GCSE Electronic Products Revision Flashcards. 555 timer 8 pin Integrated Circuit (I.C.) Analog can...
-
Upload
noel-perkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
1
Transcript of GCSE Electronic Products Revision Flashcards. 555 timer 8 pin Integrated Circuit (I.C.) Analog can...
Monostable(the egg timer)
•Has a single (mono) stable state• when it is timing
•The output is normally off
Pin 2 = Trigger
• The trigger sets the timer going
• Timer starts when trigger is < 2V
• Connects to a 10K pull-up resistor
Pin 6 = Threshold• Detects when the bucket
(capacitor) is 2/3rds full
• The capacitor fills up through a resistor
• Time to fill to 2/3rds full = Resistor Value x Capacitor Value (T = RC)
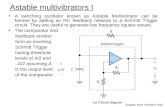
Astable(The “flasher” circuit)
• Has no stable states
• Keeps on flashing forever
• Number of flashes per second = frequency
• Automatically triggers
The Op-Amp• - input = inverting
• + input = non-inverting
• used as an inverting amplifier or a comparator
• An analog device
• A 741 I.C. is an example of an op-amp
Gain• The ability of a device
to make a signal bigger
• Op-amps have huge “open loop” gain
• Transistors also have gain
Feedback• Gain can be reduced by
using feedback
• Some of the output is taken away and added to the input
• We use resistors to do this
Comparator(Which input is bigger)
• If “+” is bigger than “-” we get a logic 1
• If “+” is smaller than “-” then we get a logic 0
• A simple analog to digital converter
+ -
P.I.C.(Peripheral Interface Controller)
• Digital• A mini-computer in a
single Integrated Circuit• Programmable using
flowcharts• Can be programmed many
times• Remembers program even
when the power is off
Diode(A one way valve)
• Current flows from anode to cathode
• Prevents current flowing the wrong way
• Protects circuits if the power supply is connected up wrong
Transducer(A device for converting energy
from one form to another• Motor – converts electrical
energy to kinetic energy• LED – converts electrical
energy to light• Microphone - converts
sound energy to electrical energy
Transducer Drivers(Things that provide power to output transducers)
• Bipolar Transistors• FET’s• Darlington Pairs
Tolerance
• The amount of “spread” in a components value
• 100Ω and 10% tolerance gives a spread between 90Ω and 110Ω
E12 Series
• The values that 10% tolerance resistors are made in to avoid value overlap
• 10, 12, 15, 18, 22 etc• 100, 120, 150, 180 etc
Polymorph – Smart Material
• Used to rapidly model complex shapes
• Granules put in hot water turn solid and can be immediately shaped
+
clock
• A digital signal that has a regular repeating on/off pattern
• Often generated by an astable
• Used by PICs & counters
HIPS
• Plastic material used for vacuum forming
• Available in different colours
• Used to make complex 3d shapes
• Boxes must have angled sides to get the mold out
Breadboard
• Used to model circuit using real component
• No soldering• Easy to change
connections• Components can be re-
used
CAD(Computer Aided Design)
• Testing by simulation
• Links to CAM (Computer Aided Manufacture)
• Easy to share designs with others and keep track of changes
• Making changes is a quick & easy process
Latch Circuit• Can be made using a
thyristor
• Can be made with NOR or NAND gates
• When activated, stays activated until reset– Remembers that it has
been activated
Thyristor• Used in latch circuits
• A pulse on the gate causes current to flow from Anode to Cathode until reset
• Reset by making the Anode voltage the same as the Cathode
Potential Divider
• A circuit for dividing voltages
• Voltage splits based upon the ratio of two resistors
Thermistor• Device for measuring
temperature
• As temperature increases, resistance decreases
• Often used as part of a potential divider
LDR(Light Dependent Resistor)
• As light increases, resistance decreases
• Often used as part of a potential divider
The 3 R’s(Helping The Environment)
• Reducecut the materials you use
• Reusemake use of existing products
• Recyclestop the product going to landfill when obsolete
Integrated Circuits
• Pin 1 is to the left of the notch
• Lots of components on a single piece of silicon
• Examples are:– PICS– 555’s– 741’s
Switch Bounce
• A problem with mechanical PTM & PTB switches
• One press of the switch generates more than one pulse
Relay
• A device that allows one circuit to turn on another circuit that works at a different voltage
• Uses electro-magnets
Variable Resistor
• Used for– volume controls
– Changing astable frequencies
– Changing mono-stable time periods
4017• Output 0 is on• When a clock pulse is
received:– Output0 turns off– Output1 turns on
• On next clock pulse– Output1 turns off– Output2 turns on
SPDT SWITCH(Single Pole Double Throw)
• One circuit• Two positions• Three pins• Two different sets of
components can be switched into one circuit
Life Cycle Analysis
• What happens to a product when it is disposed of:
– Reused in a new product
– Recycled– Goes to landfill
Multipliers
1,000,000,000 = 1G = 1 x 109
1,000,000 = 1M = 1 x 106
1,000 = 1K = 1 x 103
1 = 1 = 1 x 101
0.001 = 1m = 1 x 10-3
0.000,001 = 1µ = 1 x 10-6
0.000,000,001 = 1n = 1 x 10-9
0.000,000,000,001 = 1p = 1 x 10-12