Extracellular components and junctions. Plant cells Plasmodesmata the intracellular junction between...
-
Upload
nicholas-walton -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Extracellular components and junctions. Plant cells Plasmodesmata the intracellular junction between...
- Slide 1
- Extracellular components and junctions
- Slide 2
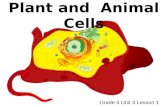
- Plant cells Plasmodesmata the intracellular junction between plant cells water and small solute can pass freely from cell to cell Cell walls Primary cell wall(found in young plants; thin and flexible) Middle lamella(thin layer rich in pectin or sticky polysaccharides) Secondary cell wall(a strong durable matrix that affords cell protection and support)
- Slide 3
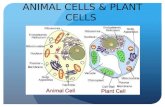
- Animal Cell Junctions Glycocalyx strengthens cell surface and helps stick animal cells together Tight junctions Prevent leakage of extracellular fluid by binding the plasma membrane of neighboring cells together Desmosomes Fasten cells together but allows fluids to be transported Gap junctions Provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to another
- Slide 4
- Extracellular components in animals Extracellular Matrix (ECM) The substance in which animal cells are embedded Main ingredients are glycoproteins or short chains of sugar Collagen is the most common glycoprotein
- Slide 5
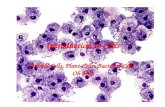
- Interactions Cell wall uses pectin to glue itself to adjacent cells. Plasmodesmata provides a channel to transport water and solvents to neighbor cells. The ability of this macrophage(blue) to recognize and destroy bacteria(yellow) is an activity of the whole cell. Its cytoplasm, lysosomes, and plasma membrane are the components functioning in this picture.
- Slide 6
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uXBOb4Zy5Sg&feature =relmfu