Chapter One Crystal Structure - ir.nctu.edu.tw · zPoint lattice – mathematical points in space a...
Transcript of Chapter One Crystal Structure - ir.nctu.edu.tw · zPoint lattice – mathematical points in space a...

1
Chapter One Crystal Structure
Drusy Quartz in Geode Tabular Orthoclase Feldspar Encrusting Smithsonite
Peruvian Pyrite
http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/xtal

2
Snow crystals
the Beltsville Agricultural Research Center

3
Solid : Crystal vs. Amorphous (glassy)
Ordered array of atoms Disordered arrangement
Competition between attractive (binding) force and repulsive force.
Regular array lowers system energy.
Complicated ! -- difficult to predict the structure of materials

4
☺ Importance : structure plays a major role indetermining physical properties of solids
☺ Determination : X-ray and neutron scattering are key toolsfor determining crystal structures. (bulk)
Also microscopic techniques such as SEM, TEM,STM, AFM… (surface)
☺ Deviations : There is no perfect crystal. Many key properties depend on deviation more. Defects – imperfection in crystal Phonons – lattice vibrations

5
Calcite(CaCO3) crystal is made from spherical particles.
Christiaan Huygen, Leiden 1690
A crystal is made from spherical particles.
Robert Hooke, London 1745
depicted by René Haüy, Paris, 1822

6
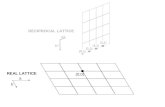
Crystalperiodic array of atoms : point lattice + basis
Point lattice – mathematical points in space
vectorslatticea,a,a
integeru,u,uauauaurr
321
321
332211
=
∈+++=′
r
2ar
1ar

7
Primitive lattice cell
2 Dimensions
• A cell will fill all space by the repetition of suitable crystaltranslation operations. ---- A minimum volume cell.⊗.One lattice point per primitive cell. ⊗.The basis associated w/. a primitive cell -- a primitive basis⊗.Not unique.
2ar
1ar
φsinaa
aaA
21
21cellrr
rr
=
×=
Same for all primitive cells
Uniform mass density
Wigner-Seitz Primitive cell -- lattice point is at its center
the highest symmetry cell possible

8
Wigner-Seitz Primitive cell in 2D (or 3D)
⊗ Draw lines to connect a given lattice point to all nearby lattice points.⊗. Draw bisecting lines (or planes) to the previous lines.⊗. The smallest area (or volume) enclosed.
2 D Oblique Lattice

9
Fundamental types of Bravais lattices
Based on symmetries :
1) Translational – same if translate by a vector
2) Rotational – same if lattice is rotated by an angle about a point2-fold by 180o 4-fold by 90o
3-fold by 120o 6-fold by 60o
3) Mirror symmetry – same if reflected about a plane
4) Inversion symmetry – same if reflected through a point (equivalent to rotation 180o and mirror ⊥ rotational axis r → -r
332211 auauauT ++=Auguste Bravais

10
Five Bravais lattices in two dimensions
Square lattice a1=a2, φ=90o
Unit cellSymmetry element
1ar2ar φ
Rectangular lattice a1≠a2, φ=90oSymmetry elementUnit cell

11
Oblique lattice a1≠ a2, φ≠60o,90oSymmetry elementUnit cell
a1= 2a2cosφCentered Rectangular latticeSymmetry element
φ1ar
2arUnit cell

12
a1=a2, φ=60oHexagonal lattice
Symmetry element
Unit cell twofold axis (dia)
threefold axis (triad)
fourfold axis (tetrad)
sixfold axis (hexad)
mirror line

13
A Bravais lattice is a lattice in which every lattice point has exactly the same environment.
A honeycomb crystal = A hexagonal lattice + two-pint basis
How about a honeycomb lattice ?

14
The seven crystal systems divided into fourteen Bravais lattices
One 3-foldrotation axis
a1 = a2≠a3
α = β = 90o, γ =120o1: SimpleHexagonal
One 3-fold rotation axis
a1 = a2 = a3
α = β = γ<120o≠ 90o1: SimpleTrigonal
Four 3-fold rotation axes
a1 = a2 = a3
α = β = γ = 90o3: Simple, BCC, FCCCubic
One 4-fold rotation axis
a1 = a2≠a3
α = β = γ = 90o2: Simple, BCCTetragonal
Three mutually orthogonal 2-fold
rotation axes
a1≠a2≠a3
α = β = γ = 90o4: BCC, FCCSimple, Base-Centered
Orthorhombic
One 2-fold rotation axis
a1≠a2≠a3
α = β = 90o ≠ γ2: Simple, Base-Centered
Monoclinic
Nonea1≠a2≠a3
α≠ β≠ γ1: SimpleTriclinic
Characteristic symmetry elements
Unit cell characteristics
Number of latticesSystem

15
a1≠a2≠a3TRICLINIC (α≠β≠γ)
三斜晶系
a1
a2
a3
α
γ
β
a1
a3
a2
MONOCLINIC (β=γ=90o ≠ α)單斜晶系
Simple
Simple Base-centered

16
a1≠a2≠a3Orthorhombic (α=β=γ=90o)正交晶系
Base-centered BCC
a1
a2
a3
α
γβ
Simple
FCC

17
a1≠aTetragonal (α=β=γ=90o)
正方晶系
a
a1
a
α
γ
β
BCCSimple

18
Cubic (α=β=γ=90o)
立方晶系
a
a
a
α
γ
β
FCCSimple BCC

19
Hexagonal (α=β=90o, γ=120o)
Trigonal(α=β=γ<120o , ≠90o )
a
aa3
γ=120o
a3≠a六角晶系三角(菱面)晶系
aa
a
Simple
Simple

20
Characteristics of cubic lattices
Packing fraction
Nearest- neighbor distance
1286Number of nearest neighbors
421Lattice points/cell
Face-centeredBody-centeredSimple
2a
a23a
524.06=
π680.0
83
=π 740.062
=π
Maximum, same as hexagonal

21
Crystal – Periodic arrangement of atoms
Bravais lattice + Basis of atom(Array of point in space) (Arrangement of atoms within unit cell)
2 Dimensions → 5 types
3 Dimensions → 14 typesBy symmetry
Crystal may have same or less symmetry than original Bravais lattice.
Basis
Symmetry “4mm”

22
Introducing new symmetries for basis with multiple atoms :
• Point group symmetries : combinations of rotation, inversion, reflection that hold one point fixed and return original structure.
2 Dimensions , 103 Dimensions , 32
• Space group symmetries : point group operations + translations that return original structure.2 Dimensions , 173 Dimensions , 230
There are many possible types by symmetry but most are never observed.
Real crystals form a few types due to energies of crystal formation.

23

24
Directions and planes in crystalsUseful to develop a notation for describing directions and
identifying planes of atoms in crystals
Consider lattice defined by
Vector direction is described as [u1 u2 u3]
where u1, u2, and u3 are the lowest reduced integers.
321 a ,a ,a
332211 auauaur ++=r
Note :
• [8 6 0] same as [4 3 0]
• use ū instead of -u
• [u1 u2 u3] not as the same as Cartesian coordinate direction except for simple cubic crystal
] 1 2 1 [

25
[ 1 1 0 ]
[ 1 1 1 ]
[ 1 0 0 ]
[ 0 0 1 ]
[ 0 1 0 ]
Cubic has highest symmetric directions
By symmetry, [ 1 0 0 ], [ 0 1 0 ], [ 0 0 1 ] are equivalent
] 1 0 0 [ ], 0 1 0 [ ], 0 0 1 [Denote { 1 0 0 } ≡ set of equivalent directions

26
Crystal planes – atoms fall on planes labeled by “Miller indices”
Note :
• Find the intercepts on the axes in terms of a1, a2, and a3 → h’ k’ l’
• Take reciprocals and make integers
• Reduce to smallest three integers
• If the plane does not intersect one of the crystal axes, that intercept is taken to be infinitely far from the origin and the corresponding index is zero.
''kh') '
1 k'1
h'1 ( l
l×
( h k l ) is called Miller index of the plane
Miller indices specify a vector normal to the plane, and not a specific plane : all parallel planes have the same indices

27
(25)
2ar
1ar
Schematic illustrations of lattice planesLines in two dimensional crystals
(01)
(11)
Low index plane : more dense and more widely spaced
High index plane : Less dense and more closely spaced

28
Most common crystal structures :
Simple Cubic lattice : Po conventional cell : 1 atom/cube
Body Centered Cubic lattice :
Conventional cell : 2 atoms/ cube
(0,0,0)
(1/2,1/2,1/2)
Not a primitive lattice
8 nearest neighbors
Alkali metals : Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs
Ferromagnetic metals : Cr, Fe
Transition metals : Nb, V, Ta, Mo, W
• BCC lattice + single atom basis
• SC lattice + basis of 2 atoms at (0,0,0) and (1/2,1/2,1/2)

29
Body Centered Cubic lattice
x
z
ya1
a2a3
)zyx(2aa
)zyx(2aa
)zyx(2aa
3
2
1
+−=
++−=
−+=

30
Body-centered Cubic lattice
Primitive cell :
Rhombohedron
w/.
1. edge
2. the angle between two adjacent edges is 109o28’
a23

31
Face Centered Cubic lattice :
Conventional cell : 4 atoms/ cube
(0,0,0)
(1/2,1/2,0)
(1/2,0,1/2)(0,1/2,1/2)
Not a primitive lattice
12 nearest neighbors
Noble metals : Cu, Ag, Au
Transition metals : Ni, Pd, Pt,
Inert gas solids : Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe
• FCC lattice + single atom basis
• SC lattice + basis of 4 atoms at (0,0,0), (1/2,1/2,0) (1/2,0,1/2), and (0,1/2,1/2)

32
Face Centered Cubic lattice
xy
z
a1
a2
a3
)zx(2aa
)zy(2aa
)yx(2aa
3
2
1
+=
+=
+=
The angle between two adjacent edges : 60o
Edge a22Rhombohedral Primitive cell

33
Hexagonal Close-Packed lattice
a1, a2, and c do not construct a primitive lattice
a1, a2, and a3 construct a primitive lattice
a633.1c
120 angle includedan with , aa
1
o21
=
=
a aa 321 ==
a1
a2
c
Basal Plane
a3 12 nearest neighbors
Transition metals : Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Co…
IIA metals : Be, Mg
Hexgonal lattice + basis of 2 atoms at (0,0,0) and (2/3,1/3,1/2)

34
HCP lattice A B A B A B …
x
y
z
FCC lattice A B C A B C A B C …

35
Diamond structure : two FCC displaced from each other by ¼of a body diagonal
0
0
0
0
0
1/2
1/2
1/2 1/2
1/4
1/43/4
3/4
FCC lattice + basis of 2 atoms at (0,0,0) and (1/4,1/4,1/4)
Tetrahedral bonding : 4 nearest neighbors12 next nearest neighbors
The maximum packing fraction = 0.34Si, Ge, Sn, C, ZnS, GaAs, …

36
Some atoms form multiple stable structures:for example, C→ diamond or graphite (hexagonal)
An STM image of a graphite surfaceclearly shows the interconnected 6-membered rings of graphite

37
graphite diamond

38
Many crystals undergo structural changes with T, P:for example,
TemperatureFe 910oC 1400oC 2100oC
LiquidBCCFCCBCC
δ-ferrite α-ferrite
TemperatureNa 36K 371K
LiquidFCCHCP

39
Compounds
NaCl structures NaCl, NaF, KCl, AgCl, MgO, MnO, …
• FCC lattice + basis of two atoms
• Cl (0,0,0), Na (1/2,1/2,1/2)
SC w/. alternating atoms
CsCl structures CsCl, BeCu, ZnCu(brass), AlNi, AgMg, …
• SC lattice + basis of two atoms
• Cs (0,0,0), Cl (1/2,1/2,1/2)
BCC w/. alternating atoms

40
ZnS, CuF, CuCl, … compounds
CdS Photoconductor
GaAs, GaP, InSb, … III-V semiconducting compounds
ZnS structures
Znicblende
• FCC lattice + basis of two atoms• Zn (0,0,0), S (1/4,1/4,1/4)• Ga(0,0,0), As(1/4,1/4,1/4)
diamond w/. alternating atoms

41

42
High Tc superconductors
a b
c
Orthorhombic O(I) (Pmmm)
O(3)
Cu(2)
Cu(1)
O(1) Ba/Pr
PrO(4)
O(2)
O(5)
Tetragonal T (P4/mmm)
Ba/Pr
Pr
O(2)
O(1)
O(3)
Cu(2)
Cu(1)
Ba/Pr
Pr
O(2)
O(1)
Cu(2)
Cu(1)O(3)
Orthorhombic O(II) (Cmmm)

43
C-60
“Bucky balls”
BuckminsterFullurene