IDD Elimination & Universal Salt Iodization Policy in Georgia Current Trends and Challenges
description
Transcript of IDD Elimination & Universal Salt Iodization Policy in Georgia Current Trends and Challenges

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD ELIMINATION IN GEORGIA
IDD Elimination & Universal Salt Iodization Policy in Georgia
Current Trends and Challenges
Ms. Mariam JashiAPO Health – UNICEF Georgia
Mr. Zurab SekhniashviliDirector, National Center for Nutrition
National Conference “Enhancing Partnership for IDD Elimination in Georgia”25-28 June 2004 - Tbilisi Georgia

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Iodine Deficiency in Georgia Traditional Concern
1745
First source describing Goiter problem - writings by Vakhushti Bagrationi
1921
Establishing Universal System for Combating Endemic Goiter - USSR
1935
Republican Dispensary for Goiter Prevention in Tbilisi, Adjara & Kutaisi
1939
Iodized Salt Manufacturing in Kutaisi supplying Racha-Letchkhumi, Imereti, Svaneti and other High-Land areas
1938-1944
Goiter prevalence in the High-Land regions reduced from 42.7% to 14%

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Lost Opportunity
1970s
IDD Virtually Eliminated in Georgia
1980s
Reducing efforts to sustain achievements - Illusion of IDD Liquidation
1990s
Social-Economic Crisis, Disruption of Iodized Salt Import & Distribution
Mid-1990s
Alarming Trend of IDD and Goiter Prevalence throughout the Country

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Samtskhe-Javakheti
Imereti
Adjara
Guria
Abkhazia
Samegrelo-Zemo SvanetiRacha-Lechkhumi & Kvemo Svaneti
Kvemo Kartli
Kakheti
Shida Kartli
Tbilisi
Mtskheta-Mtianeti
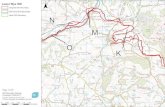
No Single District in Georgia Free of Goiter Age group >15 years old - 2003
Per cent
5.0 - 25.0
25.1 - 50.0
50.1 - 70.0
> 70.1
Missing Data

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Samtskhe-Javakheti
Imereti
Adjara
Guria
Abkhazia
Samegrelo-Zemo SvanetiRacha-Lechkhumi & Kvemo Svaneti
Kvemo Kartli
Kakheti
Shida Kartli
Tbilisi
Mtskheta-MtianetiPer cent
< 25.0
25.1 - 50.0
50.1 – 70.0
> 70.1
Missing Data
No Single District in Georgia Free of Goiter -

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
National Efforts to Combat IDD since 1990s
1996• Presidential Decrees on State IDD Programme & National Council on IDD
1997• VAT (20%) Exception Policy for Iodized Salt Import (0.15%) and Sale• Establishing district IDD committees in 71 administrative units
1998• State Standard for Iodized Salt • Special Coding for Import of Iodized Salt vs. Non-iodized• IDD Centres in Tbilisi, Kutaisi, Batumi, Telavi & Zugdidi• Lab & Ultrasound Equipment provided by UNICEF• Continuous Disease Surveillance and Database Formation

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
National Efforts to Combat IDD since 1990s
1997-2004
Free consultation provided to 500,000 patients
Medication (Levoxile) provided by ACTS Georgia for treatment of Goiter
2000-2001
Distribution of Iodized Oil Capsule to 300,000 children, pregnant & lactating women in 35 districts of 10 regions (UNICEF) - Emergency Interventions
1998-2001
Information-Communication Campaign (TV/Radio, Printed Materials)

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
National Efforts to Combat IDD since 1990s
2002
Presidential Decree overriding 1996 Decrees
Renewing membership of National Council
Drafting Law on Universal Salt Iodization
2003
Draft Law Submitted to Parliament - Banning Import of Non-iodized salt except for Industry, Medical Purposes & Re-Iodization

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Membership of National IDD Council
1996State Chancellery - Chair of NCIDD
Ministry of Health
Ministry of Food and Agriculture
Ministry of Justice
Ministry of Trade & Foreign Econ. Relations
Ministry of Education
Ministry of Economy
Ministry of Finance
State Customs Department
State Dept. for Standardization, Metrology
& Certification
2002State Chancellery - Chair of NCIDD
Ministry of Labour, Health & SA
Ministry of Food and Agriculture
Ministry of Justice
Ministry of Economy, Trade & Industry
Ministry of Education
Ministry of Finance
Ministry of Transport & Communication
State Dept. for Standardization,
Metrology & Certification
Ministry of Interior affairs
Ministry of State Security
Ministry of ENVR/Natural ResourcesRoles & Responsibilities too GeneralPrivate Sector not officially included

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Policy and Strategic Framework Guiding National Programmes
Government CommitmentWorld Summit For Children - 1990World Fit For Children - 2002Millennium Development Goals - 2000 National Health Policy & Strategy
What is the Goal? Sustainable Elimination of IDD by 2005Universal Salt Iodization (USI) by 2005All Salt for Human and Animal Consumption to be Iodized
What Indicators? Household Consumption of Iodized Salt >90%Goiter Prevalence < 5% of the populationAdequate Iodine Status - Urine Iodine Excretion > 100 mcg/dl

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
How to Verify Progress & What are Achievement?
Salt Situation Analysis in Georgia - 1999 & 2003
Household Survey on Consumption of Iodized Salt - 1999 & 2003
Iodine Status among Children - 2000-2002
Goiter Prevalence among Children and Adults - 1997-2002
Communication Assessment - 2003 John Hopkins University

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Progress and Status
Findings from
Salt Situation Analysis in Georgia
2003
Institute for Polling and Marketing

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Salt Import in TonsGeorgia 1999-2002
20175042
19041
32742
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
30000
35000
1999 2000 2001 2002
Non-iodizedIodizedIndustrial
Source: Salt Situation Analysis 2003 - IPM/UNICEF
Customs Data - 2002

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Key Findings from 2003 Salt Situation Analysis
2002 - Iodized Salt mainly imported from Ukraine (96%), also from Greece, Germany, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkey & Italy
Iodine content not tested at customs level – customs-clearance & registration based on manufacturer’s certificate or State Department of Standardization
Wholesale/Retail Quality Control – State Sanitary Inspection
No clear articulation of administrative regulations & sanctions for violating packaging, sorting, labeling, transportation & storage standards for iodized salt

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Key Findings from 2003 Salt Situation Analysis
Some violation of State Standards for Storage of Iodized Salt observed at various distribution points. Salt Expiry Dates almost always followed.
Quality Control systems at Import, Wholesale/Retail Sale needs refinement
Lab equipment for salt titration at State Sanitary Department outdated
Despite all efforts for legislative framework, no comprehensiveness achieved. Inadequacy of Legislative basis & endorsement;

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Communication on IDD/Iodized Salt
IEC campaigns in 1998-2001 - NCN, Public Health Department, UNICEF
No coordinated professional marketing & communication efforts taken.
Communication by salt importers not considered profitable given that salt import is no “Big Business”.
Communication efforts needed at all levels - decision makers, importers, distributors, Households

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Iodized Salt Prices Range 0.25 to 7.57 GEL
Price
Name of Salt Producer Min Max AverageRock Salt (“SOL’ Kamennaya”) “Artyomsol” 0.25 0.50 0.33Kalas Golden (500gr) Kalas Group 1.20 1.50 1.27Kalas Classic (400gr) Kalas Group 0.60 1.00 0.77Kalas Master (250gr) Kalas Group 0.55 0.80 0.64Kalas HPA (500 gr) Kalas Group 0.45 0.80 0.53Iodized Salt "S" Akzo Nobel Salz 3.65 3.65 3.65Picnic Salt (Dansk "S") Akzo Nobel Salz 3.10 3.10 3.10Salzina (Speise Salz, 1 kg) Akzo Nobel Salz 1.90 1.90 1.90Salzina (Speise Salz, 500 gr) Akzo Nobel Salz 1.00 1.00 1.00Salzina (Jod Salz) Akzo Nobel Salz 1.00 1.00 1.00Die Sparsamen (Speise-salz) Akzo Nobel Salz 1.00 1.00 1.00Die Sparsamen (Jodsalz) Akzo Nobel Salz 0.75 1.00 0.83Salina Iyotlu (Plastic bottle) Cihan-Kur A.S. 0.80 1.00 0.93Salina Iyotlu (Plastic bag) Cihan-Kur A.S. 0.60 0.80 0.68Sea Salt Droga 5.75 5.75 5.75Morska Sol Droga 5.60 5.60 5.60Alkyon Perla 0.50 0.50 0.50Unknown (in Iranian) N/A 0.30 0.30 0.30Salt Iran N/A 0.50 0.50 0.50Extra “Avanski Solekombinat” 0.60 0.70 0.65White Salt “Valetek Prodimpeks” 1.00 1.00 1.00Salt Iodized Extra “Enterprise MS” 1.00 1.50 1.25Salt Iodized JSC “Bassol” 2.50 2.50 2.50Salt extra “Monarkh” Ltd 2.50 2.50 2.50Marino Fino Spera and Company 1.00 1.00 1.00
Affordability issueis a
lesser concern

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Household Consumption of Iodized Salt >90%?
Findings from
Household Survey
2003
State Department for Statistics

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Availability of Iodized Salt at Household Level Georgia (except Abkhazia and South Ossetia)
1999 – 2003
77.2
30.4
8.1
67.5
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
%
0-15 ppm >= 15 ppm
1999
2003 field result/test kits
Source: MICS 1999
2003 HH Survey/
UNICEF - SDS
1117 Households

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Availability of the Iodized Salt at the Household Level Georgia (except Abkhazia and South Ossetia)
1999 - 2003
70.5
21.8
96.9
58
12.3
75.9
2.7
58.1
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
%
0-15 ppm >= 15 ppm
Urban 1999
Urban 2003
Rural 1999
Rural 2003
Source:
MICS 1999 2003 HH Survey UNICEF - SDS

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Awareness of Households on Iodine Deficiency Republic of Georgia (except Abkhazia and South Ossetia)
2003
63.8
36.2
89.2
10.8
76.8
23.2
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Rural Urban Total (Country)
Have you heard about iodine deficiency?
Yes No
Source:
2003 HH Survey UNICEF - SDS Georgia
From 67% in 1998

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Main Source of Information on Iodine Deficiency Republic of Georgia (except Abkhazia and South Ossetia)
2003
28.1 31
74
65.9
32 30.5 30.7
20.4
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
HealthWorker
Radio TV RelativeFriend
Children Journal paper
Other Do notknow
Urban
Rural

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Some Other Findings
What do you do to prevent Iodine Deficiency?
Urban Rural Total
Buy iodised salt 58.8 51.3 55.7Buy product enriched with iodine 9.6 7.0 8.6Buy vitamins 9.4 4.4 7.4Buy sea products 4.5 0.0 2.7Do nothing 36.2 39.1 37.4Other 3.4 5.3 4.1Do not know 0.5 0.9 0.7
67.9% who knows about Iodized Salt can buy it in areas where they live61.2% households are buying iodized salt monthly
Each household spends 10-11GEL/year for purchasing salt.

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
If you have a choice which salt would you buy?
77.873.5 76.9
72.5 75.1
14.4 16.2 14.818.7 16.4
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Big cities SmallCities
Cities, intotal
Villages Total
Iodized
Non Iodized
No preferences
Do not know

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Motivation for choosing iodized vs. Non-IS
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Iodized
Non-iodized
Iodized 98.1 1.1 1.6 1.1 2.5 0.6 0.2 0.5
Non-iodized 18.5 0 6.4 0 65.4 0 16 3.1
Useful for
healthCheaper
Sold in closest store
Only salt for sale
Tastes better
Smells better
Better for
canned
Do not know

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
IDD Prevalence Data
Findings from National Center of Nutrition
1. Urine Iodine Excretion data among children
2001
2. Goiter Prevalence among children and adults
1997-2003

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Urine Iodine Excretion Children Aged 1-15
0.8 %
18%
62.3 %
18 %
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
< 20 mcg/dl 20-49
mcg/dl
50-
99mcg/dl
>100mcg/dlSource: NCN, 2001
UIE Median Children
67 mcg/dlTbilisi Data 2003

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Goiter Prevalence – Adult Population 1997-2003
57.7 58.3
47.744.1
39.538.5
44*
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003
% of the TotalPopulation
Source: National Center for Nutrition, Georgia
* 2003 Data - Referral

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Goiter Prevalence – Child Population 1997-2003
54 5552
4238 38
39*
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003
% of ChildPopulation
Source: National Center for Nutrition, Georgia
2003* - Referral Data

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
IDD Impact on Mental Development
IDD PROBLEM PYRAMID
IQ Reduction by
10-15%
13.5 IQ Points in Average

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Future Challenges Summary of Recommendations
Political Commitment Re-establishment of Effective Coordination Council/Committee/Task Force
Clear delineation of roles/responsibilities & mandates
Commitment from local governments - sub-national level advocacy
Legislation Endorsement by Parliament
Banning Import of Non-Iodized Salt
Articulating clearly administrative & sanction regulations

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Future Challenges Summary of Recommendations
Establishment of a strong monitoring system for Quality Control of Iodized Salt at all levels
From Import to Household Level
Continuation of Communication & Awareness raising on IDD/USI
Research-Based Strategy with Experts - Refer to SitAn, HH Survey
Intersectoral Partnership – Health, Education, Private, Youth, NGOs
Increase networking with main Salt Importers
Exploring school based IEC and monitoring activities
Identification & Focus on Pockets with high IDD prevalence

UNICEF
PARTNERSHIP FOR IDD/USI IN GEORGIA
Eliminating IDD in Georgia by 2005?
ReachingReaching
38% of Children & Adults Affected by IDD
24% of Population Not Aware on IDD
33% of Families Not Using Iodized Salt
STILL