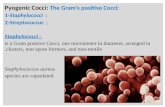
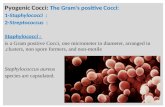
Gram + Cocci: Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Nestor T. Hilvano, M.D., M.P.H.
-
Upload
tamsyn-lewis -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
2
Transcript of Gram + Cocci: Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Nestor T. Hilvano, M.D., M.P.H.

Gram + Cocci:Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
Nestor T. Hilvano, M.D., M.P.H.

Learning Objectives 1. Contrast Staphylococcus aureus with Staphylococcus epidermis in
terms of virulence in humans. 2. Discuss the structural and enzymatic features and toxins of
Staphylococcus that allow it to evade the body's defenses. 3. Describe cutaneous lesions and systemic diseases caused by
Staphylococcus aureus. 4. Discuss briefly staphylococcal resistance to antimicrobial drugs 5. Describe two structures in Streptococcus pyogenes that allow this
organisms to survive against the human defense mechanisms. 6. Identify the conditions under which Group A streptococci cause disease. 7. Discuss the epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of
Group B (Streptococcus agalactiae ) infections. 8. Identify the normal location of viridans streptococci in the human body
and describe three serious diseases they cause. 9. Describe how the structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae affects its
pathogenicity. 10.Discuss the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of pneumococcal
diseases. 11.Describe Enterococcus as to pathogenicity and the diagnosis,
treatment, and prevention of their diseases.

Staphylococcus • Gram + in _____, facultative anaerobic• yellow in culture• Catalase positive• SEM- grapelike • S. aureus – virulent; coagulase +;1/3 pop. are
colonized (no illness) & common source of germs to others
• S. epidermidis – normal flora of human skin; opportunistic pathogens

Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus• Protein A – binds with IgG• Bound coagulase – forms
clot that hide bacteria from phagocytes• Polysaccharide slime layers – facilitate
attachment to surfaces (catheters, shunts, artificial heart valves)
• Enzymes – leukocidin, hyaluronidase, staphylokinase, lipase, and beta-lactamase
• Toxins – exfoliative toxins, TSS toxins, and enterotoxins

Epidemiology of Staph Infection
• Found in human skin
• Transmitted through
- direct contact and via fomites
• 20% - 40% adults are carriers
• Prevention
- proper hand washing, aseptic
techniques, proper cleaning of wound,
use of antiseptics

Staph. Cutaneous Diseases• Folliculitis – infection of hair follicles; pus-filled vesicles• Furuncle – commonly called _____; localized superficial• Carbuncle – extends deeper• Rx: antibiotics; drainage (I & D) What is the most common causative agent of boil?

Staph. Cutaneous Diseases
• Scalded skin syndrome – red skin; blisters; slough off within 2 days; caused by exfoliative toxin
• Impetigo – mostly in young children; red patches; pus-filled vesicles that crust; 80% caused by S. aureus
• Wound infections – surgical infection by contaminated personnel, equipment

Staphylococcus Food Poisoning
• Caused by enterotoxin-contaminated food (salad, processed meat, ice cream, pastries)
• Food remain at room temp. or warmer for several hours* Does reheating of (inoculated) food inactivate
enterotoxins? Why?
a) toxins are heat labile b) toxins are heat stable
• Symptoms appear within four hours after ingestion; self limiting; usually resolved about 24 hours (consumed staph do not continue to produce toxins)

Staph. Systemic Diseases• Toxic Shock Syndrome
- first described in 1978
- 1980 = 299 cases, 25 deaths, caused by tampons (fever, rash, hypotension, diarrhea, vomiting)
- TSS toxin in wound or abraded vagina absorbed into blood; results to low BP/ inadequate O2 supply to vital organs
- Penicillin resistant

Staph. Systemic Diseases
• Bacteremia
• Endocarditis
• Meningitis • Pneumonia and Empyema (fluid with pus)
• Osteomyelitis

Diagnosis and Treatment of Staph. Infection
• Dx: - identify S. aureus in gram stain, ______; and coagulase _____.
• Only 5% susceptible to penicillin today; methicillin drug of choice (semi-synthetic)
• MRSA – resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillin, methicillin, and cephalosporins)
- nosocomial infections
- called “superbug”, discovered in UK (1961),
now found worldwide
- vancomycin used to Rx

Streptococcus • Gram + cocci in ____ (a. chain b. clumps)
• Auxotrophs –requires complex media (Vit. B, aa., purines + pyrimidines)
• Catalase negative
• Facultative anaerobe

Group A β-hemolytic Streptococcus• Streptococcus pyogenes• Pathogenicity
– protein M and Hyaluronic capsule (evades phagocytosis) - enzymes (streptokinase dissolves blood clot; hyaluronidase facilitates spread of organisms)- toxins (pyrogenic; pyogenic)
• White colonies sorrounded by zone of beta-hemolysis (clear zone)
• Infect the pharynx or skin

Group A Streptococcal Diseases
• Strep throat (pharyngitis) – spread via ___ (a. ingestion b. respiratory droplets).
• Scarlet fever – reaction to erythrogenic toxin; fever of 101˚F (38.3˚C), strawberry tongue, red rash (by capillary distensions) within 24 hrs. and fades in a week followed by peeling.

Group A Streptococcal Diseases• Necrotizing fasciitis – flesh-eating strep (1994 England;
1998 Texas); enter thru breaks in skin; toxins destroy muscle and fat tissues, toxemia, organ failure, > 50% die; spread along fascia of muscle
• Post-streptococcal Glomerulonephritis –
autoimmune, anti-strep antibodies cross-react w/ antigens in glomerular b.m.; obstruct blood flow, HPN, and low urine output; transplant

Rheumatic Fever• Autoimmune; cardiac valve diseases• Major criteria include: carditis; polyarthritis;
chorea; subcutaneous nodules (small, painless bumps); rash (a red, irregular rash on the trunk)
• Minor criteria include: fever; arthralgia; previous rheumatic carditis; changes in the ECG pattern; abnormal sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein (laboratory tests performed on blood)
• Diagnosis - made when two of the major criteria, or one major criterion plus two minor criteria, are present along with evidence of a strep infection.

Diagnosis and Rx of Streptococcal Infection
• Identify organisms in skin
• Identify Group A strep Antigens
• Penicillin; susceptible to topical bacitracin
• Erythromycin or cephalosporin – penicillin-sensitive patients

Group B Strep: Strep. agalactiae
• Gram + cocci, in chains, beta-hemolytic• 25% in normal vaginal flora of women; can
cause UTI and endometritis in women• Cause neonatal disease (bacteremia,
meningitis, pneumonia) through birth canal or health care workers
• Dx – ELISA and agglutination tests• Pen G drug of choice

Alpha-Hemolytic Strep. viridans
• Produce a green pigment (incomplete)• Inhabit the mouth, pharynx, GIT, urinary, and
genital tracts• Opportunists; one cause of dental caries;
subacute endocarditis with vegetative growths on valves
• Susceptible to penicillin

Streptococcus pneumoniae• Gram + cocci in short chain, commonly in pairs
(lancet-shaped diplococci) • Polysaccharide capsules and phosphorylcholine in
cell walls confer virulence. • Pharyngeal microbiota• Can colonize lungs, sinuses, and middle ear • 85% of cases of pneumonia• Dx: Gram stain of sputum, quellung reaction
(anticapsular antibodies caused swelling of capsules), optochin test (differentiate S. pneumonia from other alpha-hemolytic strep, inhibition around the disc) agglutination test

Enterococcus • under Group D Strep• unencapsulated; prod. gas on sugar
fermentation; nonhemolytic• Harbor normally in intestinal tracts of human and
animals• E. faecalis and E. faecium – can be pathogenic
in human; secrete bacteriocins (proteinaceous toxins produced by bacteria to inhibit growth of other bacteria)
• Serious disease to urinary tract and bloodstream• Dx. – not sensitive to bile, lack capsule= which
distinquishes from S.pneumoniae• Prev. – good hygiene and aseptic technique

Homework 1. Define terms – pyrogenic, pyogenic, furuncle, carbuncle, folliculitis,
bacteriocins, nosocomial infection, optochin test, and Quellung reaction.
2. Differentiate staphylococcus and streptococcus as to morphology in gram stain (+/-, clusters/chain) and reaction to catalase test (+/-).
3. Identify microbes: a) gram + cocci, coagulase +; b) gram + cocci, group A beta hemolytic; c) gram + cocci, alpha hemolytic; d) gram + cocci lancet-shaped
4. Discuss staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome.
5. Identify the most common causative bacteria of :
__scalded skin syndrome a. streptococcus viridans
__sore throat (pharyngitis) b. enterococcus faecalis
__lung infection c. staphylococcus aureus
__commonly isolated in GIT d. streptococcus pneumonia
__ dental caries opportunist e. streptococcus pyogenes