DNA RNA Protein
description
Transcript of DNA RNA Protein

DNA RNA Protein

Central Central DogmaDogma
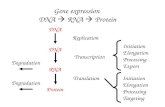
• Central Dogma – describes how information from DNA gets used to make proteins
• 3 processes:– 1. Replication copies
DNA– 2. Transcription converts
DNA message into RNA– 3. Translation interprets
an RNA message into a string of amino acids, called a polypeptide. Either a single polypeptide or many polypeptides work together to make up a protein.
DNA
RNA
PROTEIN

RNA: Ribonucleic AcidRNA: Ribonucleic AcidMade of
nucleotides with 3 parts:– 1. A sugar– 2. A phosphate– 3. A nitrogen-
containing base
Can find RNA in two places in the cell:
1.Cytoplasm2.Nucleus

RNA is different from DNARNA is different from DNA
3 ways RNA and DNA are different:
• 1. Sugar in RNA is ribose, not deoxyribose. Ribose has one more oxygen atom than deoxyribose.
• 2. RNA has four bases: A, C, G, U. A pairs with U and G pairs with C.
• 3. RNA is single stranded, not double stranded like DNA

mRNA copied from DNA mRNA copied from DNA StrandStrand
•Remember!A pairs with U and G pairs with C.
Example: GGCTATATCmRNA: CCGAUAUAG
Example: CTGCGCTATmRNA: GACGCGAUA