Class 02(Epithelium)
-
Upload
eric-cannon -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Class 02(Epithelium)
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 1/30
Cells which have similar
Morphologic characteristics
and functions
Intercellular substance
—— more or little
Tissue
Four basic types of tissues ——
Epithelial tissue
Connective tissueMuscular tissue
Nervous tissue
These tissues associate one and
another in variable proportions,
forming different organs and systems
of the body.
Epithelial tissue
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 2/30
1. Location:
on the surface of body as sheets
(external or internal )
e.g. skin, digestive tract, bladder, blood vessel,
body cavity (pleural cavity
pericardial cavity
abdominal cavity)
2. Function
Protection :
protect organs and body from physical,
chemical, biological damage
Absorption : nutrients are absorbed in
gastro-intestinal tract
Secretion : e.g. the epi. cells of gland
Sensation : receive the stimulus of chemistry or
physics,
e.g. olfactory epi. cells
Transportation :
the epithelial cells can transportions(electrolytes), e.g. in kidney
Contractility : myoepithelial cells
Reproduction:
e.g. germinal epithelium in the testis
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 3/30
3. General structural features
Sheets : Many cell a little intercellular substance
* cells are closely aggregated together forming a thin membrane
* intercellular substance is homogeneous
* adhesion between cells is strong
Polarisation :
epithelial cells have free surface and basal surface.
In different surface,
the structure and function are different
Avascularity: Generally, there are no blood vessels
in epithelium tissue.
Innervation:
Epithelium is rich in nerve ending
between epithelial cells.
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 4/30
II. The Classification of Epithelial tissue
According to their functions, epi. can be classified into :covering epi.
glandular epi.
sensory epi.
myoepitheliumgerminal epi.
III . Covering epithelium
I)
classification of covering epi.
1
The principles of classification in covering epi.
1) Cell shape :
polygonal in superficial view, three main types of cell in vertical section
columnar 柱状 height > width
cuboidal 立方 height = width
squamous 扁平 height < width
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 5/30
(2) number of the cell layer
simple layer —— simple epi.
stratified layer —— stratified epi.
(more than one layer 复层 )
squamous
Cuboidal
columnar
Simple
Stratified
2 How to name:
(superficial layer)
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 6/30
( II) Common type of covering epi.1 simple squamous epithelium
(单层扁平上皮)
Facilitates movement of viscera.
Active transport by pinocytosis.
in circulatory system —— endothelium (内皮
)
in body cavity —— mesothlium (间皮)
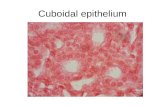
2 simple cuboidal epithelium
(单层立方上皮)
covering ovary, thyroid, kidney… Covering
Secretion
absorption
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 7/30
3 simple columnar epithelium
lining gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder...
Absorption;
Protection;
Secretion ---goblet cell
lubrication
4 pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Pseudo —— false
columnar, fusiform, pyramid, goblet
Some cells are higher, some are shorter,
their nuclei are at different levels and not all cells reach to
surface
but all cells attach to
basement membrane
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 8/30
Lining of respiratory tract
Protection, Secretion,
Transport of particles out of air passages
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 9/30
5、 Stratified squamous epithelium
(复层扁平上皮)stratif ied squamous
Keratinized (角化的) epi. —— skin
stratif ied squamous
Nonkeratinized (未角化的) epi.
—— mouth, esophagus
vagina, anal canal
Protection
Withstand wearing and tearing
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 10/30
6、 transitional epithelium
(变移上皮)
lining of urinary tract
(urinary bladder, ureter)
cell layer & cell shape can change
according to the degree of
distention of organs
Protection
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 12/30
LM: * brush border (刷状缘) —— kidney
* striated border (纹状缘) —— intestine
EM: fingerlike projection surface —— cell membrane, cell coat
core —— cytoplasm
(contain microfilaments)
Function: enlarge the surface of cells
(2) cilium (纤毛)
—— larger, longer and motile;
5-10μlong, 0.2μin diameterEM:
a central pair of microtubules
9 pairs of microtubules
9+2” arranged in a circle
Function:
make the fluid flow in one direction
by their rapid back-forth movement
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 13/30
cell cohesion:Cell cohesion between epithelium cells related to
*glycoproteins, proteoglycans, calcium…
However, the most important factors in cell
cohesion are special
—— intercellular junctions
which are specialization of lateral cell membrane.
• tight junction
• intermediate junction
• desmosome
• gap junction
2
lateral surface
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 14/30
near the lumen,
the outer lamina of
two adjacent cell membrane are fused into one
(1)Tight junction紧密连接
(zonula occludens闭锁小带)
zonula: this J form a band completely
encircling the cell
occludens: membrane fusion close off
the intercellular space
Function: to form a tight seal —— barrier
preventing the free passage of
materials across epi.
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 15/30
belt-like
But the outer lamina of cell membrane are
not fused , just adhered.
Function: adhere the cells together
(2)intermediate junction 中间连接 (zonula adherens粘着
小带)
(3) desmosome 桥粒 (macula adherens粘着斑)
elliptic patch(disk-like) —— attachment plaques
intermediate filaments (loop-like structure)
intermediate line
Function: make the cells bind together very tightly
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 16/30
(4) gap junction 缝隙连接
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 17/30
like a patch:
some tubules connect cells
Tubule-
consists of six subunits;
center is a 0.5 nm hydrophilic canal
which permit interchange of ions
Function: interchange information
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 18/30
junctional complex
(连接复合体)
two or more junctions get together
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 19/30
3、Basal surface
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 20/30
(1) basement membrane(基膜)
LM: homogeneous,acidophilic thin membrane
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 21/30
EM: basement lamina 基板
reticular lamina网板
(somewhere,the reticular lamina is absent,
and could not be seen in LM)
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 22/30
Function:
① support,connect,anchor the epi.
② orient epithelial cells location
③ selective barrier
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 23/30
2) plasma membrane infolding
(质膜内褶
)
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 24/30
LM: longitudinal striation in basal partof epi cells
EM: The cell membrane of basal surface
invaginate into cell body.
Mitochondria distribute between
these infolings.
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 25/30
Function:
• enlarge the surface of cell membrane
• Present in the cells which transport ions
and water.
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 26/30
(3) Hemidesmosome半桥粒
• Between some epithelial cells and basal lamina
• half a desmosome on the epitheliul cell membrane
•
bind the epithelial cells to basal lamina.
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 27/30
IV . Glandular epithelium (腺上皮)
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 28/30
Glandular epithelia —— tissues formed by cells specialized
to produce a fluid secretion
Gland ——
organ mainly formed by
Glandular epithelia
8/11/2019 Class 02(Epithelium)
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/class-02epithelium 29/30
Exocrine gland
Endocrine gland
Unicellular gland
multicellular gland