Immune system Chapter 43. Figure 43.1 Pathogen: Infectious agent Innate immunity: Nonspecific All...
-
Upload
junior-copeland -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
1
Transcript of Immune system Chapter 43. Figure 43.1 Pathogen: Infectious agent Innate immunity: Nonspecific All...
Pathogen:Infectious agentInnate immunity:NonspecificAll animalsAcquired immunity:Specific Previous exposure
Acquired Immunity
ActiveDiseaseVaccineTransfer of lymphocytes from a donor (bone marrow transplant)PassiveMaternal antibodiesImmunoglobulins (gamma globulins)
Defense
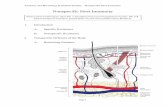
First line– Skin
Second line– Cell counterattack
Third line – Immune response (antibodies)– Specific
First-line
Skin1. Impenetrable barrier2. Oil & sweat glandsSkin pH--3-5 3. Sweat contains lysozymeEnzyme digests bacterial walls4. Prevents water loss
First line
Lysozyme in salivaStomach acid Digestive enzymes in gutAirway mucousCilia in airways Acidic urine
Second line
InvadersLymphatic systemDefense cells Adenoids, tonsils Thymus, spleenLymph nodes, lymph capillaries & ducts
Thymus
Peyer’spatches(in smallintestine)Appendix(cecum)
Lymphnodes
Spleen
Lymphaticvessels
TonsilsAdenoid
Tissuecells
LymphaticvesselLymphaticvessel
Lymphnode
Masses ofdefensive cells
Bloodcapillary
Interstitial fluid
Second line
Leukocytes (WBC)Circulating in body1. Macrophages (monocytes)Kill invaders by ingesting them PhagocytosisIngestion
Second line
2. NeutrophilsMost abundant WBC PhagocytosisRelease chemicals--kill bacteriaAlso kills other neutrophils
Second line
Antimicrobial proteins1. Complement systemProteins found in plasmaAttack bacterial or fungal cell wallsCause cells lysisSignals other defense responses
Second line
2.InterferonsParacrine polypeptideProtect cells in area of virusPrevent viral replicationCancer defense
Second line
Inflammatory responseLocal, non-specificHistamines & prostaglandinsVasodilationIncreased blood flow to area Edema or swellingWBC (phagocytic), pus formationShock, systemic
Second line
Inflammatory responseElevated temperature (fever)Interleukin-1 Released by MacrophagesDirects hypothalamus to increase tempHelps stimulate defense response
Third line
Specific responseLymphocytesT-cells---cellular responseB-cell---humoral responseAntibodies
Third line
Antigen Foreign moleculeEpitopeAntigen determinantLocated on surfaceCauses a specific immune response
Third line
Self-versus-nonself recognitionGenes code for specific proteins Major Histocompatibility Complex proteinsMHC proteinsCell recognitionGlycoproteins on surface of cells
Third line
B-cell lymphocytesMade & develops in bone marrowBecomes a plasma cellProduce antibodies in response to specific antigensImmunoglobulins (Ig)AntibodiesHumoral immunity
Third line
Light chains2 short polypeptidesHeavy chains2 identical long polypeptides 4 chains held together by disulfide bondForms Y-shaped molecules
Fig. 43-9a
Antigen-bindingsite
Antigen-binding site
Disulfidebridge
Variableregions
Constantregions
Transmembraneregion
Plasmamembrane
Lightchain
Heavy chains
Cytoplasm of B cell
(a) B cell receptor
B cell
V
V
C C
V
V
C C
Fig. 43-10
Antigen-binding sites
Antigen-bindingsites
Epitopes(antigenicdeterminants)
Antigen
Antibody B
Antibody CAntibody A
CC
CV
V
V
V
C
Antibodies
Plasma cells release antigen receptorSpecific for antigensArms of the Y shaped moleculeHave different aa sequences
Antibodies
IgM first responseAggregation of complement proteinsIgG major form, second responseStimulates phagocytosis by macrophagesIgD receptors for antigens on B cellsIgAPresent in breast milk, mucous, salivaProvide protection to newborns
Antibodies
IgERelease histaminesBind to mast cellsInsert heavy chain into mast cellsInitiate inflammatory responsePresence of antigensVasodilation
Third line
T-cell lymphocytesMade in bone marrowProcessed in thymus glandRegulate immune responsesAttack cells with specific antigensCell-mediated immunity
Fig. 43-9b
Antigen-bindingsite
Variableregions
Constantregions
Transmembraneregion
Plasmamembrane
T cell
chain chain
Disulfide bridge
Cytoplasm of T cell
(b) T cell receptor
C C
VV
Third line
T-cells1. Helper T cells (CD4)Initiate response based on antigens2. Memory T cellsRemember previous antigens
Third line
3. Cytotoxic T cell (CD8)Lyse cells infected by virus4. Suppressor T cellsTurn off immune response
Third line response
AntigenMacrophage process antigenSecrete cytokines (interleukins or interferons)Stimulates T helper cells
Third line response
Recognize antigensAntigen receptor on T-cells Bind to antigensTriggers T-cytotoxic cells, T-memory cellsCytotoxic cells destroy infected cellsStimulates B cells
Third line response
Antigen receptor on B-cellBinds foreign antigenTriggers formation of a clone of plasma cellsClones produce antibodiesAntibodies bind invading antigen Prevent affects of antigenDestruction or blocks effect
Immune response Macrophage
⇓ Helper T-cell
⇙ ⇘ B-cell Cytotoxic T-cell ⇙ ⇘ ⇙ ⇘Plasma Memory Memory Cytotoxic cells cells cells T-cells ⇓Antibodies
T-cells
Cytotoxic T-cellsAttack transplants (skin grafts) Considered foreign tissueDestroy cancer cellsInterferon (lymphomas, renal Ca, melanoma, Kaposi’s sarcoma and Breast Ca)Interleukin (tx cancer)
B-cells
Primary immune responseFirst exposureLasts about 2 weeksMemory cells are also produced during the first exposureSecondary immune responseActivates memory cellsResponse faster & lasts longer
Immune System Summary
First lineSkin, cilia, enzymes, pH of skinSecond lineWBC (macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells, eosinophils)Antimicrobial proteinsInflammatory response
Immune System Summary
Third lineLymphocytes (B & T)Antibodies (immunoglobulins)IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, IgD
Monoclonal antibodies
Antibodies specific for one antigenCell cultures produce large quantitiesUse in lab testsPregnancy testsAntibody to HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virusAttacks + destroys CD4+ T-cellsT-cells secrete a suppressing factor Blocks other T-cellsInfects macrophages & brain cells
Allergy
Allergens (antigens)Release IgEBinds mast cells & basophilsStimulates release of chemicals HistamineDrop in BP
Allergy
Anaphylactic shockWidespread histamine responseDeathBee stings or peanuts or penicillinContact dermatitis Delayed responsePoison ivy, poison oak
Blood types (ABO)
Blood type
Surfaceantigens
Antibodies
A A anti B
B B
anti A
AB AB none
O none anti A & B