Evolution Chapter 15 + 14.2 Do Now 1. What about the skeleton in the photo reminds you of a living...
-
Upload
lucy-taylor -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Evolution Chapter 15 + 14.2 Do Now 1. What about the skeleton in the photo reminds you of a living...

Evolution
Chapter 15 + 14.2

Do Now 1. What about the skeleton in the
photo reminds you of a living thing?
2. What about the skeleton reminds you of a nonliving thing?
3. What might studying this skeleton help you to learn about living things?
4. What might be some benefits of studying living things?

Answers
1/2. The skeleton is made of organic materials and was once
part of a living thing, but the skeleton cannot move on its own, reproduce, or grow.
3. Studying the skeleton could reveal how the internal structure of a living thing is supported, how bones are formed, or how living things grow.
4. The study of living things can help people to understand themselves and might lead to practical benefits such as cures for disease, improvements to the environment, and more efficient use of Earth’s resources.

What is evolution?
Change in living organisms over time

Brainstorm- How was the Earth formed?
How do scientists know this?

14.2 Origins: Early Ideas
Spontaneous Generation is the idea that life arises from non-life.
Francesco Redi: an Italian scientist tested the idea of spontaneous
generation.

If you leave meat out for a week, what happens?
Where do maggots come from?

Debating Spontaneous Generation
The Experiment: Place meat in open container and one in a closed
container

1668 Francisco Redi
Hypothesized that maggots came from flies, not meat
Therefore, maggots did not spontaneously generate

1864 Louis Pasteur
Theory of biogenesis Only living organisms can produce
other living organisms

1864 Louis Pasteur
Devised an experiment to test spontaneous generation
Nutrient rich broth was exposed to air but not dust and spores
Living organisms must be able to enter the broth in order to grow
Living things do NOT spontaneously generate

What was the atmosphere of early earth like?
What was it made of?

How did the gases get in the atmosphere?

Gases were expelled from volcanoes Water Vapor (H2O) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Carbon Monoxide (CO) Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN) Nitrogen (N2) Hydrogen (H2) NO OXYGEN!!!!!!!

Do Now
What were the conditions of early earth?

How do we know that was what the atmosphere was made of?
Miller and Urey created an experiment
Showed how first organic molecules could be formed

Miller and Urey Experiment
Primordial soup hypothesis: early hypothesis about the origin of life simple organic molecules could be made from
inorganic compounds. Primary Energy Sources:
UV light from the Sun Electric discharge in lightning
Scientists found that hydrogen cyanide could be formed from even simpler molecules in simulated early Earth environments.


Conclusion Activity-Do Now Period 6
State the scientist who came up with different theories:
1. Discovered part of cell theory. 2. Created early earth environment to test
hypothesis. 3. First to discover that spontaneous
generation was false. 4. Worked with maggots and meat 5. Discovered primordial soup hypothesis.

Cellular Evolution Scientists hypothesize that the first cells
were prokaryotes Modern prokaryotes called archaea are
the closest relatives of Earth’s first cells. Archaea are autotrophic They do not obtain their energy from the
Sun.

Photosynthesizing Prokaryotes Photosynthesizing prokaryotes
evolved not long after the archaea. Prokaryotes, called cyanobacteria,
have been found in rocks as old as 3.5 billion years.

Do Now
1. ______ is thought to be an ancestor of the first cells on Earth.
2. What gas was missing from the atmosphere of early Earth?
3. How old is the Earth?

Do Now
List the three scientists we discussed last class and a sentence about each experiment.

The Endosymbiont Theory
Eukaryotic cells lived in association with prokaryotic cells.
Relationship between the cells became mutually beneficial, and the prokaryotic symbionts became organelles in eukaryotic cells.
This theory explains the origin of chloroplasts and mitochondria.

Endosymbiont Theory

Evidence for Endosymbiont Theory
http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/organelles.html

Evidence for Endosymbiont Theory

Supporting Evidence for Endosymbiotic Theory
Mitochondria have circular DNA like bacteria
Replicates like bacteria separate from the host cell
DNA codes for proteins that are similar to bacterial proteins
Mitochondria make their own proteins Mitochondria have two membranes
(one from the host cell and one from their own cell membrane)




Do Now
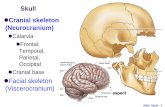
Label the following diagram

Endosymbiotic Theory

Who is Charles Darwin?

15.1 Darwin on the HMS Beagle Darwin was a Naturalist He collect biological and geological
specimens during the ship’s travel.

The Galápagos Islands Darwin collected mockingbirds, finches, and
other animals on the four islands. Darwin discovered that each island had their
own, slightly different varieties of animals. Almost all species collected were unknown
to European scientists
Frigate bird

The Galápagos Islands (Cont.)
Populations from the mainland changed after reaching the Galápagos.
Darwin hypothesized that new species could appear gradually through small changes

Do Now
Label the following diagram

Darwin’s Conclusion
Humans could change species by artificial selection, then the same process could work in nature.
Ex) Corn Selection

Artificial Selection

Brassica oleracea

Endosymbiotic Theory

What is natural selection?

Natural Selection 1. Individuals in a population show
variations.

Natural Selection (Cont.)
2. Variations can be inherited.

Natural Selection (Cont.)
3. Organisms have more offspring than can survive on available resources.

Natural Selection (Cont.) 4. Variations that increase
reproductive success will have a greater chance of being passed on.


Do Now
Explain using Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection (all 4 parts!) why tall trees evolved.

Do Now- Multiple Choice1. What did Darwin infer from his observations of artificial selection?
A. Animal breeders could create new species.B. A similar process could work in nature.C. Reproductive success could be increased.D. Variation in a species could be produced.
2. What is the relationship between natural selection and evolution?
A. They mean the same thing.B. Evolution works against natural selection.C. Evolution explains how natural selection works.D. Natural selection explains how evolution works.
3. Which explains why the tortoises on the different islands of the Galápagos had slightly different variations in their shells?
A. The different tortoises were different species.B. The environment on each island was different.C. Each type of tortoise could survive only on its own island.D. They arrived on the islands from different continents.

Use the following example and explain the four parts of natural selection.
A male peacock has bright colored feathers to attract a mate 1. Variation
2. Inherited
3. More offspring are produced than can survive
4.Varations with Reproductive Success

Sample Example Using the following example,
explain how natural selection created the evolution of this butterfly.

Explain how natural selection can lead to evolution of this moth.

Quiz on 14.2 and 15.1
Darwin Natural Selection Artificial Selection 3 Scientists (Miller/Urey, Redi, Pastuer) Endosymbiont Theory Early prokaryotes/early Earth conditions

Types of Natural Selection
1. Stabilizing Selection 2. Directional Selection 3. Disruptive Selection 4. Sexual Selection

1. Stabilizing Selection Eliminates extreme
expressions of a trait because the average expression increases survival
Ex: most human babies are born with average weights

2. Directional Selection This happens when an extreme version
of a trait makes an organism more fit. Ex. Speed; faster is always better so a
population will tend to get faster over time.

3. Disruptive Selection
A process that splits a population into two groups because the organisms that express either extreme trait survive and the average trait does not. Ex: Snake coloration

4. Sexual Selection
Frequency of a trait is based on the ability to attract a mate.
Males evolve with threatening characteristics or bright colors to attract females.

Worksheet**
Video – Planet Earth (Jungles)

Do Now
In a population of mice, the colors range from light to dark grey. The mice live among dark colored rocks.
1. What mice to you think would survive natural selection?
2. What would happen over time to the entire mice population?
3. What is the name of this type of natural selection?

Think – Pair - Share
Brainstorm- How do scientist know that evolution occurred?
What are some evidence for evolution?

15.2 Evidence for Evolution
1. Fossil Evidence 2. Evidence from Anatomy 3. Embryology 4. Biochemistry
Genetic Evidence 5. Geographic Distribution 6. Direct Observation

1. Fossil Evidence
Fossils provide a record of species that lived long ago.
Fossils show that ancient species share similarities with species that now live on Earth.

2. Evidence from Anatomy
A. Homologous Parts Anatomically similar structures
inherited from a common ancestor are called homologous structures.

2. Evidence from Anatomy
B. Vestigial Structures Structures that are the reduced forms
of functional structures in other organisms.

2. Evidence from Anatomy
C. Evolutionary Theory Predicts that features of ancestors that no
longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are lost.
.

Do Now – Period 1
Use Darwin’s idea about natural selection to explain how green beetles became the predominant color over time.

2. Evidence from Anatomy D. Analogous Structures:
Can be used for the same purpose (look similar), but not inherited from a recent common ancestor
Ex. Wings of an eagle and beetle

Think-pair-share
Compare and contrast analogous and homologous structures.
List 3 examples of each not mentioned in class.

3. Embryology
Vertebrate embryos exhibit homologous structures during certain phases of development
Become totally different structures in the adult forms.


4. Biochemistry
Common ancestry can be seen in the complex metabolic molecules that many different organisms share. Ex. Hemoglobin, amino acids

4. Biochemistry – Genetic Evidence
Mutations are the raw material for evolutionary change
Genetics can tell us how different groups of organisms are related back through time.

5. Geographic Distribution The distribution of plants and animals
that Darwin saw first suggested evolution to Darwin.
Ex. Animals on S. America mainland were more similar to other S. American animals than to animals living in comparable environments in Europe

6. Direct Observations Some evolution takes place more
rapidly than others Ex. evolution of drug resistant
bacteria. This type of evolution can be directly observed by scientists.

Conclusion Activity- Match the following with the type of evidence
1. The HIV virus is constantly changing and evolving.
A. Fossil Evidence
2. All living things share the same amino acids
B. Biochemical Evidence
3. Evidence that Dinosaurs were once on earth
C. Embryology
4. Humans and Chimps have similar bone structures
D. Direct Observation
5. The fetus of a pig and dog go through similar developments
E. Evidence from Anatomy

Do Now
What is a species?
Can two different species mate?
If so, what happens?

15.3 Speciation (pgs. 438-441) A species -group of organisms that can
interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature.
Interspecies breeding can sometimes produce offspring that are infertile
EX. horses and donkeys producing mules

Adaptation
A trait shaped by natural selection that increases an organism’s reproductive success
Fitness: How well an organism is suited for an environment How well an organism can pass it’s traits to the next
generation

Types of Adaptation 1. Camouflage:
Allows an organism to become almost invisible to predators

Types of Adaptation (Cont.)
2. Mimicry: One species evolves to resemble
another species.
Western coral snake (poisonous) California kingsnake (harmless)

Do Now
List 3 evidences for evolution and provide an explanation of each.

Types of Evolution
A. Divergent Evolution Adaptive Radiation
B. Convergent Evolution C. Coevolution

A. Divergent Evolution Divergent Evolution
When one species evolves into two or more species with different characteristics
One type of Divergent evolution is called adaptive radiation.

A. Divergent Evolution (cont.) Adaptive Radiation: One species gives
rise to many different species in response to the creation of new habitat or some other ecological opportunity
Can occur in a relatively short time

A. Divergent Evolution (cont.) Divergent evolution can sometimes lead
to reproductive isolation. Prevents two species from mating. It can be caused by:
1. geographic isolation (allopatric speciation) 2. genetic mutations (sympatric speciation)
Polyploidy:

B. Convergent Evolution Unrelated species evolve similar traits
even though they are not closely related. These traits are often structurally very
different.


Examples
Bird Wing Bat Wing

Analogous Structures Result from Convergent Evolution
Human Eye
Squid Eye

C. Coevolution Relationship between two species in which
the evolution of one species affects the evolution of the other species.
Mutualism Coevolutionary arms race
Orchid Fly Garter snake consumes a poisonous newt
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/01/3/l_013_07.html

Label the following:

Do Now
Explain the difference between divergent and convergent evolution

Explain the differences between:
Homologous and analogous structures Convergent and divergent evolution

Tempo of Speciation
Gradualism: Evolution proceeds in small, gradual
steps according to a theory called gradualism.
Punctuated Equilibrium: Punctuated equilibrium explains
rapid spurts of genetic change causing species to diverge quickly.


EvolutionChapter 15

Do Now
Explain this picture. Use as many vocab words as possible…

Do Now
How did humans evolve?

Human Evolution Ch. 16.2
Primate adaptations high level of problem solving ability large brain size when compared to
body weight flexible shoulders flexible hand with an opposable thumb

Primate Evolution
The lineage that most likely led to humans split off from the other African apes sometime between 8 and 5 mya.
Hominins have bigger brains.Thinner and flatter faceSmaller teethHigh manual dexterityBipedal
Hominins
16.2 Hominoids to Hominins

African Origins


Human Evolution

Conclusion Activity
Compare and Contrast Apes and Humans

Notebook File

Do Now
Homologous and analogous structures Convergent and divergent evolution

Do Now
Explain how simple mutations can cause the evolution of a new species. Use the following words: Adaptation Natural Selection Divergent Evolution Reproductive Isolation Sympatric or Allopatric Speciation