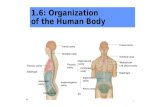
Glands. – Exocrine Glands – Exocrine: secretion into a body cavity.
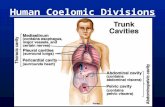
Development of Body Cavity
Transcript of Development of Body Cavity
8/6/2019 Development of Body Cavity
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/development-of-body-cavity 1/3
eve opmen o o y av y ap ragm
Diaphragm
Fibromuscular septum separate thoracic cavity from abdominal cavity Parts
y Central tendon
y Greater muscular
y Right crus & Left crus
Superior & Inferior surfaces are covered by serous membranes
Development of Mesodermal Germ Layer
At beginning of 3rd
week of development, the intra-embryonic mesoderm is
differentiated into
y Paraxial mesoderm (PAM)
y Intermediate mesoderm (In M)
y Lateral plate mesoderm (LP M)
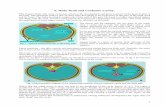
Formation of Intraembryonic Cavity
At the end of 3rd
week, intercellular clefts appear in lateral plate mesoderm on
each side of the midline
When the spaces fuse, the intraembryonic cavity (body cavity) is formed
Cavity is bordered by
y Somatic mesoderm
y Splanchnic mesoderm
Folding of Embryo
2 types of folding in embryo
y Cephalocaudal folding (head to tail fold)
y Lateral folding
8/6/2019 Development of Body Cavity
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/development-of-body-cavity 2/3
Development of Diaphragm
Diaphragm develops from 4 components
y Septum transversum central tendon
y 2 Pleuroperitoneal membranes
y Lateral & Dorsal body wall muscular part
y Dorsal mesentery of esophagus right & left crus
Growth of lung buds in pericardioperitoneal canals
Development of Diaphragm
Positional changes & Innervation of Diaphragm
During 4th
Week During 5th
Week By 6th
Week
Septum transversum
(prior to its descent
with the heart) lies
opposite the 3rd
5th
cervical somites
Myoblasts from these
somites migrate into
developing diaphragm
bringing their nerve
(eg. Phrenic nerves)
Apparent descent of
diaphragm occur at
level of thoracic somites
Phrenic nerve moves
8/6/2019 Development of Body Cavity
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/development-of-body-cavity 3/3
Diaphragmatic Hernias
Foramen of Morgagni (retrosternal or parasternal hernia)
Herniation through sternocostal hiatus (opening for superior epigastric vessels
in retrosternal area) may occur
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH)
Most frequently caused by failure of 1 or both of pleuroperitoneal membranes
to close the pericardioperitoneal canals.
85-90% cases Hernia is on the left side
Intestinal loops, stomach, spleen, part of liver may enter thoracic cavity
Cause hypoplastic lungs & heart
Most common cause of Pulmonary Hypoplasia
Figure A Figure B
Hernia is on the left side
Stomach & Bowel are herniated
Hernia is on left side but
underneath, the liver is herniated
into left chest cavity
Polyhydramnios may also present
Also known as Foramen of Bochalek (clinically)
Diaphragmatic Hernias
Esophageal Hernia
Due to congenital shortness of esophagus
Upper portions of stomach are retained in thorax
Stomach is constricted at level of diaphragm
Eventration of Diaphragm
Uncommon condition
Half of diaphragm has defective musculature
Balloons into thoracic cavity as aponeurotic sheet
Form Diaphragmatic pouch
Failure of muscle tissue from body wall to extend into pleuroperitoneal
membraneSuperior displacement of abdominal viscera into pouch
Congenital Hiatal Hernia
Herniation of fetal stomach through excessively large esophageal hiatus
(opening through which esophagus & vagus nerve pass)
Uncommon congenital defect
(acquired lesion occur during adult)