Database Normalization Il-Han Yoo CS 157A Professor: Sin-Min Lee.
-
date post
21-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Database Normalization Il-Han Yoo CS 157A Professor: Sin-Min Lee.

Database Database NormalizationNormalization
Il-Han Yoo
CS 157A
Professor: Sin-Min Lee

Database normalization relates to the level of redundancy in a relational database’s structure.
The key idea is to reduce the chance of having multiple different version of the same data.
Well-normalized databases have a schema that reflects the true dependencies between tracked quantities.
Any increase in normalization generally involves splitting existing tables into multiple ones, which must be re-joined each time a query is issued.
Database NormalizationDatabase Normalization

Normal FormsNormal Forms
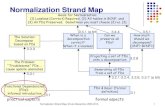
Edgar F. Codd originally established three Edgar F. Codd originally established three normal forms: 1NF, 2NF and 3NF.normal forms: 1NF, 2NF and 3NF.
3NF is widely considered to be sufficient. 3NF is widely considered to be sufficient. Normalizing beyond 3NF can be tricky with Normalizing beyond 3NF can be tricky with
current SQL technology as of 2005current SQL technology as of 2005 Full normalization is considered a good exeFull normalization is considered a good exe
rcise to help discover all potential internal rcise to help discover all potential internal database consistency problems.database consistency problems.

First Normal Form ( 1NF )First Normal Form ( 1NF )
““What is your favorite color?”What is your favorite color?”
““What food will you not eat?”What food will you not eat?”
TABLE 1TABLE 1 Person / Favorite ColorPerson / Favorite Color Bob / blue Bob / blue Jane / green Jane / green
TABLE 2TABLE 2 Person / Foods Not EatenPerson / Foods Not Eaten Bob / okra Bob / okra Bob / brussel sprouts Bob / brussel sprouts Jane / peas Jane / peas

Second normal Form ( 2NF )Second normal Form ( 2NF )
2NF prescribes full functional dependency on the pr2NF prescribes full functional dependency on the primary key.imary key.
It most commonly applies to tables that have compIt most commonly applies to tables that have composite primary keys, where two or more attributes coosite primary keys, where two or more attributes comprise the primary key.mprise the primary key.
It requires that there are no non-trivial functional deIt requires that there are no non-trivial functional dependencies of a non-key attribute on a part (subset) pendencies of a non-key attribute on a part (subset) of a candidate key. A table is said to be in the 2NF iof a candidate key. A table is said to be in the 2NF if and only if it is in the 1NF and every non-key attribf and only if it is in the 1NF and every non-key attribute is irreducibly dependent on the primary key ute is irreducibly dependent on the primary key

2NF Example2NF Example
PART_NUMBER PART_NUMBER (PRIMARY KEY) (PRIMARY KEY) SUPPLIER_NAMESUPPLIER_NAME (PRIMARY KEY) (PRIMARY KEY) PRICE PRICE
SUPPLIER_ADDRESS SUPPLIER_ADDRESS
• The PART_NUMBER and SUPPLIER_NAME form the composite primary key.• SUPPLIER_ADDRESS is only dependent on the SUPPLIER_NAME, and therefore this table breaks 2NF.

SUPPLIER_NAME (PRIMARY KEY) SUPPLIER_NAME (PRIMARY KEY) SUPPLIER_ADDRESS SUPPLIER_ADDRESS
2NF Example (Con’t)2NF Example (Con’t)
•In order to find if a table is in 2NF, ask whether any of the non-key attributes of the table could be derived from a subset of the composite key, rather than the whole composite key. •If the answer is yes, it's not in 2NF. •This is solved sometimes by using a correlation file, such as the supplier table above.

Third normal formThird normal form
• 3NF requires that there are no non-trivial functional dependencies of non-key attributes on something other than a superset of a candidate key.
• A table is in 3NF if none of the non-primary key attributes is a fact about any other non-primary key attribute.
• In summary, all non-key attributes are mutually independent.

3NF Example3NF ExamplePART_NUMBER (PRIMARY KEY) PART_NUMBER (PRIMARY KEY) MANUFACTURER_NAME MANUFACTURER_NAME MANUFACTURER_ADDRESS MANUFACTURER_ADDRESS
MANUFACTURER_NAME (PRIMARY KEY) MANUFACTURER_NAME (PRIMARY KEY) MANUFACTURER_ADDRESS MANUFACTURER_ADDRESS
PART_NUMBER (PRIMARY KEY) PART_NUMBER (PRIMARY KEY) MANUFACTURER_NAME MANUFACTURER_NAME

ExampleExample
Problems ?
1.Not very efficient with storage
2.This design does not protect data integrity
3.This table does not scale well

First Normal Form


Defining Relationships
•One to One
•One to Many
•Many to Many

Second Normal Form



Third Normal Form
•This new table violate Second Normal Form as the street and city will be verically redundant.
•Province will need to be in its own table which the city table will refer to as a foreign key.

Boyce-Codd normal form (BCNF)Boyce-Codd normal form (BCNF)
• BCNF requires that there are no non-trivial functional dependencies of attributes on something other than a superset of a candidate key (called a superkey).
• All attributes are dependent on a key, a whole key and nothing but a key (excluding trivial dependencies, like A->A).

• A table is said to be in the BCNF if and only if it is in the 3NF and every non-trivial, left-irreducible functional dependency has a candidate key as its determinant.
• In more informal terms, a table is in BCNF if it is in 3NF and the only determinants are the candidate keys.

Fourth normal form Fourth normal form (4NF)(4NF) 4NF4NF requires that there are no non-trivial m requires that there are no non-trivial m
ulti-valued dependencies of attribute sets ulti-valued dependencies of attribute sets on something else than a superset of a caon something else than a superset of a candidate key (called a superkey).ndidate key (called a superkey).
A table is said to be in 4NF if and only if it A table is said to be in 4NF if and only if it is in the BCNF and multi-valued dependencis in the BCNF and multi-valued dependencies are functional dependencies. ies are functional dependencies.

4NF Example4NF ExampleEMPLOYEE_ID EMPLOYEE_ID
QUALIFICATION_ID QUALIFICATION_ID
TRAINING_COURSE_ID TRAINING_COURSE_ID
employee_qualification table: EMPLOYEE_ID employee_qualification table: EMPLOYEE_ID QUALIFICATION_ID QUALIFICATION_ID
employee_training_course table: EMPLOYEE_ID employee_training_course table: EMPLOYEE_ID TRAINING_COURSE_ID TRAINING_COURSE_ID

EMPLOYEE_ID EMPLOYEE_ID
DEGREE_ID DEGREE_ID
UNIVERSITY_ID UNIVERSITY_ID
4NF Expample (con’t)4NF Expample (con’t)
•This would require no changes to fit the fourth normal form requirements.

Fifth normal form (5NF and also Fifth normal form (5NF and also PJ/NF)PJ/NF)
5NF requires that there are no non-5NF requires that there are no non-trivial join dependencies that not trivial join dependencies that not follow from the key constraints.follow from the key constraints.
A table is said to be in the 5NF if and A table is said to be in the 5NF if and only if it is in 4NF and every join only if it is in 4NF and every join dependency in it is implied by the dependency in it is implied by the candidate keys.candidate keys.

Domain/key normal form(DKNF)Domain/key normal form(DKNF)
DKNF requires that each key DKNF requires that each key uniquely identifies each row in a uniquely identifies each row in a table. table.
A domain is the set of permissible A domain is the set of permissible values for an attribute. values for an attribute.
By enforcing key and domain By enforcing key and domain restrictions, the database is assured restrictions, the database is assured of being freed from modification of being freed from modification anomalies.anomalies.

While sometimes called the 6NF, the DKNF While sometimes called the 6NF, the DKNF should not be considered together with the should not be considered together with the seven other normal forms (1–6 and Boyce-seven other normal forms (1–6 and Boyce-Codd), because contrary to them it is not aCodd), because contrary to them it is not always achievable; furthermore, tables in thlways achievable; furthermore, tables in the real 6NF are not always in the DKNF.e real 6NF are not always in the DKNF.

Sixth normal form(6NF)Sixth normal form(6NF) This normal form was, as of 2005, only recently This normal form was, as of 2005, only recently
conjectured: the sixth normal form (6NF) was onlconjectured: the sixth normal form (6NF) was only defined when extending the relational model to y defined when extending the relational model to take into account the temporal dimension (ie. timtake into account the temporal dimension (ie. time). e).
Unfortunately, most current SQL technologies as Unfortunately, most current SQL technologies as of 2005 do not take into account this work, and of 2005 do not take into account this work, and most temporal extensions to SQL are not relationmost temporal extensions to SQL are not relational.al.