Epithelium i
-
Upload
kohlschuetter -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.555 -
download
5
Transcript of Epithelium i

Epithelial tissuesEpithelial tissues I.I.

1.1. Simple squamous epitheliumSimple squamous epithelium2.2. Simple cuboidal epithelium Simple cuboidal epithelium 3.3. Simple columnar epithelium Simple columnar epithelium 4.4. Pseudostratified columnar Pseudostratified columnar
epithelepitheliium with ciliaum with cilia

Characteristics of the epithelial cellsCharacteristics of the epithelial cells::
They are tightly packed together with They are tightly packed together with very little intercellular very little intercellular matrixmatrix. (Intercellular junctions: . (Intercellular junctions: t ight junct ions, zonulae t ight junct ions, zonulae adherentes, desm osom es, gap junct ionsadherentes, desm osom es, gap junct ions). ). Epithelia are derived Epithelia are derived from all three em bryonic germ layersfrom all three em bryonic germ layers..The principal functions of epithelial tissues are The principal functions of epithelial tissues are covering and covering and lining of surfaceslining of surfaces ((covering epitheliacovering epithelia ), ), absorpt ion of absorpt ion of subtances subtances ((absorpt ive epitheliumabsorpt ive epithelium ), ), secret ion of secret ion of subsubsstancestances ((glandular epitheliumglandular epithelium ), ), sensationsensation ((sensory sensory epithelium/neuroepitheliumepithelium/neuroepithelium).).The epithelial cells rest on a The epithelial cells rest on a basem ent m em branebasem ent m em brane (lamina (lamina lucidalucida + lamina densa+ lamina densa + lamina fibroreticularis), and are + lamina fibroreticularis), and are connected to this membrane by connected to this membrane by hemihemi-- desmosomesdesmosomes..The apical surface of the epithelial cells may be equipped The apical surface of the epithelial cells may be equipped with structures that greatly with structures that greatly increase the surface area increase the surface area (microvilli, stereocilia), and structures which are (microvilli, stereocilia), and structures which are responsible for responsible for motilitymotility (kinocilia, flagellum).(kinocilia, flagellum).

The simple squamous epithelium consists of a single row of The simple squamous epithelium consists of a single row of flattened cells. In cross section the cytoplasm of these cells flattened cells. In cross section the cytoplasm of these cells is extremely attenuated, so that it is hardly visible. The part is extremely attenuated, so that it is hardly visible. The part of the cell containing the nucleus is enlarged, the nucleus of the cell containing the nucleus is enlarged, the nucleus stands out in relief.stands out in relief.
Location: squamous alveolar cells in the lung (type I Location: squamous alveolar cells in the lung (type I pneumocytes), parietal wall of the renal Bowman capsule, pneumocytes), parietal wall of the renal Bowman capsule, the narrow segment of renal loop of Henle.the narrow segment of renal loop of Henle.
Special types of simple squamous epithelium:Special types of simple squamous epithelium:1. Endothelium: epithelium lining the inner surface of the 1. Endothelium: epithelium lining the inner surface of the heart and blood vesselsheart and blood vessels2. Mesothelium: epithelium of serous membranes lining 2. Mesothelium: epithelium of serous membranes lining certain body cavities (pericardium,certain body cavities (pericardium, pleura,pleura, peritoneum)peritoneum)

Simple squamous epitheliumSimple squamous epithelium1.Mesenterium (Ag)1.Mesenterium (Ag)
Actually it is not a section, Actually it is not a section, but a very thinly stretched but a very thinly stretched membrane (mesenterium membrane (mesenterium of frog or rat), and each of frog or rat), and each side of this membrane side of this membrane presents mesothel cells presents mesothel cells arranged mosaically, side arranged mosaically, side by side.by side.
The cellThe cell--boundaries are boundaries are visible by silver nitrate visible by silver nitrate treatment as silver treatment as silver granules deposit in the granules deposit in the intercellular spaces.intercellular spaces.
Mesothelcells

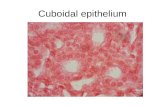
It is formed by one row of cuboidal cells that possess It is formed by one row of cuboidal cells that possess spherical nucleispherical nuclei..
Location:Location:FolFollliciclesles of the thyroid glandof the thyroid glandDistal and proximal renal tubulesDistal and proximal renal tubulesEpithelium germinativum covering the ovaryEpithelium germinativum covering the ovaryAmniotic epitheliumAmniotic epithelium
The cuboidal cells may have resorbing function, The cuboidal cells may have resorbing function, presenting presenting micrm icroovilliv illi attached to their apical surface attached to their apical surface (e.g. proximal renal tubules).(e.g. proximal renal tubules).

Simple cuboidal epithelium:Simple cuboidal epithelium:68. Thyroid gland (HE)68. Thyroid gland (HE)
The simple cuboidal The simple cuboidal epithelium of the follicles epithelium of the follicles represent an epithelium of represent an epithelium of both covering and both covering and endocrine glandular type endocrine glandular type involved in the secretion of involved in the secretion of thyroxin. The cells are thyroxin. The cells are flattened in hypofunction flattened in hypofunction of the gland, and they are of the gland, and they are taller in hyperfunction.taller in hyperfunction.The cell boundaries are The cell boundaries are hardly visible, and the hardly visible, and the cuboidal epithelium might cuboidal epithelium might be recognized according to be recognized according to the spherical shape of the the spherical shape of the nuclei.nuclei.
FolliclesCell nuclei

Simple columnar epitheliumSimple columnar epithelium::
It consists of a single row of cells that have cylindrical or It consists of a single row of cells that have cylindrical or prismatic shape and oval nuclei.prismatic shape and oval nuclei.
Location:Location:In the digestive tract from the In the digestive tract from the cardiacardia to the anal canal.to the anal canal.Striated ducts of the salivary glandsStriated ducts of the salivary glandsEpithelium of the uterus Epithelium of the uterus
Cells that have resorbing function present brush border Cells that have resorbing function present brush border formed by microvilli that are disposed on the apical surface.formed by microvilli that are disposed on the apical surface.
Location of the simple columnar epithelium with brush Location of the simple columnar epithelium with brush border:border:
Small and large intestineSmall and large intestine
Location of the simple ciliated columnar epitheliumLocation of the simple ciliated columnar epithelium::OviductOviduct

Simple columnar epithelium:Simple columnar epithelium:49. Gallbladder (HE)49. Gallbladder (HE)
The inner surface of the The inner surface of the gallbladder is lined by gallbladder is lined by simple columnar simple columnar epithelium equippedepithelium equipped with with brush border.brush border.
The cell boundaries are not The cell boundaries are not clearly visible, but this clearly visible, but this form of epithelium maform of epithelium may y be be recognized by the oval recognized by the oval nuclei disposed in one row. nuclei disposed in one row. The brush border exhibits The brush border exhibits positive PAS reaction.positive PAS reaction.
Oval cell nuclei

The cells form a single row, but their nuclei are disposed at The cells form a single row, but their nuclei are disposed at different levels so that it gives the illusion of stratificationdifferent levels so that it gives the illusion of stratification. . Every cell is lying on the basal membrane, thatEvery cell is lying on the basal membrane, that s why this is s why this is a type of simple epithelium. Cells that reach the surface a type of simple epithelium. Cells that reach the surface usually present cilia.usually present cilia.
Location of the pseudostratified epithelium with stereocilia:Location of the pseudostratified epithelium with stereocilia:Ductus epididymidis Ductus epididymidis Ductus deferens Ductus deferens
Location of the pseudostratified epithelium with kinocilia:Location of the pseudostratified epithelium with kinocilia:Respiratory tract to bronchiolesRespiratory tract to bronchiolesAuditory tube, lining of the tympanic cavityAuditory tube, lining of the tympanic cavityInner surface of the lacrimal sacInner surface of the lacrimal sac

The inner surface of the The inner surface of the trachea is covered by trachea is covered by pseudostratified pseudostratified epithelium with kinocilia.epithelium with kinocilia.
Goblet cells appear Goblet cells appear among the ciliated among the ciliated columnar cellscolumnar cells;; their their secretsecretionion product is not product is not stainable with H.E., but stainable with H.E., but exhibits positive PAS exhibits positive PAS reactionreaction..
The epithelial lining of the trachea
Unstained goblet cells

I dent ify the type of the epithelium I dent ify the type of the epithelium in the follow ing sect ions!in the follow ing sect ions!













1.1. Simple columnar epithelium (gallbladder)Simple columnar epithelium (gallbladder)2.2. Simple cuboidal epithelium (medulla of kidney)Simple cuboidal epithelium (medulla of kidney)3.3. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (respiratory tract)Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (respiratory tract)4.4. Simple columnar epithelium (small intestine)Simple columnar epithelium (small intestine)5.5. Simple ciliated columnar epithelium (oviduct)Simple ciliated columnar epithelium (oviduct)6.6. Simple cuboidal epithelium (medulla of kidney)Simple cuboidal epithelium (medulla of kidney)7.7. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (respiratory tract)Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (respiratory tract)8.8. Simple columnar epithelium (uterus)Simple columnar epithelium (uterus)9.9. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (tail of the Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (tail of the
epididymis)epididymis)10.10. MesotheliumMesothelium11.11. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (tail of the Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium (tail of the
epididymis)epididymis)