Future tense Presentation
Transcript of Future tense Presentation

FUTURE TIME

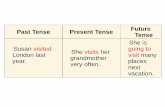
Simple Future has two different forms in English: "will" and "be going to." Although the two forms can sometimes be used interchangeably, they often express two very different meanings. These different meanings might seem too abstract at first, but with time and practice, the differences will become clear. Both "will" and "be going to" refer to a specific time in the future.

BE GOING TOForm Be going to [am/is/are + going to + verb]
Examples:You are going to meet Josh tonight. Are you going to meet Josh tonight? You are not going to meet Josh tonight

“Be going to" to Express a Plan”"Be going to" expresses that something is a plan.
It expresses the idea that a person intends to do something in the future. It doesn’t matter whether the plan is realistic or not.
Examples: He is going to spend his money on clothes. She is not going to spend her money on
clothes. I'm going to be an actor when I grow up. Michelle is going to begin medical school next
year. Who are you going to invite to the party? Brittany is going to make John's birthday cake.

"Be Going to" to Express a Prediction
“B e going to” can express the idea of a general prediction about the future. Predictions are guesses about what might happen in the future. In "prediction" sentences, the subject usually has little control over the future.
Examples: The year 2012 is going to be a very
interesting year. John Smith is going to be the next President. The movie “Avatar" is going to win several
Academy Awards.

WILL Form Will [will + verb]
Examples: You will help Jim later. Will you help Jim later? You will not help Jim later

"Will" often suggests that a speaker will do something voluntarily. A voluntary action is one the speaker offers to do for someone else. Often, we use "will" to respond to someone else's complaint or request for help. We also use "will" when we request that someone help us or volunteer to do something for us. Similarly, we use "will not" or "won't" when we refuse to voluntarily do something.
Examples: Will you help me move this heavy table? Will you make dinner? I will not do your homework for you. I won't do all the housework myself I'll make some sandwiches. I'll get you some coffee. A: The phone is ringing. B: I'll get it.

USING A COUPLE OF OR A FEW WITH AGO AND IN
A couple of and a few are also commonly used. A couple of means “two”. A couple of months ago= two months ago
Examples My grandmother visited us a couple of
weeks ago. Jane give birth in a couple of months.

A few means “a small number, not a large number”. A few weeks ago= three, four or five weeks ago.
Examples
The test is in a few days. Our Aunt came a few days ago.

TodayTonightThis morning
This afternoon
This evening
This weekThis weekendThis monthThis year
These words can express
present, past, or future time

Examples
Present I am playing cards tonight
PastI played cards tonight
FutureI’m going to play cards
tonight

USING WHAT + A FORM OF DOWhat + a form of do is used to ask aboutactivities.
PresentWhat are you doing?
What do you do every morningPast
What did you do last night?Future
What are you going to do next week?What will they do if it’s closed?

May We can use 'may' to ask for permission.
However this is rather formal and not used very often in modern spoken English
May I borrow your pen? May we think about it? May I go now? We use 'may' to suggest something is
possible It may rain later today. I may not have time to do it today. Pete may come with us

Might We use 'might' to suggest a small possibility ofsomething. Often we read that 'might' suggests asmaller possibility that 'may', there is in fact littledifference and 'might is more usual than 'may' inspoken English. She might be at home by now but it's not sure at
all. It might rain this afternoon. I might not have time to go to the shops for you. I might not go. For the past, we use 'might have'. He might have tried to call while I was out. I might have dropped it in the street.

Note May and Might are
not used wiht will

FUTURE CLAUSE WIHT BEFORE, AFTER AND WHEN
The simple present is used in a future time clause. Be going to and will are not used in a future time clause.
BeforeAfterwhen
+ subject and verb = a time clause

Example Before I go to class tomorrow, I’m going to eatbreakfast.
The speaker is talking about two events: going to
class and eating breakfast. Both events are in the
future. However, the speaker uses the simplepresent( not be going to or will) to talk aboutgoing to class because the verb occurs in timeclause.

I’m going to eat dinner at 6:00 tonight. After I eat dinner, I’m going to study in my room.
I’ll give Mary your message when I see her tomorrow.
I’m going to go to bed after I finish my homework.

CLAUSES WIHT IFWhen the meaning is future, the
simple present( not be going to or will ) is used in an
“if clause”.FormIf + subject and verb = an “if clause”Example:Maybe it will rain tomorrow. If it rains
tomorrow,I’m going to stay home.

By Dayana and
MainorGod Bless you