Environmental Science. What is Environmental Science? Relationships between people and the natural...
-
Upload
peregrine-little -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
2
Transcript of Environmental Science. What is Environmental Science? Relationships between people and the natural...

Environmental Science

What is Environmental Science?
Relationships between people and the natural environment.
InterdisciplinaryBroad fieldEcology is a basic tool (Oikos – Logos)
GoalsEstablish general principles about how the natural
world functionsIdentifying, understanding, and solving problems

What is Earth Science?
• All the sciences that collectively seek to understand Earth and its neighbors in space.
• Four Sciences:
• Geology• Oceanography• Meteorology• Astronomy

How are earth science, environmental science and people connected?
Earth Science
Environmental science
People
Environment:
-Biologic
al
-Physica
l
Resources:-Renewable-Non-renewable
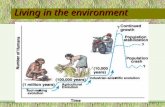
Population growth
Environmental problems

How do Earth scientists know all this stuff?
• Observation• Experimentation• Understanding other sciences – Biology – Physics– Chemistry

The Nature of Scientific Inquiry
The Scientific Method
1) Collection of scientific facts through observation and measurement
2) Hypothesis: tentative explanations to observations
3) Extensive testing and analysis4) Acceptance, modification or
rejection
Models
Useful when dealing with natural processes that occur over very long periods of time (scales of time) or in inaccessible locations.

The nature of Scientific Inquiry
Theory• A well tested and widely
accepted view that the scientific community agrees best explains certain observable facts
Paradigms• Theories that are
extensively documented and explain a large number of interrelated aspects of the natural world.
Scientific laws• A basic principle that describes a particular behavior of
nature that is generally narrow in scope and can be stated briefly

STUDYING EARTH FROM SPACE… pg 8.
How can satellite images be used to study Earth from space?
• Know the composition of Earth’s surface• Precipitation data• Understanding global climate change

Scales of Space and Time

The Nebular Hypothesis and Origins of Earth and the Solar System
A. solar nebula
B. contraction into rotating disk
C. Cooling causing condensing into tiny (dust sized) solid particles
D. Collisions between these form larger bodies
E. These accrete to form planets
Oceanography 100 Animations

Earth’s Spheres
Atmosphere
Geosphere
Biosphere
Hydrosphere

HYDROSPHERE
• Oceans 97%• Freshwater– Streams– Lakes– Glaciers– Underground

Atmosphere
• Life-giving gaseous envelope• ½ lies below an altitude of
5.6 km• 90 % occurs within just 16
km• Protects from the
dangerous radiation emitted by the Sun.
• Site of weather and climate

Biosphere
• All life on Earth• Depend and respond to their physical environment• Have an effect on their physical environment

GeosphereLayers defined by
composition:
• Crust– Oceanic, 40 km, d= 3g/cm3– Continental, 70 km, d = 2,7 g/cm3
• Mantle, 2900 km, d=3,4 g/cm3
• Core, d= 13 g/cm3

Geosphere
Layers defined by physical properties:
• Lithosphere
• Asthenosphere
• Lower mantle
• Outer core
• Inner core

Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics


Mountainbelts
OCEAN BASIN
CONTINENTS

Earth as a System
What is a SYSTEM?• Group of interacting parts that form a complex
whole.
• Two types:– Closed system: energy moves freely in and out,
but matter does not enter or leave the system.– Open system: both matter and energy flow into
and out of the system.

Earth as a System
• Within the Earth system, the spheres are interconnected.

Earth as a System
• Energy for the Earth system is powered by two sources:1) Sun: drives external processes that
occur in the atmosphere, hydrosphere and at Earth’s surface.
2) Heat from Earth’s interior: powers internal processes that produce volcanoes, earthquakes and mountains.

Earth as a System
• Most Earth systems have positive or negative feedback mechanisms.
– Positive feedback: enhance or drive change
– Negative feedback: work to maintain the system as it is

Sources
• http://www.enov.co.uk/pages/Environment.html• http://www.myrrh-art.com/Levels_in%20Matter_T.html• http://volcano.oregonstate.edu/volcanoes-national-park
s• http://www.northeducation.ac.th/elearning/ed_sc30/ch
ap07/sc7112_1.html• http://animals.howstuffworks.com/marine-life/coral-reef
.htm• http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-kids/0040-intro
duction-to-our-atmosphere.php• http://sciencerevolution.net/dict_m.html• http://www.crystalinks.com/platetectonics.html• http://bumileluhur.blogspot.com/2011/01/seafloor-feat
ures.html• http://www.eoearth.org/article/Physiography_of_the_E
arth's_terrestrial_surface