DNA Jurassic Park Clip 1. What is the difference? Mitosis vs Meiosis 2.
-
Upload
aniyah-musgrave -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of DNA Jurassic Park Clip 1. What is the difference? Mitosis vs Meiosis 2.

DNAJurassic Park Clip
1

What is the difference?
Mitosis vs Meiosis
2

Mitosis
3
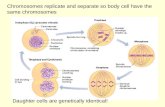
Mitosis is how somatic--or non-reproductive cells--divide. Somatic cells make up most of your body's tissues and organs, including skin, muscles, lungs, gut, and hair cells.
In mitosis, the important thing to remember is that the daughter cells each have the same chromosomes and DNA as the parent cell.

Meiosis
4
Meiosis is cell division that creates sex cells, like female egg cells or male sperm cells.
Meiosis is why we have genetic diversity in all sexually reproducing organisms.
Genetic recombination is the reason full siblings made from egg and sperm cells from the same two parents can look very different from one another.

Meiosis
• Is the reason we study genetics.
5

Livestock Breeding and Genetics
Dominant and Recessive Genes

Objectives for this Lesson:
• Determine who Gregor Mendel is and what he did.
• What does “dominant” mean and “recessive” and provide an example of this with livestock.
• What do we mean by genotype and phenotype?
• What are the differences between heterozygous and homozygous?
• How do we complete Punnett Squares? With one trait? Two traits?

Mendel and Genetics• Monk
• Discovered what inheritance is.
• Discovered dominant and recessive traits through experiments with pea plants
• His work allows us to understand how genes determine traits in livestock and other creatures.

Qualitative Traits
Dominant and recessive traits are traits controlled by 1 pair of genes, and are referred to as QUALITATIVE TRAITS.
Some examples include:
1) coat color in Angus cattle
2) polled or horned trait in cattle
3) white color in swine
4 ) white wool in sheep
So what is meant by the term dominant?

Define DOMINANT
DOMINANT : when one gene completely masks the effect of the other.
For example:• The black coat color is dominant over red
coat color in Angus cattle.

11
How is Dominant Indicated?
• The dominant trait is indicated by a capital letter, such as "B" for the black coat color.
• The degree of dominance depends upon the animal's entire genetic makeup together with the environment to which it is exposed.
11

Define Recessive!
RECESSIVE: when a gene will not show its effects if there is a dominant gene present. For example:
• The red coat color is recessive in Angus cattle.
• Recessive is Represented with: • a lower case letter, such as "b" for red coat
color.

Dominant vs. RecessiveAngus Cattle
Which is which, you tell me!

Genotype
Moving on to genotypes: • The genetic makeup of an organism
or group of organisms with reference to a single trait, set of traits, or an entire complex of traits.
• This will be represented with Letters!
What are the categories of genotypes?

15
Phenotype
• This refers to the physical characteristic of the animal.
• Notice both Phenotype and Physical start with P!
• This is what we see in the animal, such as color.
15

Homozygous = SAME
HOMOZYGOUS means that the gene on each chromosome in the pair codes for the same variation of the trait. For example:
• A cow that is homozygous for black coat color could be indicated by a genotype of "BB".
• If she is red, her genotype must be "bb", since red color is recessive (this only occurs when there are no dominant genes present).

Heterozygous = Different
HETEROZYGOUS means that the two alleles at a gene locus are different; each codes for one of the variations of the trait.
For example:
• A cow that is heterozygous for black coat color could be indicated by a genotype of "Bb".
• The black gene is the dominant one and is displayed phenotypically (physically).

Punnett Square! The fun part!
• Now we move on to the Punnett Square:
This may be used to determine the percentage of offspring that will show each variation of the trait.
For example…

Scenario: Monohybrid Cross
A black cow with the genotype "Bb" is bred to a black bull with the genotype "Bb".
What will be the percentage of calves having each possible genotype?

The bull produces sperm carrying 50 percent "B" genes and 50 percent "b" genes, the cow has the same percent of eggs - 50 percent "b" and 50 percent "B" genes.
So in the problem, each animal is represented with Bb.

21
Here’s how we set it up...
21
B
B
b
b

22
Here’s how we set it up...
22
B
B
b
b
BB
bbBb
Bb

Genotype
• 25 percent "BB"• 25 percent "bb"• 50 percent "Bb".

24
Phenotype
• 25 percent red • and 75 percent black since "Bb" and
"BB" have the same phenotype.
24

Dihybrid Cross
• This refers to crosses using two separate traits. For example:
a. The polled trait "P" and black coat color "B" will be used to demonstrate the dihybrid cross.
b. Remember that GENES DETERMINING THESE DIFFERENT TRAITS ARE TRANSMITTED INDEPENDENTLY.

Use the Punnett Square
a. Let's say a cow has the genotype "BbPp" ("B" = black, "b"= red, "P" = polled, and "p" = horned).
b.The bull has the genotype "BbPp" also
If we breed these two, what are the genotypic percentages of the
offspring?

Steps of Action
1) First, determine which genotypes would be present in the eggs and sperm as they will be the same for both the cow and the bull.
2) "Bp", "BP", "bp", and "bP" are the possible genotypes.
3) Next, draw a square and put the genotypes for the cow down the side of the square and the genotypes for the bull across the top of the square

Lets work this out...
Bp BP bp bP
Bp
BP
bp
bP

• We can determine the percentages of the various genotypes by adding up similar genotypes.
• What are all the possible genotypes?

• "BBpp" = 1/16 • "bbPp" = 2/16 (1/8)• "BBPp" = 2/16 (1/8) • "BBPP" = 1/16• "Bbpp" = 2/16 (1/8) • "BbPP" = 2/16 (1/8)• "BbPp" = 4/16 (1/4) • "bbpp" = 1/16• "bbPP" = 1/16

What are the possible phenotypes?
• Black and polled = 9/16• Red and polled = 3/16• Red and horned = 1/16• Black and horned = 3/16

Sources
• California Ag Ed Tech Prep• Scientific Farm Animal Production: An
Introduction to Animal Science