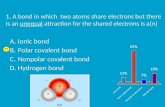
Ionic bond Polar covalent bond Nonpolar covalent bond Hydrogen bond
Covalent Bonding Objectives: 1. Describe the characteristics of a covalent bond. 2. Describe the...
-
Upload
baldwin-booker -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of Covalent Bonding Objectives: 1. Describe the characteristics of a covalent bond. 2. Describe the...

Covalent Bonding
Objectives:• 1. Describe the characteristics of a covalent bond.• 2. Describe the difference between polar and
nonpolar covalent bonds.Key Terms:• Molecule, molecular substance, molecular formula,
structural formula, Lewis structure, unshared pair, single covalent bond, double covalent bond, triple covalent bond, polar, nonpolar

Covalent Bonds• A covalent bond is one where the electrons are shared. • A group of covalently bonded atoms is called a molecule.
– These molecular substances include DNA, sugar and carbon dioxide. The molecules can contain as few as 2 atoms and as many as a million.
• Rules for covalent bonds: – electrons are shared in covalent molecules – covalently bonded molecules follow the octet rule (some exceptions -
BF3) – atoms will share electrons in order to fill their valence orbitals – covalent molecules can form single, double, or triple bonds – covalent bonds can be rearranged to form different molecules (glucose,
fructose, & maltose)

Properties of Molecules
• relatively low boiling points• present in all phases• poor conductors of heat and charge• usually dull in appearance• not malleable or ductile

Types of Covalent Bonds
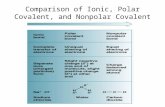
• Most covalent bonds are slightly polar in nature– Electrons are unequally shared between atoms due to
electronegativity differences between the atoms• < 0.4 non-polar covalent• 0.4 – 1.9polar covalent• > 1.9 ionic
Example: Water (H2O)• electronegativity of H = 2.1 • electronegativity of O = 3.5
– Difference 3.5 – 2.1 = 1.4 polar covalent

Formulas - Empirical
• lists atom ratios in the ratios that are present in the molecules
• not good for describing covalently bonded molecules – (CH2O)n is wood, sugar, lactic acid, etc ...

Formulas - Molecular
• lists the atoms in the found in the molecule without reducing
• better that the empirical formula but not the best for describing molecules – C6H12O6 - fructose, C6H12O6 - glucose, C6H12O6 -
galactose

Formulas - Structural
• shows where the individual atoms are bonded • Lewis structures are an example of this type of
formula • Dashes are a shorthand way of showing bonds – Each represents 2 electrons

Formulas – Ball-n-Stick
• shows the 3 dimensional structure of the molecule