HEATING and COOLING - Eastern Mediterranean …me.emu.edu.tr/atikol/MENG449/ME449-UA-CH7.pdf ·...
Transcript of HEATING and COOLING - Eastern Mediterranean …me.emu.edu.tr/atikol/MENG449/ME449-UA-CH7.pdf ·...

HEATING and COOLING

HEATING and COOLING

PSYCHROMETRIC CHART

Temperature
• In the HVAC area, we talk about two kinds of temperatures.– One is called dry bulb (DB) temperature,
a fancy name for the reading from an ordinary Mercury bulb thermometer or regular temperature sensor.
– The other is called the wet bulb temperature (WB). It is found by taking a standard Mercury bulb thermometer, covering the tip with cotton or material of some kind, wetting it thoroughly with water and moving it around in the air. As the water evaporates – if it can – it cools the tip of the therm-ometer and the reading is the wet bulb temperature.

HumiditySpecific humidity is the actual amount of water vapor in 1 kg of dry air, whereas relative humidity is the ratio of the actual amount of moisture in the air to the maximum amount of moisture air can hold at that temperature.

• Relative humidity is the percent weight of water vapor that air is currently holding compared to the weight of water vapor it could potentially hold at its present temperature.
• Thus, relative humidity, or RH, is always less than or equal to 100 percent.
• When the RH is 100 percent, we say that the air is saturated – that is, it cannot hold any more water vapor at its present temperature.
• Adding water vapor to air is called humidification.• Removing water vapor from air is called
dehumidification.
Relative Humidity
g
v
g
v
g
v
PP
TRVPTRVP
mm
===//φ

PSYCHROMETRIC CHART

PSYCHROMETRIC CHART

COMFORT ZONE

• The primary purpose of the HVAC system is to provide a comfortable and safe environment for the occupants, equipment and processes being conducted.
• We would also like the HVAC system to accomplish its purpose with minimum energy use and minimum cost.
• The environmental factors that need to be controlled by the HVAC system for comfort and safety are: temperature, relative humidity, and air quality.
THE NEED FOR HVAC

Air Quality - ASHRAE 62.1-2004
• Air quality or indoor air quality (IAQ) is a complex issue in general, but at the Energy Manager level, we restrict our discussion to meeting the requirements of the ASHRAE ventilation standard – ASHRAE 62.1 -2004
• Purpose: “…to specify minimum ventilation rates and indoor air quality that will be acceptable to human occupants…”
• Ventilation: 7 – 9 L/s outside air per personor CO2 less than 1000 ppm

Power, energy and air-conditioning
• For air-conditioning systems, the most common term for heat removal capacity of the HVAC system is the kW, which is a heat removal rate of 3600 kJ per hour.– One kW equals 3600 kJ per hour.
• Since this is a rate of flow of energy (kJ/h), it is a measure of power, not energy.
• The unit of energy in the HVAC system is the kW-hour, which is equal to 3600 kJ. – One kWh equals 3600 kJ.

Example A large room in a commercial office building has a heat production rate of 600,000 kJ/h from lights, equipment, people and heat flow from the outside. How many kW of air-conditioning is required to remove this heat?How many kW is the power input if the COP is 3.0Solution
kW6755003kW167kWX el .
.==
kW167=1kW1
kJ600,3kJ000,600
=kWX

Typical Design Conditions:
• Temperature: 23 °C 20 – 26 °C
• Relative Humidity: 50%40 – 60%
• Ventilation: 7 – 9 L/s outside air per personor CO2 less than 1000 ppm
(ASHRAE 62.1– 2004 Ventilation Standard)
COMFORT and SAFETY

Types of HVAC Equipment
• Cooling– Air based systems
» Window units, split systems, rooftop units– Water based systems
» Chillers, Air Handling Units
• Heating– Air based systems
» Gas, oil and electric heaters; heat pumps– Water based systems
» Hot water boiler, Air handling units

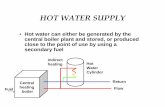
CENTRAL HEATING
Combi-boiler
Radiators
Shower
Two-pipe systemThere is a flow and a return pipe.
Hydro-flow (or water circulation) Heating System

CENTRAL HEATING

CENTRAL COOLING
Outdoor Unit Indoor Unit
Refrigerant Piping
AIR BASED SYSTEMS:Ducted Split-unit Systems
THE AIR CONDITIONER IS SPLIT INTO TWO UNITS

OutdoorUnit Indoor
Unit
CENTRAL COOLINGDucted Split-unit Systems

Supply grilles
CENTRAL COOLING
Ducting
Outdoor unit Indoor unit
Ducted Split-unit Systems

CENTRAL COOLINGAIR BASED SYSTEMS: Roof-top A/C unit

CENTRAL COOLINGRoof-top unit


CENTRAL COOLINGDuct Configurations

Plans of anAmphi-theatrewith the applicationof roof-top a/c
Roof-top unit
E.F.

Roof top unitRoof top unit
Duct
Fresh air intakeFresh air intake

WATER BASED SYSTEMS: Chillers, Boilers, Air handling Units (AHUs)
CENTRAL COOLING

CENTRAL COOLING
Pump
AHU
FCU-1 FCU-2 FCU-3
Duct
Cool Air
Flow
Return
Flow water ~ 7 deg CReturn water ~ 13 deg C



System Improvement Options
• Make building envelope improvements to reduce HVAC load–insulation, high performance windows
and roofs• Replace old HVAC units and chillers
with more efficient models• Consider multiple chillers• Consider a chiller with a variable
speed drive

• Consider installing a small chiller or separate HVAC system for 24/7 loads
• Use VSDs on pumps, cooling towers • Replace constant volume systems with
VAV - variable air volume systems. Get large fan law savings
• Consider adding a gas engine driven chiller with heat recovery for hot water
• Retrofit to DDC controls• Use cooling towers where possible