Power Plate Training Increases Strength and Muscle Mass in ...
Illinois State University Metabolic Adaptations to Training Chapter 5 u Aerobic training: –...
-
Upload
clara-gray -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Illinois State University Metabolic Adaptations to Training Chapter 5 u Aerobic training: –...

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Metabolic Adaptations to TrainingChapter 5
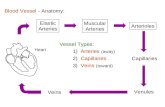
Aerobic training:Aerobic training:– increases increases numbernumber of capillaries of capillaries per per muscle muscle
fiberfiber – increasesincreases and the and the numbernumber of capillaries for a of capillaries for a
given given cross-sectional area cross-sectional area of muscle of muscle Both of these changes improve blood Both of these changes improve blood
perfusion in the muscles.perfusion in the muscles.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Fiber Types
Type I Type I – ST – Red – Aerobic – Fatigue – ST – Red – Aerobic – Fatigue Resistant – Few Fibers per Motor UnitResistant – Few Fibers per Motor Unit
Type IIa Type IIa – FTO – Pink – Anaerobic – FTO – Pink – Anaerobic w/aerobic capabilityw/aerobic capability
Type IIb – FTG – White – Purely Type IIb – FTG – White – Purely Anaerbobic - Multiple Fibers per Motor Anaerbobic - Multiple Fibers per Motor
Unit – Power FibersUnit – Power Fibers

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Response and Adaptation
Endurance training Endurance training stresses stresses STST muscle muscle fibers more than FT fibers. fibers more than FT fibers.
Result - ST fibers enlarge with training.Result - ST fibers enlarge with training.
Hunters Hunters

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Response and Adaptation
PercentagesPercentages of ST and FT fibers of ST and FT fibers do not do not appear to change appear to change
Endurance training causes FtEndurance training causes Ftbb fibers to take fibers to take on more Fton more Ftaa characteristics. characteristics.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Response and Adaptation
Endurance training increases muscle Endurance training increases muscle myoglobinmyoglobin content by about 75% to 80% content by about 75% to 80%
Myoglobin stores oxygen.Myoglobin stores oxygen.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Response and Adaptation
Endurance training increases both the Endurance training increases both the number and the size of the number and the size of the mitochondriamitochondria..
Activities of many Activities of many oxidative enzymes oxidative enzymes are are increased with training.increased with training.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Response and Adaptation
These changes occurring in the muscles, These changes occurring in the muscles, combined with adaptations in the oxygen combined with adaptations in the oxygen transport system, lead to enhanced transport system, lead to enhanced functioning of the oxidative system and functioning of the oxidative system and improved endurance.improved endurance.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Fuel Storage
Endurance-trained muscle stores Endurance-trained muscle stores considerably more considerably more glycogenglycogen than does than does untrained muscle.untrained muscle.
Endurance-trained muscle also stores more Endurance-trained muscle also stores more fat fat (triglyceride) (triglyceride) than does untrained than does untrained muscle.muscle.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Fuel Storage
The activities of many enzymes involved in The activities of many enzymes involved in oxidation of fat oxidation of fat increase with training, increase with training, thus thus free fatty acid levels increasefree fatty acid levels increase. .
This leads to increased use of fat as an This leads to increased use of fat as an energy source, sparing glycogen.energy source, sparing glycogen.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Training
The ideal training regimen should have a The ideal training regimen should have a caloric expenditure of a minimum of 2,000 caloric expenditure of a minimum of 2,000 to a maximum of about 5,000 to 6,000 kcal to a maximum of about 5,000 to 6,000 kcal per week. per week.
There seems to be little benefit beyond this There seems to be little benefit beyond this level in consideration of the added risk of level in consideration of the added risk of injury.injury.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Training
IntensityIntensity is also a critical factor in is also a critical factor in improving performance. improving performance.
Adaptations are specific to the speed and Adaptations are specific to the speed and duration of training bouts, so those who duration of training bouts, so those who perform at higher intensities must train at perform at higher intensities must train at higher intensities.higher intensities.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Training
Aerobic Aerobic interval training interval training involves repeated involves repeated bouts of high-intensity performance bouts of high-intensity performance separated by brief rest periods.separated by brief rest periods.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Training
This training, although traditionally This training, although traditionally considered only anaerobic, generates considered only anaerobic, generates aerobic benefits because the rest period is aerobic benefits because the rest period is so brief that full recovery can’t occur, thus so brief that full recovery can’t occur, thus the aerobic system is stressed.the aerobic system is stressed.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Training
Continuous training Continuous training is done as one is done as one prolonged bout of exercise, some many prolonged bout of exercise, some many exercisers find it boring.exercisers find it boring.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Training
The aerobic benefits from both interval The aerobic benefits from both interval training and continuous high-intensity training and continuous high-intensity training seem to be about the same.training seem to be about the same.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Anaerobic Training
Anaerobic training bouts improve Anaerobic training bouts improve anaerobic anaerobic performanceperformance, but the improvement appears , but the improvement appears to result more from to result more from strength gains strength gains than from than from improvements in the functioning of the improvements in the functioning of the anaerobic energy systems.anaerobic energy systems.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Anaerobic Training
Anaerobic training also improves the Anaerobic training also improves the efficiency of movement, and more efficient efficiency of movement, and more efficient movement requires less energy expenditure.movement requires less energy expenditure.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Anaerobic Training
Although sprint-type exercise is anaerobic Although sprint-type exercise is anaerobic by nature, part of the energy used during by nature, part of the energy used during longer sprint bouts comes from oxidation, longer sprint bouts comes from oxidation, so muscle aerobic capacity can also be so muscle aerobic capacity can also be increased with this type of training.increased with this type of training.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Anaerobic Training
Muscle buffering capacity Muscle buffering capacity is increased by is increased by anaerobic training, allowing the anaerobic training, allowing the achievement of higher muscle and blood achievement of higher muscle and blood lactate levels. lactate levels.
This allows the HThis allows the H++ that dissociates from the that dissociates from the lactic acid to be neutralized, thus delaying lactic acid to be neutralized, thus delaying fatigue.fatigue.

Illinois State UniversityIllinois State University
Anaerobic Training
Changes in muscle enzyme activity are Changes in muscle enzyme activity are highly specific to the type of training.highly specific to the type of training.