
b. The number of external and internal examiners shall be equal.
c. One external& internal examiner each shall be marked for a group of 100 students.
d. Candidates may be divided into groups practical examinations and be standardized by
incorporating OSPE stations.
e. Practical examination shall be held after the theory examination of the subject but in
special cases, it may be held before the theory examination with the approval of the
Controller of Examinations. For the purpose of practical/clinical examination, the
candidates may be divided into subgroups by the examiners.
f. The assessment of the practical examination duly signed by internal & external
examiner shall be furnished to the Controller of Examinations within one week of the
conclusion of examination.
• Pass Marks
a. Pass marks for all subjects shall be 50 % in theory and practical, separately.
b. No grace marks shall be allowed to any student in any examination.
• Declaration of Result
Every effort shall be made to declare the result of each examination within one month
of the last practical examination or earlier.
• Promotion

65
No student shall be promoted to the higher classes unless he/she passes all the subjects
of the previous class
• Re-totaling
Any student may apply to the Controller of Examinations on a prescribed form along
with the specified fee.
• Supplementary Examination
The interval between a supplementary examination and the previous professional
examination shall not be more than two months. There shall be no special
supplementary examination.
• Academic Audit
The Vice Chancellor may get any academic matter deliberated in the manner as deemed
appropriate.
• Issue of Academic Transcript/Detailed Marks Sheet
A student desirous of obtaining Academic Transcript / Detailed Mark Sheet may
apply to Controller of Examinations along with the prescribed fee for each original
copy.
• Withdrawal/Failure
Any student who fails to clear the first Professional in BDS orfirst in four chances,
availed or un-availed, shall be expelled as per PM& DC policy and shall not be eligible
for fresh admission as a fresh candidate in either BDS.

66
Table of specifications for Annual Professional Examination: Theory
Marks of Written Paper
Marks of Int. Asses
= 90
= 10
Time Allowed = 03 hrs
(Including MCQs)
Max Marks = 100 Date:
Pass Marks = 50
25 x MCQs (on separate sheet) (25 Marks) (Time = 30 min) 05 x SAQs/SEQs (C1 & C2) = 07 marks each 03 x SAQs/SEQs (C3) = 07 marks each (65 Marks) (Time = 2hrs 30 min) 01 x SAQs/SEQs (C3) = 09 marks each
S. NO
TOPIC
No. of MCQs (25) (C1=10, C2= 7, C3= 8) 01 mark each
No. of SAQs/SEQs (9)
• 05 x SAQs (C1&C2) = 07 marks each
• 03 x SAQs/SEQs (C3) = 07 marks each
• 01 x SAQs/SEQs (C3) = 09 marks each
1 WHITE LESIONS 02
2 EPITHELIAL PATHOLOGY 02 01
3 DENTAL CARIES 02
4 DEVELOPMENTAL DISTURBANCES of the ORAL REGION
02 01
5 PERIAPICAL DISORDERS 02 01
6 IMMUNE-MEDIATED DISORDERS 02
7 SALIVARY GLAND PATHOLOGY 02 01
8 VIRAL INFECTIONS 01
01
9 FUNGAL INFECTIONS 01
10 BACTERIAL INFECTIONS + GRANULOMATOUS DISEASES
02
11 ODONTOGENIC TUMOURS 01 01
12 ODONTOGENIC CYSTS 01 01
13 Non-ODONTOGENIC CYSTS 01
14 BONE PATHOLOGY 01 01
15 CONNECTIVE TISSUE LESIONS 02
16 HAEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES (Lymphomas)
01 01
Total 25 (25 Marks) 09 (65 Marks)

67
A. Internal Assessment Calculation (Theory Annual)
A B C D
Roll No. Name All Modules/ Pre annual Exams or any other exam
Total Marks of internal Assessment out of 10
Total Marks Sum of Marks obtained x 10 / sum of total marks in all exams
Table of Specifications for Annual Professional Exam: Practical
VIVA
50 marks
Practical (OSPE • Draw and label
Task) 40 marks
Total
Examiner I
Examiner 2 OSPE
Total = 15 Stations
Practical
Notebook
25 marks 25 marks 30 marks 10 marks 90 marks
Internal Assessment Calculation (Practical)
A B C D
Roll no. Name OSPE/ PTT/ Class
tests though out the
year/ Pre annual
Exams or any other
exam
Total Marks of
Internal assessment
Out of 10
Total Marks
Sum of Marks
obtained x 10 / sum
of total marks in all
exams

68
Sample MCQs and SEQs
Multiple Choice Question (MCQs)
• A multiple choice question (MCQ) consist of a stem that states the question or problem
followed by a set of possible answers that contain an option that is best answer to the
question.
• After reading the questions students should select the appropriate option from the given
possible answers.
• The correct answer carries one mark and incorrect carries zero. There is no negative marking.
Sample MCQ
A cyst occurring under the tongue, caused by obstruction of salivary gland duct, is called as:
a) Follicular cyst
b) Dentigerous Cyst
c) Ranula
d) Epidermoid cyst
Key: c
Short essay question (SEQs)
• Short essay questions require students to present written answers that are used to asses basic
knowledge of key facts and provide students with an opportunity to demonstrate reasoning
and explain their understanding of the subject.
Sample SEQ
Q. A 12 years of boy presented with painless, bilateral symmetrical expansion of mandible,
apparent upward tilt of eyes with cervical lymphadenopathy.
a) What is your diagnosis? (1)
b) Give probable histopathological and radiographical features of your diagnosis? (4)
c) Give D/D of other Giant Cell Lesions in the oral cavity? (2)
Key:
a) Cherubism
b) Histopathological features:
The tissue contains some area in which cellular fibrous connective tissue predominates and other
areas are dominated by immature metaplastic bone with a woven pattern. There is blending of

69
lesional tissue with surrounding normal bone and cortical plates. Multinucleated osteoclast-like giant
cells near bone and within soft fibrous stroma.
Radiographic Features:
The radiologic findings of cherubism are characterized by bilateral relatively symmetric jaw involvement
that is limited to the maxilla and mandible, showing expansile remodeling of the involved bones, thining
of the cortexes, and mixed radiopaque and radiolucent “cotton ball” pattern with a coarse trabecular
pattern.
c) D/D for Giant cell lesions:
1) Central giant cell granuloma
2) Peripheral Giant cell Granuloma
3) Cherubism
4) Aneurysmal bone cyst
5) “Brown tumor” of hyperparathroidim

70
INTRODUCTION TO ORAL MEDICINE
Oral medicine is the discipline of dentistry concerned with the oral health. Diagnosis and management
of medical conditions that affect the oral and maxillofacial region such as; orofacial pain, oral
manifestations of systemic diseases, salivary gland disorders, and the management of medically
compromised patients with oral health issues by non-surgical treatments.
Curricular Map for Oral Medicine

71
Resources a) Teaching resources
b) Infrastructure resources
Teaching resources
Sr. #. Faculty Name Designation as per PM
& DC certificate Qualification
1 Dr. Fareed Ahmad Assistant Professor BDS, MCPS
2 Dr. Muhammad Shairaz Sadiq Assistant Professor BDS, MCPS
3 Dr. Aleena Saeed Registrar BDS
4 Dr. Manal Registrar BDS
5 Dr. Ayesha Noor Registrar BDS
Infrastructure resources
Sr. #. Infrastructure Resources Quantity
1 Oral Medicine and Diagnosis Dental Hall
1
2
Dental Units
• Oral Medicine
• Diagnosis
2
2
3
Dental Stools
• Oral Medicine
• Diagnosis
2
2
4 Reception 1
5 Mini Library 1
7 Dental equipment and materials

72
Teaching and Learning Strategies
Multiple educational methods will be used comprising of self-study, interactive lectures, group
discussions, practical, and manual dexterity skill sessions.
(i) Methods for achieving cognitive objectives
• Interactive lectures using audio visual aids on power point presentation
• Group discussions in form of large group and small group
• Collaborative learning
• Self-study and reading from learning resources
(ii) Methods for achieving psychomotor objectives
• Theoretical information provided in lectures
• Clinical demonstrations provided by teaching faculty on models and patients
• Supervised practice on patients
(iii) Methods for achieving affective objectives
• Interaction with peers, group members, teachers, support staff etc.
• Group discussions (small and large)
• Oral presentations by students
Learning Methodologies
The following teaching /learning methods are used to promote better understanding:
• Interactive lectures
• Small group discussions
• Practical
• Skill sessions
• Self-directed learning
• Assignments
• Oral presentations by students

73
Interactive lectures
In large group, the lecturer introduces a topic which explains the underlying phenomena through
questions, pictures, exercise, etc. Students are actively involved in the learning process.
Small group discussions
This format helps students to clarify concepts and acquire skills and attitudes. Students exchange
opinions and apply knowledge gained from lectures and self-study. The facilitator role is to ask probing
questions, summarize, or rephrase to help clarify concepts.
Practical
In practical sessions students observe demonstrations from faculty members on proper instrument use
and handling both inside and outside the patient’s mouth. The students are trained in diagnosing and
treating a periodontal disease as per protocols set by the department.
Skill session
Students are required to practice suturing techniques on inanimate materials.
Self- directed learning
Students' take responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing
with peers, seeking information from Learning Resource Center, teachers and resource persons within
and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hours or afterwards
for self-study.
Assignments
Students are given written formative assignments on designated topics. Revision of the topics already
covered by anatomy and physiology departments are given to students as oral presentations.
Oral presentations by students
Students are assigned topics during revision session to enhance their communication skills and group
learning.

74
Curriculum Implementation
Curriculum implementation refers to putting into practice the official document including course
content, objectives, learning and teaching strategies. Implementation process helps the learner to
achieve knowledge, skills and attitudes required of the learning tasks. Learners are a pertinent
component of the implementation process. Implementation occurs when the learner achieves the
intended learning experiences, knowledge, ideas, skills and attitudes which are aimed to make the
learner an effective part of the society. Curriculum implementation also refers to the stage at which
curriculum is put into effect. There has to be an implementing agent as well. Teacher is an important
part of this process and implementation of the curriculum is the way the teacher selects and utilizes
various components of the curriculum. Implementation occurs when the teacher’s formulated course
content, teacher’s personality and teaching and learning environment interact with the learners.
Therefore, curriculum implementation is how the officially planned course of study is translated and
reflected by the teacher into schemes of work, lesson plans, syllabus and resources are effectively
transferred to the learners. Curriculum implementation can be affected by certain factors such as
teachers, learners, learning environment, resource materials and facilities, culture and ideology,
instructional supervision and assessments.
Personnel involved in teaching and facilitation
(iv) Lectures delivery by:
Dr Fareed Ahmad (Assistant Professor)
Dr Muhammad Shairaz Sadiq (Assistant Professor)
(ii) Demonstrators for practical and small group discussion sessions:
Dr Mannal Sohail
Dr Ayesha Noor
Dr Bareerah Idrees
(iii) Support staff: 3 (3 Dental Assistants) as nominated by college
Time frame
Course duration: 36 weeks
Lectures: Monday (10:00am to 10:50am), Friday (8:00 am to 8:50am)
Clinical rotation: 6 weeks - Tuesday and Thursday (10:00 am to 3:00 pm), Friday (10:00 am
to 1:00pm)

75
Course Outline
Normal mucosa assessment and investigations
• Histology
• General health status
• Oral examination (including lips oral mucosa floor of the mouth teeth gingival occlusion salivary glands jaw bones)
• Examination of temporomandibular joint
• Laboratory aids
• Analysis treatment planning and patient management
Soft tissue lesions
• White lesions
• Pigmented lesions
• Ulcerative lesions
• Vasculo-bulbous lesions
• Pre-malignant lesions clinical features diagnosis and management
• Disorders of the tongue and lips clinical features, diagnosis and treatment planning
• Diseases of salivary glands xerostomia: clinical features, diagnosis and management
Hard tissue lesions
• Diseases of jaw bones; clinical features diagnosis and management
• Diseases of tempro-mandibular joint; clinical features diagnosis and treatment planning
• Disorders of teeth clinical features diagnosis and treatment
• Focal infection; Significance diagnosis and management of effect cases
• Clinical features diagnosis and treatment of pain
Systemic disorders
• Anaemia
• Leukaemia
• Bleeding disorders
• Patients on anti-coagulant therapy management

76
Overview
A1. History taking A2. Clinical
examination
A3. Investigations A4. Management
A4a. prescribing &
therapeutics
A4b. operative
interventions
B1. Normal
mucosa
assessment
B2. Soft
tissue lesions
B3. Hard
tissue lesions
B4. Systemic
disorders
B5. Pain in
orofacial
region
B6. Medical
emergencies
Histology White lesions Jawbone
diseases
Anaemia Facial pain prevention
General
health status
Pigmented
lesions
TMJ diseases Leukaemia
and leukopenia
Neuropathic
pain
Emergency drugs
and equipment
Mucosa of
lips, floor of
mouth and teeth, gingiva
and occlusion.
Ulcerative
lesions
Disorders of
teeth
Bleeding
disorders
Migraine,
cluster,
tension type headaches
Vesiculo bulbous
lesions
Focal infections
Nutritional deficiencies
Neurological dysfunction
Pre-malignant
and malignant lesions
Endocrine
disturbances
Disorders of
tongue and lips
Renal
diseases
Salivary
glands
diseases
+ No. of MCQs (13)
• (C1=2, C2= 5, C3= 6)
• 01 mark each
* No. of SAQs/SEQs (6)
• 02 x SAQs/SEQs (C1&C2) = 05 marks each

77
• 01 x SAQs/SEQs (C1&C2) = 04 marks each
• 03 x SAQs/SEQs (C3) = 06 marks each
S.
No
Topic +
MCQs
*SAQs/
SEQs
Weightage
(%)
Weeks
1.
Principles of oral medicine:
assessment and investigation of
patient
1
1
11
4
2.
Infections of gingiva and oral mucosa
3.
Oral ulceration 02
02
31
11
4.
Diseases of lips and tongue
5.
Swellings of face and neck
01
6.
Salivary glands and saliva
7.
Inflammatory overgrowths,
developmental and benign lesions
and oral pigmentation
01
01
18
7
8.
Precancerous lesions and conditions
9.
Oral Carcinoma & Carcinogenesis 01
10.
Muco-cutaneous diseases and
connective tissue disorders
01
11.
Oral manifestation of systemic
diseases
01
01
24
9
12.
Orofacial pain & Psychogenic Pain 01
13.
Temporomandibular disorders 01
14.
Immunity and oral reactions to drug
therapy
01
15.
Disorders of teeth and bone 01
16.
Medical emergencies in dentistry 01 01 16 5

78
TOPICS and
OBJECTIVES
FACULTY
LEARNIN
G DOMAIN
(CPA)
LEARNING
STRATEGY
ASSESSMENT
Oral Medicine
Clinical Viva OSPE NUMS
MCQs
NUMS
SEQs
12. The Oral Mucosa
3
1
• Discuss Normal
oral Mucosa
o Structure
o Function
o Age
changes
Dr.
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
C
Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Discuss Abnormal
oral mucosa C
Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Oral mucosa in
generalized
disease C
Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Periodontium in
generalized
disease C
Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
13. Principles of oral medicine: assessment and investigation of
patients
3 1
• Speciality of oral
medicine
Dr.
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
C Interactive
lecture
• Patient assessment
o History taking
• Examination
CPA
Interactive
lecture/ clinic
visits
• Investigations
o Blood
examination
o Clinical chemistry
o Immunological
tests
o Endocrine
function
o Urinalysis
C
Interactive
lecture/small
group
discussion

79
o Biopsy
o Microbiol
ogical
investigati
ons
• Imaging
techniques
• Discuss how to
form diagnosis C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
14. Therapy
• Discuss Principles
of Therapy
Dr.
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
C
Interactive
lecture
• Discuss topical
therapy
o Covering agents
o Topical
antiseptics
o Topical analgesics
o Topical antibiotics
• Topical
corticosteroids
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Discuss Creams
and ointments C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
• Discuss systemic
therapy
o Systemic
corticosteroids
o Azathioprine
• Other systemic
drugs used in oral
medicine
C
Interactive
lecture/
Case based
discussion

80
• Discuss
Limitations of
therapy
C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
15. Infections of gingivae and oral muosa
• Discuss Bacterial
infections
o Acute necrotizing
ulcerative
gingivitis
o Syphilis
o Gonorrhea
o Non-specific
urethritis
o Tuberculosis
Dr. Fareed
Ahmad
C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
• Discuss Fungal
infections
Oral candidiosis C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
• Discuss Viral
infections
o Herpes simplex
virus infections
o Varicella zoster
virus infections
o Epstein-Barr virus
infections
o Paramyxovirus
infections
o Human
papillomavirus
infections
o Human
immunodeficiency
virus and AIDS
C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
16. Oral Ulceration
• Discuss Traumatic
ulceration
o Aetiology
o Clinical features
o Management
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion

81
• Discuss Recurrent
aphthous
stomatitis (RAS)
o Clinical features
o Aetiology of RAS
o Histopathology
and
immunopathogene
sis of RAS
o Systemic
conditions and
RAS like lesions
o Management of
RAS
Dr
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Behcet’s disease C
Interactive
lecture
17. Diseases of the lips and tongue and
disturbances of taste and halitosis
• Discuss diseases of
the lips
o Swelling of the lips
o Angular cheilitis
(angular stomatitis,
chelosis, perleche)
o Lip fissures
o Allergic cheilitis
o Actinic cheilitis (solar
keratosis)
o Exfoliative cheilitis
o Perioral dermatitis
o Lick eczema
o Cheilocandidosis
C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
• Discuss diseases of
tongue
o Developmental
abnormalities and
morphological
variations
o Tongue fissures
o Coated tongue
o Hairy tongue
o Atrophy of the lingual
epithelium
o Traumatic irritation of
the tongue
Dr. Fareed
Ahmad
C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion

82
o Enlargement of the
foliate papillae
o Geographic tongue
(erythema migrans,
benign migratory
glossitis), median
rhomboid glossitis
• Discuss disturbances
of taste and halitosis
o Disturbances of taste
C Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
18. Swellings of the face and neck
• Discuss facial
swellings
Differential
diagnosis
Dr.
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
C
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Discuss Swellings
in the neck C
Interactive
lecture
• Discuss Cervical
lymphadenopathy
o Differential
diagnosis
o Examination of
the lymph nodes
o Inflammatory
causes
• Neoplastic causes
of lymph node
enlargement
C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
19. Salivary glands and saliva
• Discuss saliva and
salivary glands
o Saliva
o Salivary glands
Dr. Fareed
Ahmad
C
Interactive
lecture
• Discuss
assessment of the
salivary glands
Examination
o Measurement of
the salivary flow
o Salivary gland
imaging
o Sialochemistry
o Biopsy
CPA
Interactive
lecture/clinica
l session

83
• Discuss salivary
gland diseases
o Sialdenitis
o Sialosis
o Necrotizing
sialometaplasia
o Sarcoidosis
o HIV-associated
salivary gland
disaease
o Salivary gland
tumors
C
Interactive
lecture/ case
based
discussion
20. Inflammatory overgrowths, developmental and benign
lesions, and pigmentation of the oral mucosa
• Inflammatory
overgrowths
o Epulides
o Fibroepithelial
polyp
o Denture
granuloma
o Focal epithelial
hyperplasia
(Heck’s disease)
Dr Fareed
Ahmad
CA
Interactive
lecture/SGD
• Developmental
lesions
o Hamartomas
• Developmental
white lesions
CA
Interactive
lecture/SGD
• Benign neoplasms
• Squamous cell
papilloma CA
Interactive
lecture/SGD
• Miscellaneous
benign conditions
o Traumatic
keratoses
o Nicotinic
stomatitis (pipe
smokers’ palate)
• Leukoedema
CA
Interactive
lecture/SGD
• Pigmentation of
the oral mucosa
o Amalgam tattoos
C
Interactive
lecture/SGD

84
o Melanotic
pigmentation
• Oral melanoma
21. Precancerous Lesions and Conditions
• Precancerous
lesions
o Leukoplakia
o Erythroleukoplaki
a
o Speckled
leukoplakia
o Candidal
leukoplakia
(chronic
hyperplastic
candidosis)
o Malignant
transformation of
precancerous
lesions
o Management of
precancerous
lesions Dr.
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Precancerous
conditions
o Oral submucous
fibrosis (OSF)
o Sidropenic
dysplagia
o Lichen planus
• Other
precancerous
conditions
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics
• Oral carcinoma
and
carcinogenesis
o Aetiological
factors for oral
squamous cell
carcinoma
o Clinical features
and diagnosis of
oral carcinoma
o Staging systems
for oral carcinoma
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion/
Clinics

85
o The management
of oral carcinoma
o Prevention of oral
carcinoma
• Oral carcinoma as
a genetic disease
22. Mucocutaneous disease and connective tissue disorders
• Mucocutaneous
disease
Dr Fareed
Ahmad
C Interactive
lecture
• Lichen planus and
lichenoid
reactions
CPA
Interactive
lecture/case
based
discussions/
clinical
session
• Immunobulbous
diseases
o Pemphigus
o Pemphigoid
o Dermatitis
herpetiformis
• Linear IgA
disease
CA
Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Epidermolysis
bullosa C
Interactive
lecture
• Erythema
multiforme
CA Interactive
lecture/SGD
• Idiopathic oral
blood blisters
(Angina bullosa
Haemorrhagica)
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Connective tissue
diseases
o Lupus
erythematosus
o Morphoea and
systemic sclerosis
o Mixed connective
tissue disease
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
23. Gastrointestinal diseases
• Coeliac disease
(glutensensitive
enteropathy)
C Interactive
lecture

86
o Oral manifestation
of celiac disease
Dr
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
• Inflammatory
bowel disease
(IBD)
o Crohn’s disease
o Oral Crohn’s
disease
o Orofacial
granulomatosis
o Ulcerative colitis
• Stomatosis and
inflammatory
bowel disease
CA
Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Gastro
oesophageal
reflux disorder
(GORD)
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
24. Blood and nutrition, endocrine disturbances, and renal
disease
• Disorders of the
blood
o Anaemias
o Oral signs and
symtopms in
anaemia
o Management of
patients with
anaemias and
haematinic
deficiencies
o Leukemia
o Leukopenia
o Myelodysplastic
syndrome
o Platelet
abnormalities
o The selection of
patients for
haematological
examination
Dr
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
C Interactive
lecture
• Disorders of
nutrition
o Nutritional
deficiencies
• Scurvy
C Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion

87
• Endocrine
disturbances
o Normal endocrine
changes
o Adrenocortical
diseases
o Thyroid disease
• Diabetic mellitus
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Renal disease
o Chronic renal
failure
o Renal patients
undergoing
dialysis
• Renal transplant
patients
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
25. Immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity,
autoimmunity and oral reactions to drug
therapy
• Immunodeficienc
y
Dr
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
C Interactive
lecture
• Hypersensitivity C Interactive
lecture
• Angioedema CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• C1 esterase
inhibitor
deficiency
C Interactive
lecture
• Autoimmunity CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Oral reactions to
drug therapy
o Spectrum of
adverse reactions
o Oral reactions o
antibiotics
o Oral reactions to
steroids
o Drug therapy and
periodontal tissues
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion

88
o Fixed drug
eruptions
26. Facial Pain and neurological disturbances
• Facial pain: an
overview
o The nerve supply
o the face
o The evaluation of
facial pain
Dr Fareed
Ahmad
Dr Fareed
Ahmad
C Interactive
lecture/case-
based
• Neuropathic pain
o Trigeminal
neuralgia
o Glossopharyngeal
neuralgia
o Postherpetic
neuralgia
o Neuropathic pain
secondary to other
conditions
C Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Migraine CA Interactive
lecture/clini
cal sessions
/small group
discussion
• Cluster headaches
(periodic
migrainous
neuralgia/
migrainous
neuralgia)
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Tension type
headache
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Facial Pain:
miscellaneous
conditions
o Giant cell arteritis
(temporal
arteritis/cranial
arerirtis)
o Auriculotemporal
syndrome (Frey’s
syndrome)
CA Interactive
lecture/clini
cal sessions
/small group
discussion

89
• Neurological
disturbances
o Facial nerve
deficits
o Anaesthesia and
paraesthesia
o Bell’s palsy
o multiple sclerosis
o Extrapyramidal
syndromes
Interactive
lecture/clini
cal sessions
/small group
discussion
27. Temporomandibular disorders
• Investigation of
the
stomatognathic
system
o History
o Examination
o Imaging
o Arthroscopy
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Temporomandibul
ar pain and
dysfunction
syndrome
(TMPDS)
o Management
Dr Fareed
Ahmad
C Interactive
lecture
• Internal
derangement
o Disc displacement
with reduction
o Disc displacement
without reduction
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
• Rheumatoid
arthritis
CA Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Osteoarthrosis
(osteoarthritis)
C Interactive
lecture/
case-based
discussion

90
• Masseteric
Hypertrophy
C Interactive
lecture /
case-based
discussion
• Tumors CPA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion/c
ase-based
discussion
28. Psychogenic orofacial problems
• Chronic orofacial
pain
o Atypical facial
pain
o Atypical
odontalgia
o Oral dysaesthesia
(Burning mouth
syndrome)
o Management of
chronic orofacial
pain
Dr Fareed
Ahmad
CPA Interactive
lecture/
small group
discussion
• Disturbances in
taste and
salivation
C Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Dysmorphophobia C Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Self-injurious
behavior
C Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Eating disorders C Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Drugs and
Alcohol
C Interactive
lecture/case-

91
based
discussion
29. Disorders of teeth and bone
• Disorders of teeth
o Hypodontia
o Variation in
eruption
o Variation in size
of teeth
o Non carious tooth
surface loss
o Discoloration of
the teeth
o Disturbances of
the structure and
enamel and
dentine
Dr
Muhammad
Shairaz
Sadiq
C Interactive
lecture/case-
based
discussion
• Disorders of bone
o Inherited and
development
disturbances
o Metabolic and
endocrine
disturbances
o Disorders of
unknown
aetiology paget’s
disease
C Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
30. Medical emergencies in dentistry
• The prevention of
medical
emergencies
Dr Fareed
Ahmad
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion
/role plays
• Administration of
drugs
o Routes of
administration of
drugs
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion/
role plays
• Emergency drugs
and equipment
CA Interactive
lecture/smal
l group

92
Learning resources
Topic Resources
The Oral Mucosa Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Principles of oral medicine: assessment and
investigation of patients
Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Therapy Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
discussion/
role plays
• Management of
emergencies
CAP Interactive
lecture/smal
l group
discussion/
role plays

93
Infections of gingivae and oral mucosa Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Oral Ulceration Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Diseases of the lips and tongue and disturbances
of taste and halitosis
Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Swellings of the face and neck Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Salivary glands and saliva Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.

94
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Inflammatory overgrowths, developmental and
benign lesions, and pigmentation of the oral
mucosa
Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Precancerous lesions and conditions. Oral
carcinoma and carcinogenesis
Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Mucocutaneous disease and connective tissue
disorders
Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Gastrointestinal diseases Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Blood and nutrition, endocrine disturbances, and
renal disease
Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.

95
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity,
autoimmunity and oral reactions to drug therapy
Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Facial Pain and neurological disturbances Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Temporomandibular disorders Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Psychogenic orofacial problems Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.

96
Disorders of teeth and bone Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Oral and Maxillofacial Medicine, the Basis of
Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
Medical Problems in Dentistry, 6th Edition, by
Crispian Scully.
A Clinical guide to Oral Medicine by P J
Lamely & M A O Lewis.
Medical emergencies in dentistry Tyldesley's Oral Medicine, 5th Edition, by Anne
Field & Lesley Longman.
Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial surgery
6th Edition by James R. Hupp, Edward Ellis III,
Myron R. Tucker
Other Learning Resources
Clinics / Practical Students will be involved in clinical work in the clinics of Oral Medicine and
diagnosis
Videos Videos to familiarize the students with the procedures and protocols to assess
patients.
Computer
Lab/CSs/DVDs/ Internet
Resources:
To increase the knowledge, students should utilize the available internet
resources and CDs/ DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase
learning.
Self-Learning
Self-Learning is scheduled to search for information to solve cases, read
through different resources and discuss among the peers and with the faculty
to clarify the concepts.

97
Assessment methods
Internal Assessment (IA)
a. Weightage of internal assessment shall be 10 %, each for theory and practical, in BDS
Professional Examination.
b. The Internal Assessment shall comprise of monthly test / PBL / assignments / Clinical tests /
clinical vivas etc
c. The Internal Assessment record shall be kept in the respective department of the College /
Institute and after approval of Principal, a summary as per University registration number shall
be furnished to the Controller of Examinations, at least two weeks before the commencement
of final examination.
d. The result of all the class tests / tools which contribute towards IA will be displayed to the
students during an academic year.
e. The same internal assessment shall be counted both for annual and supplementary
examinations. The students who are relegated, however, can improve the internal assessment
during subsequent year
f. Internal assessment tools of any subject may be changed after the approval of
respective FBS
Annual Examination
a. The weightage of Annual Examination shall be 90%, each for theory and practical, in BDS.
b. The examination comprises of a theory paper and practical/clinical examinations as per
PM&DC regulations and the Table of Specifications (TOS) of the University.
c. The gap between two consecutive theory papers shall not be more than two days.
d. The Theory Paper shall be of 2-hours duration, held under the arrangements of the university.
It shall have two parts; MCQs (30%) and SAQs/SEQs (70 %) for the year 2018. It may be
changed after the approval of Academic Council.
e. Allocated time for MCQs for 2019 shall be as under:
i. 25 MCQs - 30 Minutes
ii. 30 MCQs - 40 Minutes
iii. 40 MCQs - 50 Minutes
iv. 45 MCQs - 60 Minutes
f. Each MCQs shall have four distractors
g. The distribution of SAQs/SEQs as well as MCQ difficulty levels for BDS annual examinations
is as under: -

98
Total Marks = 50 Total Time Allowed = 2 hours
Marks of Written Paper = 45
Marks of Int. Asses = 05
(Including MCQs)
13 x MCQs (on separate sheet)
(13 Marks) (Time = 20 min)
02 x SAQs/SEQs (C1 & C2) = 05 marks
each
01 x SAQs/SEQs (C1 & C2) = 04 marks
each
03 x SAQs/SEQs (C3) = 06 marks each (32 Marks) (Time = 1hrs 40 min)
S. No Topic No. of MCQs (13)
(C1=2, C2= 5, C3= 6)
01 mark each
No. of SAQs/SEQs (6)
• 02 x SAQs/SEQs (C1&C2)
= 05 marks each
• 01 x SAQs/SEQs (C1&C2)
= 04 marks each
• 03 x SAQs/SEQs (C3) = 06
marks each
1. Principles of oral medicine: assessment and
investigation of patient
01 01
2. Infections of gingiva and oral mucosa
3. Oral ulceration 02
02 4. Diseases of lips and tongue
5. Swellings of face and neck 01
6. Salivary glands and saliva
7. Inflammatory overgrowths, developmental and
benign lesions and oral pigmentation
01
01 8. Precancerous lesions and conditions
9. Oral Carcinoma & Carcinogenesis 01
10. Muco-cutaneous diseases and connective tissue
disorders
01
11. Oral manifestation of systemic diseases 01
01
12. Orofacial pain & Psychogenic Pain 01
13. Temporomandibular disorders 01
14. Immunity and oral reactions to drug therapy 01
15. Disorders of teeth and bone 01
16. Medical emergencies in dentistry 01 01
Total 13 (13 Marks) 06 (32 Marks)

99
Internal Assessment Calculation (Theory Annual)
A B C D
Roll No. Name All Modules/
Pre annual Exams or any other exam
Total
Marks of internal
Assessment out of 05
Total Marks Sum of Marks obtained x 05 / sum of
total marks in all exams
Table of specifications for Annual Professional Exam: Practical Clinical Assessment
Total = 50
OSPE = 20
VIVA = 20
Logbook = 05
Internal Assessment = 05
OSPE (20 Marks)
Stations Marks Time
Static Stations 5 5×2=10 2 min each station
Interactive Stations 2 2×5=10 5 min each station
Internal Assessment Calculation (Practical)
A B C D
Roll No. Name OSPE/ Practical Class tests though out the
year/ Pre annual Practical Exams or any
other exam
Total Marks of internal
assessment Out of 05
Total Marks Sum of Marks obtained x 05 / sum of total
marks in all exams
Internal Examiner
He/she shall be Professor and Head of Department who has been involved in teaching of the class being
examined for at least six months. Second preference shall be Associate/Assistant Professor who is
involved in teaching of the class and posted there for one year. Third preference shall be a recognized
Professor of the subject.

100
External Examiner
He/she shall be a Professor/Associate Professor of a recognized Medical/Dental College or at least an
Assistant Professor with three years teaching experience in the relevant subject.
Conflict of Interest
No person shall serve as an examiner whose close relative (wife, husband, son, daughter, adopted son,
adopted daughter, grand-son, grand-daughter, brother, sister, niece /nephew, son and daughter- in-law
brother and sister- in-law, parental and maternal uncle and aunt etc) is appearing in the examination.
All examiners likely to serve as an examiner shall render a certificate in compliance to this para.
Paper Setting
a. Each College / Institute shall forward a set of two question papers as per TOS along with
the key for each subject to the Controller of Examinations, at least three months in advance
of the annual examination. The question paper as a whole / a question without a
comprehensive key shall not be considered towards final paper setting.
b. The set of question papers shall be prepared by the respective Head of Department (HoD)
and furnished to Controller of Examinations through Head of Institution (HoI)
c. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the final paper setting having
fair representation of each college / institute.
Paper Assessment
a. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the theory paper marking, to be
undertaken in the manner as deemed appropriate.
b. The Examination Directorate shall coordinate directly with the faculty, earmarked for the paper
marking
c. A student who scores 85% and above marks in any subject shall qualify for distinction in that
particular subject.
d. A fraction in aggregate marks of a subject shall be rounded off to whole number. If it is less
than 0.5 then it will be rounded off to the previous whole number while 0.5 or more will be
rounded off to the next whole number.
Practical / Clinical Examinations
a. The Controller of Examiners shall approve the faculty to serve as the internal & external
examiners.
b. The number of external and internal examiners shall be equal.
c. One external & internal examiner each shall be marked for a group of 100 students.
d. Candidates may be divided into groups in the clinical and practical examinations and be
standardized by incorporating clinical exam
e. Practical/clinical examination shall be held after the theory examination of the subject
but in special cases, it may be held before the theory examination with the approval of the
Controller of Examinations. For the purpose of practical/clinical examination, the candidates
may be divided into sub groups by the examiners.
f. The assessment of the practical / clinical examination duly signed by internal & external
examiner shall be furnished to the Controller of Examinations within one week of the
conclusion of examination

101
Pass Marks
a. Pass marks for all subjects less Islamic / Pakistan Studies, shall be 50 % in theory and practical,
separately.
b. Pass marks for Islamic / Pakistan Studies shall be 33 % which, however shall not be counted
towards final scoring of the professional examination.
c. No grace marks shall be allowed to any student in any examination.
Declaration of Result.
Every effort shall be made to declare the result of each examination within one month of the last
practical examination or earlier.
Promotion.
No student shall be promoted to the higher classes unless he/she passes all the subjects of the previous
class
Re-Totaling.
Any student may apply to the Controller of Examinations on a prescribed form along with the
specified fee.
Supplementary Examination.
The interval between a supplementary examination and the previous professional examination
shall not be more than two months. There shall be no special supplementary examination.
Sample MCQ
A 22 years female presented to the oral medicine department with eruptions on face (butterfly
pattern) and fever. Intra-oral examination revealed superficial erosions and erythematous patches
on the mucosa. Which of the following investigations you would suggest her?
A. Haemoglobin, CBC and serum B12
B. Liver function tests
C. Microbiological sampling of mucosal sites
D. Serum Anti ds-DNA
KEY: D
Sample SEQ/SAQ
A young boy belonging to poor socio-economic status visits the diagnostic department of your
hospital with crater-like ulceration of gingiva & mal-odor.
a. What is your provisional diagnosis? (1)

102
b. What are the predisposing factors of this condition? (2)
c. How would you manage his condition? (3)
KEY:
a. Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis
b. Predisposing Factors
* Local irritation
* Poor oral hygiene
* Stress
* Nutritional deficiency
* Blood dyscrasias
* HIV
* Immunosuppression
* Intense smoking
c. Management
• Identification and elimination of predisposing factor
• Good oral hygiene
• Antiseptic/Antibacterial Mouthwashes/Gel
• Topical analgesics
• Systemic antibiotics
• Metronidazole
– 200 mg TDS for 3 days (drug of Choice)
• Systemic Analgesics
• Subgingival plaque control
• Debridement of necrotic gingival tissue
• Ultrasonic scaling
• Home care

103
INTRODUCTION TO GENERAL MEDICINE
The BDS undergraduate students learn General Surgery during third year of the
program and are evaluated in the Third Professional BDS Examination
Resources d. Teaching resources
e. Infrastructure resources
Teaching resources
Sr. #. Faculty Name Department as per PM &
DC certificate Qualification
1 Dr. Javed Iqbal HOD-Associate Professor MBBS, FCPS
2 Dr. Ashfaq Zia Assistant Professor MBBS, FCPS
3 Dr. Raja Yasser Shahbaz Assistant Professor MBBS, FCPS
Infrastructure resources
Sr. #. Infrastructure Resources Quantity
1 Lecture hall 1
2 Opd
2
3 Medical wards
4 80 BEDDED
5 Class rooms 1
6 Mini Library 1

104
Teaching and Learning Strategies
Multiple educational methods will be used comprising of self-study, interactive lectures, group
discussions, practical, and manual dexterity skill sessions.
(i) Methods for achieving cognitive objectives
• Interactive lectures using audio visual aids on power point presentation
• Group discussions in form of large group and small group
• Collaborative learning
• Self-study and reading from learning resources
(ii) Methods for achieving psychomotor objectives
• Theoretical information provided in lectures
• Clinical demonstrations provided by teaching faculty on models and patients
• Supervised practice on patients
(iii) Methods for achieving affective objectives
• Interaction with peers, group members, teachers, support staff etc.
• Group discussions (small and large)
• Oral presentations by students
Learning Methodologies
The following teaching /learning methods are used to promote better understanding:
• Interactive lectures
• Small group discussions
• Practical
• Skill sessions
• Self-directed learning
• Assignments
• Oral presentations by students

105
Interactive lectures
In large group, the lecturer introduces a topic which explains the underlying phenomena through
questions, pictures, exercise, etc. Students are actively involved in the learning process.
Small group discussions
This format helps students to clarify concepts and acquire skills and attitudes. Students exchange
opinions and apply knowledge gained from lectures and self-study. The facilitator role is to ask
probing questions, summarize, or rephrase to help clarify concepts.
Practical
In practical sessions students observe demonstrations from faculty members on proper instrument use
and handling both inside and outside the patients mouth. The students are trained in diagnosing and
treating a periodontal disease as per protocols set by the department.
Skill session
Students are required to practice suturing techniques on inanimate materials.
Self- directed learning
Students' take responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing
with peers, seeking information from Learning Resource Center, teachers and resource persons within
and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hours or afterwards
for self-study.
Assignments
Students are given written formative assignments on designated topics. Revision of the topics already
covered by anatomy and physiology departments are given to students as oral presentations.
Oral presentations by students
Students are assigned topics during revision session to enhance their communication skills and group
learning.

106
Curriculum Implementation
Curriculum implementation refers to putting into practice the official document including course
content, objectives, learning and teaching strategies. Implementation process helps the learner to
achieve knowledge, skills and attitudes required of the learning tasks. Learners are a pertinent
component of the implementation process. Implementation occurs when the learner achieves the
intended learning experiences, knowledge, ideas, skills and attitudes which are aimed to make the
learner an effective part of the society. Curriculum implementation also refers to the stage at which
curriculum is put into effect. There has to be an implementing agent as well. Teacher is an important
part of this process and implementation of the curriculum is the way the teacher selects and utilizes
various components of the curriculum. Implementation occurs when the teacher’s formulated course
content, teacher’s personality and teaching and learning environment interact with the learners.
Therefore, curriculum implementation is how the officially planned course of study is translated and
reflected by the teacher into schemes of work, lesson plans, syllabus and resources are effectively
transferred to the learners. Curriculum implementation can be affected by certain factors such as
teachers, learners, learning environment, resource materials and facilities, culture and ideology,
instructional supervision and assessments.
Personnel involved in teaching and facilitation
(v) Lectures delivery by:
Sr. #. Faculty Name Department as per PM &
DC certificate Qualification
1 Dr. Javed Iqbal Associate Professor MBBS, FCPS
2 Dr. Ashfaq Zia Assistant Professor MBBS, FCPS
3 Dr. Raja Yasser Shahbaz Assistant Professor MBBS, FCPS
(iv) Computer assistant: 1 as nominated by the college
Time frame
Course duration: 36 weeks
Lectures: Tuesday (8:50 to 9:50 am), Thursday (8:50 to 9:50 am)
Clinical rotataion:9 weeks - Monday and Wednesday (12:00 am to 3:00 pm),

107
Course Outline
Outline of Clinical Teaching in the Subject of Medicine
3rd year BDS 2018-2019
1st Rotation • History taking and GPE
• Symptomatology and history taking pertaining to CVS +
respiratory system
• Clinical examination of CVS and respiratory system
2nd Rotation • Symptomatology and history taking pertaining to GIT
• Clinical examination of GIT
• Nomenclature symptomatology and history taking pertaining to
CNS and musculoskeletal system
• Clinical examination of CNS and musculoskeletal system
3rd Rotation • Revision of clinical methods
• Case discussion of common clinical conditions
4th Rotation • Revision of clinical methods
• Case discussion of common clinical conditions

108
Course Objectives
This program aims to ensure that the dental graduates will make the bio-psycho-social care of medical
patients their first concern by applying their knowledge and skills in a competent and ethical manner
and using their ability to provide leadership to analyze complex and uncertain situations.
GENERAL OUTCOMES OF THE BDS GENERAL MEDICINE COURSE:
The General outcomes of this course are:
1. Development of the graduate as a scholar and a scientist; 2. Development of the graduate as a practitioner; and
3. Development of the graduate as a professional.
SPECIFIC OUTCOMES OF THE BDS GENERAL MEDICINE COURSE:
At the completion of this course the BDS graduate will be able to:
1. Apply biomedical scientific principles, method and knowledge to clinical practice.
2. Apply the principles, method and knowledge of population health and the improvement of health and healthcare to clinical practice.
3. Apply scientific method and approaches to medical research.
4. Carry out a consultation with a medical patient.
5. Diagnose and suggest management of common General Medical conditions relevant to Dental practice.
6. Communicate effectively with patients and colleagues in a medical context.
7. Provide immediate care in medical emergencies relevant to Dental practice. 8. Prescribe drugs safely, effectively and economically.
9. Carry out common practical procedures involved in general care of medical patients safely
and effectively. 10. Use information effectively in a medical context.
11. Behave according to ethical and legal principles.
12. Reflect, learn and teach others.
13. Learn and work effectively within a multi-professional team. 14. Protect patients and improve care.
ANNEX-A: TOPICAL DETAILS OF THEORY COMPONENT MODULES

109
TOPIC AND OBJECTIVES
FACULTY
LEARNIN
G
DOMAIN
LEARNI
NG
STRATE
GY
Lectures /
Ward
Demonstr
ations
ASSESSMENT
General Medicine
Written
Test
MCQS/S
EQS
Ward
Test
Viva OSPE Midterm
Exam
Send Up
Exam
Feed
Back
from
Faculty
and
Student
s
Counse
ling
• Acute chest
pain differential
diagnosis and
management
principles
All
Faculty
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Ischemic Heart
Disease
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Hypertension
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Rheumatic
fever
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Enteric fever
J
Interact
ive
lecture
• Dengue fever J
Interact
ive
lecture/

110
based
discuss
ion
• Malaria
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• HIV/AIDS and
other STDS
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Infective
endocarditis
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Fungal
infections
diagnosis and
treatment
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Acute hepatitis
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Acid peptic
disease
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group

111
discuss
ion
• Chronic
hepatitis
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
Cirrhosis of liver
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Liver Disease
and Dentistry
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Ascites
diagnosis and
management
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Pneumonia
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Bronchial
asthma
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group

112
discuss
ion
• Tuberculosis
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• COPD
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Meningitis and
Encephalitis
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Cerebrovascula
r accident
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Epilepsy
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Clotting
disorders
(Hemophilia,
Von-Willibrand
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group

113
discuss
ion
• Bleeding
Disorders
(ITP,DIC
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
•
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Anemia
classification ,
diagnosis and
treatment
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Nephrotic
syndrome
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Acute renal
failure
• Chronic renal
failure
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Hyperthyroidis
m and
• Hypothyroidis
m.
• Parathyroid
disorders
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group

114
Clinical Teaching Schedule
3rd
Year BDS Institute of Dentistry 2018-19
Morning Clinical Teaching Schedule
(Mondays, Wednesdays) Timings: (12:00pm to 03:00pm)
The assigned students will be divided into two batches
discuss
ion
• Diabetes
mellitus Type 1
• Diabetes
mellitus Type 2
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• Osteoporosis
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• RA
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion
• SLE
J
Interact
ive
lecture/
small
group
discuss
ion

115
Batch 1 Lt. Col. Muhammad Farooq (Mondays, Wednesdays) (12:00pm to 01:30pm)
Batch 2 Lt. Col. Muhammad Farooq (Mondays, Wednesdays) (01:30pm to 03:00pm)
Batch 2 Dr. Muhammad Siddique (Mondays, Wednesdays) (12:00pm to 01:30pm)
Batch 1 Dr. Muhammad Siddique (Mondays, Wednesdays) (01:30pm to 03:00pm)
3rd Year BDS Institute of Dentistry 2018-19
Afternoon Clinical Teaching Schedule Timings: 03:00pm to 05:00pm
Day Teaching Schedule
Mondays
• Batch I Self Learning: Practice History Taking and Clinical Skills
• Batch II Self Learning: Practice History Taking and Clinical Skills
Wednesdays
• Batch II Self Learning: Practice History Taking and Clinical Skills
• Batch I Self Learning: Practice History Taking and Clinical Skills
➢ Attendance is compulsory
GENERAL MEDICINE
(Bedside)
(Third Year BDS)
INTRODUCTION

116
The subject of general Medicine at undergraduate level enables the students to learn the clinical
medicine and application of the knowledge in clinical dental practice.
The course curriculum is designed to give the students a touch of the major areas of General
Medicine while keeping in mind the limitations and time constrains of the BDS curriculum.
This practice will ensure patient safety and better understanding of the correlations of the
disease with other dental pathologies. The practical component of the course involves
structured ward rotations and patient interaction for better learning.
SECTION I CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
This section introduces students to the brief overview of different types of diseases related to
cardiovascular system.
Aims
The section aims to provide basic background knowledge regarding important diseases of
cardiovascular system.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:
1. Understand differential diagnosis of acute chest pain and its principles of management.
2. Understand spectrum of ischemic heart disease and its management.
3. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and guidelines of management of hypertension.
4. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic fever.
5. Describe the pathophysiology, etiology, investigations and management of cardiac
failure.
SECTION II INECTIONS
This section familiarizes students with common infections causing patients to seek medical
advise and overview of its principles of management.
Aims

117
The aim of this section is to allow students to develop knowledge, understanding and
competence in identification of various common infections.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:
1. Identify and discuss the common causes of clinical presentation of fever like enteric
fever, dengue fever and malaria.
2. Identify and discuss the infections like HIV/AIDS and other STDs.
3. Describe the infectious agents of infective endocarditis and its diagnosis, investigations
and management.
4. Describe the important fungal infections, their diagnosis, investigations and treatment.
SECTION III GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
This section introduces students to the different types of diseases related to gastrointestinal
system.
Aims
The section aims to provide basic background knowledge regarding important diseases of
gastrointestinal system.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:
1. Describe the etiology, clinical features, investigations and management of acute
hepatitis..
2. Explain the causes of chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis of liver and its management.
3. Understand the clinical implications of the liver diseases in dental procedures.
4. Explain the diagnosis and management of ascites.
5. Describe the pathophysiology of the acid peptic disease and its appropriate
investigations and management.

118
SECTION IV RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
This section introduces students to the key themes of different systemic diseases related to
cardiovascular system.
Aims
The section aims to provide basic scientific knowledge and understanding regarding important
diseases of respiratory system.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:
1. Explain the risk factors of pneumonia, its classifications, investigations and appropriate
treatment..
2. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and guidelines of management of bronchial asthma.
3. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and treatment tuberculosis.
4. Describe the pathophysiology, etiology, investigations and management of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease.
SECTION V NERVOUS SYSTEM
This section introduces students to the brief overview of different types of diseases related to
nervous system.
Aims
The section aims to provide basic background knowledge regarding important diseases of
nervous system.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:

119
1. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and guidelines of management of meningitis and
encephalitis.
2. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and management of cerebrovascular accident.
3. Describe the classification, etiology, investigations and management of epilepsy.
SECTION VI HAEMATOLOGY
This section familiarizes students with common hematological disorders causing patients to
seek medical advice and overview of its principles of management.
Aims
The aim of this section is to allow students to develop knowledge, understanding and
competence in identification of hematological disorders.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:
1. Identify and discuss the common clotting disorders like hemophilia and Von-
Willibrand disease.
2. Identify and discuss the diseases like immune thrombocytopenic pupura and
disseminated intravascular coagulation.
3. Describe the classification of anemia and its diagnosis, investigations and management.
SECTION VII NEPHROLOGY
This section introduces students to the brief overview of different types of diseases related to
renal system.
Aims
The section aims to provide basic background knowledge regarding important diseases of renal
system.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:

120
1. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and management of nephrotic syndrome.
2. Describe the classification, etiology, investigations and management of acute and
chronic renal failure.
SECTION VIII ENDOCRINOLOGY
This section introduces students to the different types of diseases related to endocrinology.
Aims
The section aims to provide basic background knowledge regarding important diseases of
endocrinology.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:
1. Describe the etiology, clinical features, investigations and treatment of hypothyroidism,
hyperthyroidism and parathyroid disorders.
2. Describe the pathophysiology, classification of diabetes mellitus and its appropriate
investigations and management.
SECTION IX BONES AND MUSCLES
This section introduces students to the brief overview of different types of diseases related to
musculoskeletal system.
Aims
The section aims to provide basic background knowledge regarding important diseases of
musculoskeletal system.
Learning outcomes
By the end of a unit, candidates will be able to:
1. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and guidelines of management of osteoporosis.

121
2. Understand the etiology, diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus.
3. Describe the etiology, investigations and management of rheumatoid arthritis.
Learning Resources
1. Davidson text book of medicine
2. P.J kumar text book of medicine
3. Current medical diagnosis and treatment
4. Oxford pocket book of medicine
5. Hutchison clinical book
6. McLeod clinical book
7. Viva in medicine
OTHER LEARNING RESOURCES
Clinics / Practical Students will be involved in clinical work in the periodontology clinic
Videos Video familiarize the student with the procedures and protocols to assist
patients
Computer
Lab/CSs/DVDs/ Internet
Resources:
To increase the knowledge, students should utilize the available internet
resources and CDs/ DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase
learning.
Self Learning
Self Learning is scheduled to search for information to solve cases, read
through different resources and discuss among the peers and with the faculty
to clarify the concepts.

122
ASSESSMENT METHODS:
Internal Assessment
a. Weightage of internal assessment shall be 10 %, each for theory and practical, in BDS
Professional Examination.
b. The Internal Assessment shall comprise of monthly test / PBL / assignments / Clinical
tests / clinical vivasetc
c. The Internal Assessment record shall be kept in the respective department of the College /
Institute and after approval of Principal, a summary as per University registration number
shall be furnished to the Controller of Examinations, at least two weeks before the
commencement of final examination.
d. The result of all the class tests / tools which contribute towards IA will be displayed to the
students during an academic year.
e. The same internal assessment shall be counted both for annual and supplementary
examinations. The students who are relegated, however, can improve the internal
assessment during subsequent year
f. Internal assessment tools of any subject may be changed after the approval of
respective FBS
Annual Examination
a. The weightage of Annual Examination shall be 90%, each for theory and practical, in BDS.
b. The examination comprises of a theory paper and practical/clinical examinations as per
PM&DC regulations and the Table of Specifications(TOS) of the University.
c. The gap between two consecutive theory papers shall not be more than two days.
d. The Theory Paper shall be of 3-hours duration, held under the arrangements of the university.
It shall have two parts; MCQs (30%) and SAQs/SEQs (70 %) for the year 2018. It may be
changed after the approval of Academic Council.
e. Allocated time for MCQs for 2019 shall be as under:
i. 25 MCQs - 30 Minutes
ii. 30 MCQs - 40 Minutes
iii. 40 MCQs - 50 Minutes
iv. 45 MCQs - 60 Minutes
f. Each MCQs shall have four distractors
g. The distribution of SAQs/SEQs as well as MCQ difficulty levels for BDS annual examinations
is as under: -

123
Ser. Subject
Theory Practical
Grand
total MCQs PBQs/SAQs Int
Assess
Sub
Total
Oral
&
pract
Int
Assess
Sub
total
2. Gen
Medicine 45 45 10 100 90 10 100 200
Internal assessment calculation (Theory/ Annual)
A B C D F G
Roll No. Name All modules/ Pre Annual Exams or any other exam Total Marks of internal
assessment out of 10
Total Marks Sum of Marks obtained x 10 / sum of total marks
in all exams
Multiple Choice Question (MCQs)
• A multiple choice question (MCQ) consist of a stem that states the question or problem
followed by a set of possible answers that contain an option that is best answer to the
question.
• After reading the questions students should select the appropriate option from the given
possible answers.
• The correct answer carries one mark and incorrect carries zero. There is no negative marking.
Short essay question (SEQs)
• Short essay questions require students to present written answers that are used to asses basic
knowledge of key facts and provide students with an opportunity to demonstrate reasoning
and explain their understanding of the subject.
Internal Examiner
He/she shall be Professor and Head of Department who has been involved in teaching of the class being
examined for at least six months and has delivered 50% of the total lectures. Second preference shall

124
be Associate/Assistant Professor who is involved in teaching of the class and posted there for one year.
Third preference shall be a recognized Professor of the subject.
External Examiner
He/she shall be a Professor/Associate Professor of a recognized Medical/Dental College or at least an
Assistant Professor with three years teaching experience in the relevant subject.
Conflict of Interest
No person shall serve as an examiner whose close relative (wife, husband, son, daughter, adopted son,
adopted daughter, grand-son, grand-daughter, brother, sister, niece /nephew, son and daughter- in-law
brother and sister- in-law, parental and maternal uncle and aunt etc) is appearing in the examination.
All examiners likely to serve as an examiner shall render a certificate in compliance to this para.
Paper Setting
a. Each College / Institute shall forward a set of two question papers as per TOS along with
the key for each subject to the Controller of Examinations, at least three months in advance
of the annual examination. The question paper as a whole / a question without a
comprehensive key shall not be considered towards final paper setting.
b. The set of question papers shall be prepared by the respective Head of Department (HoD)
and furnished to Controller of Examinations through Head of Institution (HoI)
c. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the final paper setting having
fair representation of each college / institute.
Paper Assessment
a. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the theory paper marking, to
be undertaken in the manner as deemed appropriate.
b. The Examination Directorate shall coordinate directly with the faculty, earmarked for the
paper marking
c. A student who scores 85% and above marks in any subject shall qualify for distinction in
that particular subject.
d. A fraction in aggregate marks of a subject shall be rounded off to whole number. If it is
less than 0.5 then it will be rounded off to the previous whole number while 0.5 or more
will be rounded off to the next whole number.
Practical / Clinical Examinations
a. The Controller of Examiners shall approve the faculty to serve as the internal & external
examiners.
b. The number of external and internal examiners shall be equal.
c. One external & internal examiner each shall be marked for a group of 100 students.
d. Candidates may be divided into groups in the clinical and practical examinations and be
standardized by incorporating clinical exam
e. Practical/clinical examination shall be held after the theory examination of the subject
but in special cases, it may be held before the theory examination with the approval of the
Controller of Examinations. For the purpose of practical/clinical examination, the
candidates may be divided into sub groups by the examiners.
f. The assessment of the practical / clinical examination duly signed by internal & external
examiner shall be furnished to the Controller of Examinations within one week of the
conclusion of examination

125

126
Pass Marks
a. Pass marks for all subjects less Islamic / Pakistan Studies, shall be 50 % in theory and
practical, separately.
b. Pass marks for Islamic / Pakistan Studies shall be 33 % which, however shall not be counted
towards final scoring of the professional examination.
c. No grace marks shall be allowed to any student in any examination.
Declaration of Result.
Every effort shall be made to declare the result of each examination within one month of the last
practical examination or earlier.
Promotion.
No student shall be promoted to the higher classes unless he/she passes all the subjects of the previous
class
Re-Totaling.
Any student may apply to the Controller of Examinations on a prescribed form along with the
specified fee.
Supplementary Examination.
The interval between a supplementary examination and the previous professional examination
shall not be more than two months. There shall be no special supplementary examination.

127
SEQ SAMPLE
A 28 years old female presented in outpatient department with 3 days history of fever, haemoptysis and left
sided pleuritic chest pain. Examination revealed dull percussion and inspiratory crackles in left mid chest.
Her TLC is 14300 per ml.
a) What is the diagnosis? 1.5
b) How will you investigate this patient? 02
c) How will you manage this patient 03
MCQ SAMPLE
A 55-year-old female came to hospital with fever, pain abdomen, reversal of sleep cycle, drowsiness
and abdominal distension of 10 days. She was operated 30 years ago for perforated duodenal ulcer and
was transfused 3 units of blood at a local private hospital. She was febrile, drowsy and having ascites,
splenomegaly and generalized abdominal tenderness. What is the diagnosis?
a) Perforated duodenal ulcer
b) Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
c) Acute hepatitis
d) Acute Pancreatitis

128
INTRODUCTION TO GENERAL SURGERY
INTRODUCTION:
General surgery is the science and art of treating injury, deformity, and disease using operative
procedures. General surgery is frequently performed to alleviate suffering when this is unlikely through
medication alone. Surgical operative procedures may range from minor procedures performed in a
physician's office, to more complicated operations requiring a medical team in a hospital setting. The
BDS undergraduate students learn General Surgery during third year of the program and are evaluated
in the Third Professional BDS Examination.
Teaching and Learning Strategies
Multiple educational methods will be used comprising of self-study, interactive lectures, group
discussions, practical, and manual dexterity skill sessions.
(i) Methods for achieving cognitive objectives
• Interactive lectures using audio visual aids on power point presentation
• Group discussions in form of large group and small group
• Hands on demonstrations
• Tutorials
• Journal club
• Collaborative learning
• Self-study and reading from learning resources
(ii) Methods for achieving psychomotor objectives
• Diagnosis and treatment planning
• Patient handling

129
• Clinical skills
(iii) Methods for achieving affective objectives
• Interaction with peers, group members, teachers, support staff etc.
• Group discussions (small and large)
• Oral presentations by students
• Case presentation
Learning Methodologies
The following teaching / learning methods are used to promote better understanding:
• Interactive Lectures
• Hospital / Clinic visits
• Small Group Discussion
• Case- Based Learning
• Clinical rotations (CR)
• Skills session
• E- Learning
• Self- Directed Study
INTERACTIVE LECTURES
In large group, the lecturer introduces a topic or common clinical conditions and explains the underlying
phenomena through questions, pictures, videos of patients, interviews, exercise etc. students are actively
involved in the learning process.
HOSPITAL VISITS:
In small groups, students observe patients with signs and symptoms in hospital or clinical settings. This
helps students to relate knowledge of basic and clinical science of the relevant module.
SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION (SGD)
This format helps students to clarify concepts acquire skills or attitudes. Sessions are structured with
the help of specific exercise such as patient case, interviews or discussion topics. Students exchange
opinions and apply knowledge gained from lectures, tutorials and self-study. The facilitator role is to
ask probing questions, summarize, or rephrase to help clarify concepts.
CASE- BASED LEARNING
A small group discussion format where learning is focused around a series of questions based on a
clinical scenario. Students’ discuss and answer the questions applying relevant knowledge gained in
clinical and basic health sciences during the module.

130
Clinical Rotations (CR)
Clinical rotations for clinical subjects like Operative Dentistry, Orthodontics, Prosthodontics and Oral
Surgery are scheduled for student learning.
SKILLS SESSION
Skills relevant to respective module are observed and practiced where applicable in skills laboratory or
Department of Physiotherapy.
SELF DIRECTED STUDY
Students’ assume responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing
with peer, seeking information from Learning Resource center, teachers and resource persons within
and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hours of self- study.
E- LEARNING
E-Learning is a strategy by which learning occurs through the utilization of electronic media, typically
the Internet. The basic aspects of medical professionalism and ethics will be addressed through and E-
Learning course.

131
Curriculum Implementation
Curriculum implementation refers to putting into practice the official document including course
content, objectives, learning and teaching strategies. Implementation process helps the learner to
achieve knowledge, skills and attitudes required of the learning tasks. Learners are a pertinent
component of the implementation process. Implementation occurs when the learner achieves the
intended learning experiences, knowledge, ideas, skills and attitudes which are aimed to make the
learner an effective part of the society. Curriculum implementation also refers to the stage at which
curriculum is put into effect. There has to be an implementing agent as well. Teacher is an important
part of this process and implementation of the curriculum is the way the teacher selects and utilizes
various components of the curriculum. Implementation occurs when the teacher’s formulated course
content, teacher’s personality and teaching and learning environment interact with the learners.
Therefore, curriculum implementation is how the officially planned course of study is translated and
reflected by the teacher into schemes of work, lesson plans, syllabus and resources are effectively
transferred to the learners. Curriculum implementation can be affected by certain factors such as
teachers, learners, learning environment, resource materials and facilities, culture and ideology,
instructional supervision and assessments.
Personnel involved in teaching and facilitation
Curriculum delivery by: Dr. Muhammad Imran Hameed Daula (Professor of Surgery)
Dr. Fahim Anwer Rao (Associate Professor of Surgery)
Dr. Brig. (R) Anwaar-ul-Haq, (Professor of ENT)
Time frame
Course duration: 36 weeks
Lectures: Monday: (1050 to 1150 hours)
Wednesday: (1200 to 1500 hours)
Clinical teaching / visits: Monday: (1200 to 1500 hours)
Wednesday: (1200 to 1500 hours)
Self-study: 6 hours per week
OVERVIEW OF GENERAL SURGERY CURRICULUM
AIM OF THE BDS GENERAL SURGERY COURSE:

132
This program aims to ensure that the dental graduates will make the bio-psycho-social care of surgical
patients their first concern by applying their knowledge and skills in a competent and ethical manner
and using their ability to provide leadership to analyze complex and uncertain situations.
GENERAL OUTCOMES OF THE BDS GENERAL SURGERY COURSE:
The General outcomes of this course are:
1. Development of the graduate as a scholar and a scientist;
2. Development of the graduate as a practitioner; and
3. Development of the graduate as a professional.
SPECIFIC OUTCOMES OF THE BDS GENERAL SURGERY COURSE:
At the completion of this course the BDS graduate will be able to:
1. Apply biomedical scientific principles, method and knowledge to clinical practice.
2. Apply the principles, method and knowledge of population health and the improvement of health and healthcare to clinical practice.
3. Apply scientific method and approaches to medical research.
4. Carry out a consultation with a surgical patient.
5. Diagnose and suggest management of common General Surgical conditions relevant to Dental practice.
6. Communicate effectively with patients and colleagues in a medical context.
7. Provide immediate care in surgical emergencies relevant to Dental practice. 8. Prescribe drugs safely, effectively and economically.
9. Carry out common practical procedures involved in general care of surgical patients
safely and effectively. 10. Use information effectively in a medical context.
11. Behave according to ethical and legal principles.
12. Reflect, learn and teach others.
13. Learn and work effectively within a multi-professional team. 14. Protect patients and improve care.

133
GENERAL SURGERY COURSE ORGANISATION
PMDC Course minimum requirements
200 teaching hours (50 Theory, 150 Clinical)
Proposed Course Duration 30 weeks minimum (excluding scheduled holidays)
Course Components 1. Theory component
2. Clinical component
Theory Component sub-
divided into fiveNon-
integrated modules (Details as per ANNEX-
A)
1. Principles of Surgery (Surgical Physiology, Pathophysiology,
Infection Control, Pre and Post-Operative Care of the Surgical
patient) 2. Trauma and its management
3. Common Surgical disorders relevant to Dental practice
4. Anesthesia and its Risks 5. Ethics and Professionalism in Clinical practice
Mode of Information
Transfer (MIT) for
Theory Component
1. Minimum of 02 lectures OR 02 Small Group Discussions of
one-hour duration per week (Minimum 02 hours / week)
2. Student presentations
Clinical Component
(Details as per ANNEX-B, C and D)
1. Learning of Clinical Skills (ANNEX-B) at the bedside or in
the clinical skills laboratory 2. Learning of Clinical Skills (ANNEX-C) through workshops
3. Observation of surgical procedures (ANNEX-D) in the
operating room, emergency department and surgical ward. A
log book should be maintained for skills and procedures mentioned in ANNEX-D
Mode of Information
Transfer (MIT) for Clinical Component
Minimum of 02 Clinical sessions based in General Surgery ward /
Clinical Skills laboratory per week. Each session should be at least of 02 hours and 30 minutes duration (Minimum 05 hours / week)
Assessment Plan of
Theory Component
1. Written assessment at the end of each module comprising 50
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) 2. Midterm Examination at the end of Module 2 (replacing the
end of Module 2 written assessment). Details as per ANNEX-
C 3. Final Term Examination at least four weeks prior to
University Professional Examination. Details as per ANNEX-
D
4. A total of 05 written assessments for the theory component are to be carried out during each academic year
Assessment Plan of
Clinical Component
1. Two OSPE / Clinical Examination of Short Cases clinical
assessments to be conducted during clinical teaching sessions over an academic year in addition to Clinical assessments
carried out during Mid and Final Term examinations

134
2. OSPE / Clinical Examination of Short Cases as part of Midterm and End Term Examinations. Details as per
ANNEX-C and D
3. A total of 04 OSPE / Clinical Examination for the clinical
component are to be carried out during each academic year
Feedback to Students 1. Regular FORMATIVE Student Feedback & Counseling
Sessions (SFCS) to be conducted after each Theory / Clinical
component assessment
2. Specific FORMATIVE Student Feedback & Counseling Sessions (SFCS) to be arranged by the Head of Department
(HoD) as and when required during the academic year
Internal Assessment 1. 10 marks will be allocated for Internal Assessment 2. Marks obtained by a student in ALL the Theory and Clinical
assessments during the academic year will be totaled and
divided by the grand total of all the assessments. The
percentage of the final figure from 10 will be awarded as internal assessment
3. If a student has been exempted from an assessment (Theory or
Clinical) the result of the same will NOT be included while calculating internal assessment
4. If a student is absent from an assessment (Theory or Clinical)
he / she will be awarded zero marks for the same while calculating internal assessment
Pre requisite to Course
delivery
1. The HoD will ensure that ‘Learning Outcomes’ (LOs) are
developed for each of the topics included in the Theory and
Clinical Module. These LOs will be taken into account while developing assessments
2. The HoD will ensure that the type and frequency of MITs for
each of the topics included in the Theory and Clinical Module are decided
Course Evaluation and
Improvement Cycle
3. HoD will convene a meeting of the faculty at the end of each
module, clinical rotation and the complete course
4. Faculty will provide informal feedback for each of the above mentioned periods
5. Students will provide formal feedback in written form for
each of the above mentioned periods 6. The meeting will review the course delivery and its progress
and identify areas of weakness along with recommendations
to bring improvements. These will be authorized by the HoD
7. Minutes of all such meetings will be recorded 8. Issues relating to course delivery and administration may be
addressed based on the recommendations of the HoD on as
and when required basis 9. A final course evaluation meeting will be conducted at the end
of each academic session
Recommended books and
resources
1. Bailey and Love’s Sort Practice of Surgery – 26th edition
2. An Introduction to the Symptoms & Signs of Surgical Disease by Norman S Browse
3. A Manual on Clinical Surgery by S. DAS
4. Clinical Methods in General Surgery by Hamilton & Bailey

135
GENERAL SURGERY CURRICULUM ANNEXURES
ANNEX-A: TOPICAL DETAILS OF THEORY COMPONENT MODULES
S NO TOPIC
MODULE 1: PRINCIPLES OF SURGERY
1. Body’s response to trauma and stress
2. Shock, Pathology, Types and management
3. Wound Healing & its complications
4. Types of Wound closure
5. Wound Infection / Surgical Site Infection
6. Cross infection control in the clinical environment
7. Blood transfusion in surgical patients
8. Colloids and Crystalloids used in surgical patients
9. Common fluid & electrolyte disorders in surgical patients
10. Common acid base disorders in surgical patients
11. Nutritional management of surgical patients
12. Risk assessment in surgery
13. Pre-operative preparation of Surgical patients
14. Post-operative care of Surgical patients
15. Principles of Minimal Access Surgery
16. Application of invasive and non-invasive diagnostic modalities in surgical practice
MODULE 2: TRAUMA AND ITS MANAGEMENT
17. Trauma Management based on ATLS protocol
18. Head injury
19. Cervical spine injury
20. Maxillofacial trauma
21. Neck trauma
22. Chest trauma and its management, Thoracotomy / Use of Chest drains
23. Hemorrhage its types and management
24. Burns
MODULE 3: COMMON SURGICAL DISORDERS RELEVANT TO DENTAL PRACTICE
25. Benign disorders of the Thyroid gland
26. Malignancies of Thyroid gland
27. Thyroidectomy & its complications
28. Disorders of the Parathyroid gland and their surgical management

136
29. Differential diagnosis & diagnostic approach to neck swellings
30. Cervical lymphadenopathy
31. Neck dissections& its types
32. Oral cancer and precancerous conditions (Carcinoma tongue and lip)
33. Skin malignancies (Squamous and Basal celled carcinoma, Malignant Melanoma)
34. Carcinoma Larynx
35. Tracheostomy, indications, care and complications
36. Benign and Malignant disorders of the Salivary glands
37. Benign disorders of the Oesophagus / Dysphagia
38. Malignant disorders of the Oesophagus / Oesophagectomy
39. Skin grafts, flaps, basics of reconstructive surgery
40. Surgical drains (NG tube, Foley catheter, Chest drain)
41. Principles of Surgical anastomosis
42. Cellulitis, Carbuncle, Abscess
43. Tetanus, Gas gangrene, Necrotizing fasciitis
44. Parasitic infections – Surgical aspects of Amoebiasis and Hydatid disease
45. General introduction to fractures, their healing and complications
46. Osteomyelitis
47. Common benign skin swellings (Lipoma, Epidermoid and Dermoid cysts)
48. Cleft lip and palate
49. Surgical biopsy and its types
MODULE 4: ANESTHESIA AND ITS RISKS
50. General anesthesia and its complications
51. Regional anesthesia (Spinal and Epidural anesthesia) and its complications
52. Local anesthesia and its complications
MODULE 5: ETHICS AND PROFESSIONALISM IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
53. Introduction to Clinical Ethics and Professionalism
54. Maintaining Quality of care
55. Evidence Based Medicine
56. Patient safety in the clinical environment
57. Professionalism in clinical practice
58. Maintaining ethics and professionalism in Clinical research
59. Occupational hazards in the clinical environment

137
ANNEX-B: TOPICAL DETAILS OF CLINICAL SKILLS TO BE LEARNED AT THE
BEDSIDE OR IN THE CLINICAL SKILLS LABORATORY
S NO TOPIC
1. Clinical history taking
2. General physical examination of a patient
3. Systemic physical examination of a patient with special emphasis on chest examination
4. Formulating a diagnosis and treatment plan for a patient
5. Clinical examination of a swelling
6. Clinical examination of an ulcer
7. Clinical examination of a patient with cervical lymphadenopathy
8. Clinical examination of a parotid swelling
9. Clinical examination of a submandibular gland swelling
10. Clinical examination of facial and trigeminal cranial nerve lesions
11. Clinical examination of a patient with oral lesion suspected to be malignant
12. Clinical examination of a goiter
13. Examination of a branchial cyst / fistula, thyroglossal cyst, cystic hygroma
14.
Identification and uses of:
a. Common surgical instruments
b. Chest drain with under water seal. c. Common drains (NG tube, foley catheter)
d. Commonly used surgical sutures
e. Commonly used intravenous cannulas, central venous catheters, LP needles, intra-venous fluids
f. Instruments used for airway management (guedel’s airway,
endotracheal tube, cricothyroidotomy / tracheostomy tube.
g. Diathermy machine h. General anesthesia apparatus
15. Identification of radiologic anatomy in a normal Chest X ray
16.
Identification of following pathologies on X ray:
a. Pleural effusion. b. Pneumothorax
c. Cervical spine injury
17. Identification of typical presentations of extra-dural, sub-dural intracranial hematomas
and sub-arachnoid hemorrhage on CT scan
18. Introduction to protocols of operation theatre, ward work, patient clerking and out-
patient clinics

138
ANNEX-C: TOPICAL DETAILS OF CLINICAL SKILLS TO BE LEARNED THROUGH
WORKSHOPS
S NO TOPIC
1. Intravenous access
2. Introduction to basic surgical skills
3. Antisepsis, cross infection control and gowning up in the operating room
4. Primary Trauma Care based on the ATLS protocol
5. Clinical communication (Role modeling) with special emphasis on counseling and
taking written informed consent

139
ANNEX-D: TOPICAL DETAILS OF CLINICAL SKILLS AND SURGICAL
PROCEDURES TO BE OBSERVED (O) OR PERFORMED (P) IN THE OPERATING
ROOM (OR), EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT AND SURGICAL WARD (LOG BOOK TO
BE MAINTAINED FOR THESE SKILLS / PROCEDURES)
S NO TOPIC
1. Collection of samples of blood, urine, sputum, pus swab (P)
2. Administration of drugs by intramuscular and intravenous routes (P)
3. Wound care and dressings (P)
4. Skin suturing and suture removal (P)
5. Needle biopsies, aspiration of localized fluids (P)
6. Pre-operative preparations, sterilization, and disinfection techniques in the OR (O)
7. Incision and drainage of an abscess (O)
8. Excision of soft tissue lumps (O)
9. Thyroidectomy (O)
10. Excision of a major salivary gland (Parotidectomy, sub-mandibular excision) (O)
11. Application of skin graft (O)
12. Administration of General anesthesia (O)
13. Administration of Spinal and Epidural anesthesia (O)
14. Application of POP cast to a long bone fracture (O)
KEY FOR COMPETENCY LEVEL OF PROCEDURES TO BE PERFORMED (TO BE
MENTIONED IN LOG BOOK):
1- Observer Status
2- Assistant
3- Performed under supervision
4- Performed under indirect supervision
5- Performed independently

140
OTHER LEARNING RESOURCES
Hands- on Activities / Practical
Students will be involved in Practical sessions and hands-on activities that
link with the blood module to enhance the learning
Labs
Utilize the lab provides the simulated learning to the specimens and models
available.
Skills Lab
A skills lab provides the simulated learning experience to learn the basic
skills and procedures. This helps patients
Videos
Video familiarize the student with the procedures and protocols to assist
patients
Computer
Lab/CSs/DVDs/ Internet
Resources:
To increase the knowledge, students should utilize the available internet
resources and CDs / DVDs. This will be an additional advantage to increase
learning.
Self Directed Learning
Self Directed Learning is scheduled to search for information to solve cases,
read through different resources and discuss among the peers and with the
faculty to clarify the concepts.

141
Summative assessment methods and policies:
Internal Assessment
a. Weightage of internal assessment shall be 10 %, each for theory and practical, in BDS
Professional Examination.
b. The Internal Assessment shall comprise of monthly test / PBL / assignments / Clinical tests /
clinical viva etc.
c. The Internal Assessment record shall be kept in the respective department of the College /
Institute and after approval of Principal, a summary as per University registration number shall
be furnished to the Controller of Examinations, at least two weeks before the commencement
of final examination.
d. The result of all the class tests / tools which contribute towards IA will be displayed to the
students during an academic year.
e. The same internal assessment shall be counted both for annual and supplementary
examinations. The students who are relegated, however, can improve the internal assessment
during subsequent year
f. Internal assessment tools of any subject may be changed after the approval of
respective FBS
Annual Examination
a. The weightage of Annual Examination shall be 90%, each for theory and practical, in BDS.
b. The examination comprises of a theory paper and practical/clinical examinations as per
PM&DC regulations and the Table of Specifications (TOS) of the University.
c. The gap between two consecutive theory papers shall not be more than two days.
d. The Theory Paper shall be of 3-hours duration, held under the arrangements of the university.
It shall have two parts; MCQs (30%) and SAQs/SEQs (70 %) for the year 2019. It may be
changed after the approval of Academic Council.
e. Allocated time for MCQs for 2019 shall be as under:
i. 25 MCQs - 30 Minutes
ii. 30 MCQs - 40 Minutes
iii. 40 MCQs - 50 Minutes
iv. 45 MCQs - 60 Minutes
f. Each MCQs shall have four distractors
Internal Examiner
He/she shall be Professor and Head of Department who has been involved in teaching of the class being
examined for at least six months and has delivered 50% of the total lectures. Second preference shall
be Associate/Assistant Professor who is involved in teaching of the class and posted there for one year.
Third preference shall be a recognized Professor of the subject.
External Examiner
He/she shall be a Professor/Associate Professor of a recognized Medical/Dental College or at least an
Assistant Professor with three years teaching experience in the relevant subject.
Conflict of Interest

142
No person shall serve as an examiner whose close relative (wife, husband, son, daughter, adopted son,
adopted daughter, grand-son, grand-daughter, brother, sister, niece /nephew, son and daughter- in-law
brother and sister- in-law, parental and maternal uncle and aunt etc) is appearing in the examination.
All examiners likely to serve as an examiner shall render a certificate in compliance to this para.
Paper Setting
a. Each College / Institute shall forward a set of two question papers as per TOS along with
the key for each subject to the Controller of Examinations, at least three months in advance
of the annual examination. The question paper as a whole / a question without a
comprehensive key shall not be considered towards final paper setting.
b. The set of question papers shall be prepared by the respective Head of Department (HoD)
and furnished to Controller of Examinations through Head of Institution (HoI)
c. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the final paper setting having
fair representation of each college / institute.
Paper Assessment
a. The Controller of Examinations shall approve the faculty for the theory paper marking, to
be undertaken in the manner as deemed appropriate.
b. The Examination Directorate shall coordinate directly with the faculty, earmarked for the
paper marking
c. A student who scores 85% and above marks in any subject shall qualify for distinction in
that particular subject.
d. A fraction in aggregate marks of a subject shall be rounded off to whole number. If it is
less than 0.5 then it will be rounded off to the previous whole number while 0.5 or more
will be rounded off to the next whole number.
Practical / Clinical Examinations
a. The Controller of Examiners shall approve the faculty to serve as the internal & external
examiners.
b. The number of external and internal examiners shall be equal.
c. One external & internal examiner each shall be marked for a group of 100 students.
d. Candidates may be divided into groups in the clinical and practical examinations and be
standardized by incorporating clinical exam
e. Practical/clinical examination shall be held after the theory examination of the subject
but in special cases, it may be held before the theory examination with the approval of the
Controller of Examinations. For the purpose of practical/clinical examination, the
candidates may be divided into sub groups by the examiners.
f. The assessment of the practical / clinical examination duly signed by internal & external
examiner shall be furnished to the Controller of Examinations within one week of the
conclusion of examination
Pass Marks
a. Pass marks for all subjects less Islamic / Pakistan Studies, shall be 50 % in theory and
practical, separately.
b. Pass marks for Islamic / Pakistan Studies shall be 33 % which, however shall not be counted
towards final scoring of the professional examination.
c. No grace marks shall be allowed to any student in any examination.

143
Declaration of Result.
Every effort shall be made to declare the result of each examination within one month of the last
practical examination or earlier.
Promotion.
No student shall be promoted to the higher classes unless he/she passes all the subjects of the previous
class
Re-Totaling.
Any student may apply to the Controller of Examinations on a prescribed form along with the
specified fee.
Supplementary Examination.
The interval between a supplementary examination and the previous professional examination shall
not be more than two months. There shall be no special supplementary examination.

144
Table of Specification (TOS) for Third Professional
BDS Examination
General Surgery
Table of Specifications for Annual Professional Examination: Theory
Marks of Written Paper = 90 Time Allowed = 03 hrs
Marks of Int. Asses = 10 (Including MCQs)
Max Marks = 100 Date: _____________
Pass Marks = 50
Part A
45 x MCQs (on separate sheet) (Time = 55 min) (45 Marks)
Part B
Q. No. 1 PBQ (05 Marks)
Q. No. 2 PBQ (05 Marks)
Q. No. 3,4,5,6,7,8,9 SAQ (05 Marks Each)
TOPIC MCQs PBQ/SAQ
Principles of surgery 9 2
Trauma and its management 9 2
Common Surgical Disorders
Relevant To Dental Practice 9 2
Anesthesia And Its Risks 9 2
Ethics And Professionalism In
Clinical Practice 9 1
Total 45 (45 Marks) 09 (05 Marks Each)

145
Internal Assessment calculation (Theory Annual)
Table of Specifications for Annual Professional Exam: Practical
VIVA
50 marks PRACTICAL TOTAL
Examiner 1 Examiner 2 OSCE
10 stations of
3 marks each
Short Case 1 Short Case 2
15 15 30 15 15 90
Internal Assessment calculation (Practical)
A B C D F
Roll No. Name Periodical/
Clinical exam
Pre-annual
exams
90 marks
Total Marks
E= D x05/90 C+E
Out of 05 Out of 05 10 Marks
Award List for Professional Examination
S/N Roll
No.
Name Theory IA Total Practical IA Total
Grand
Total
Remarks
(90) (10) (100) (90) (10) (100) (200) Pass/Fail
A B C E H
Roll No. Name Total Marks obtained in 2
terms exams
(1+2)=(50+50)
Pre-annual
exams
90 marks
Total
Marks of internal
Assessment out of 10
D+F
D= (C x 05)/ 100 F= E x05/90
Out of 05 Out of 05 Out of 10