Medical terminology terminology Of Of urinary system urinary system.
Chapter 9 Medical Terminology and Chapter 20 Body Structures: THE URINARY SYSTEM
-
Upload
katelyn-hogan -
Category
Documents
-
view
29 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Chapter 9 Medical Terminology and Chapter 20 Body Structures: THE URINARY SYSTEM

Chapter 9 Medical Chapter 9 Medical TerminologyTerminology
andandChapter 20 Body Chapter 20 Body
Structures:Structures:
THE URINARY SYSTEMTHE URINARY SYSTEM

FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEMSYSTEM
• Balances water, salts, and acids by Balances water, salts, and acids by removing excess fluids or reabsorbing removing excess fluids or reabsorbing water as neededwater as needed
• Filters the blood to remove urea (major Filters the blood to remove urea (major waste product of protein metabolism) waste product of protein metabolism) and other waste materials and other waste materials
• Converts waste products and excess Converts waste products and excess fluids into urine in the kidneys and fluids into urine in the kidneys and excretes them from the body thru the excretes them from the body thru the urinary bladderurinary bladder
**all functions required to maintain homeostasis in body

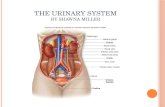
STRUCTURES OF THE URINARY STRUCTURES OF THE URINARY SYSTEMSYSTEM
• The KidneysThe Kidneys– The Renal PelvisThe Renal Pelvis– The NephronsThe Nephrons
• The UretersThe Ureters– 10 – 12 inches long, carry urine from each 10 – 12 inches long, carry urine from each
kidney to the urinary bladderkidney to the urinary bladder• The Urinary BladderThe Urinary Bladder
– Hollow muscular organ, reservoir for urineHollow muscular organ, reservoir for urine• The UrethraThe Urethra
– Extends from the bladder to the outside of Extends from the bladder to the outside of the bodythe body
www.sua.org.sg/ articles_1a.htm

THE KIDNEYSTHE KIDNEYS – – renal: pertaining torenal: pertaining to the kidney the kidney
• Constantly filtering blood Constantly filtering blood to remove waste and to remove waste and excess waterexcess water
• Location: Location: retroperitoneum, retroperitoneum, bilaterally below the bilaterally below the diaphragmdiaphragm
• Renal cortex: outer layer Renal cortex: outer layer of kidney, contains of kidney, contains nephronsnephrons
• Medulla: inner layer, Medulla: inner layer, contains urine-collecting contains urine-collecting tubulestubules
www.cornwallis.kent.sch.uk/.../ 1organs1.htm

THE NEPHRONSTHE NEPHRONS
• Functional units of the kidneysFunctional units of the kidneys• Form urine by the process of filtration, Form urine by the process of filtration,
reabsorption, and secretionreabsorption, and secretion• Glomerulus: cluster of capillaries Glomerulus: cluster of capillaries
surrounded by a membrane called the surrounded by a membrane called the Bowman’s CapsuleBowman’s Capsule
• Blood flows into kidney via the renal Blood flows into kidney via the renal artery, waste is filtered in the capillaries artery, waste is filtered in the capillaries of the glomerulus (urine), then blood of the glomerulus (urine), then blood leaves the kidney through the renal veinleaves the kidney through the renal vein
• Waste products are transported to the Waste products are transported to the renal pelvis before entering the uretersrenal pelvis before entering the ureters

• RENAL ARTERY (1)RENAL ARTERY (1)• RENAL VEIN (2)RENAL VEIN (2)• RENAL PELVIS (3)RENAL PELVIS (3)• MEDULLA (4)MEDULLA (4)• RENAL CORTEX (5)RENAL CORTEX (5)• URETER (6)URETER (6)• ????????????????????????????????????
???????? ???????? WHAT IS WHAT IS THE NAME OF THE THE NAME OF THE PIGMENT THAT PIGMENT THAT GIVES URINE IT’S GIVES URINE IT’S STRAW COLOR??STRAW COLOR??
• UROCHROMEUROCHROMEwww.revisioncentral.co.uk/.../ human_kidneys.html

THE URETHRATHE URETHRA• (2) Urinary sphincters: (2) Urinary sphincters: control the flow of control the flow of urine from the bladder urine from the bladder into the urethra into the urethra (proximally) and out of (proximally) and out of the urethra (distally) the urethra (distally) through the urethral through the urethral meatusmeatus
• Urinary meatus: Urinary meatus: external opening of the external opening of the urethraurethra
• The neck of the male The neck of the male urethra is surrounded urethra is surrounded by the prostate gland by the prostate gland www.4woman.gov/faq/ urinary.htm

THE EXCRETION OF URINETHE EXCRETION OF URINE
• Micturition Micturition (voiding)(voiding)– Requires coordinated Requires coordinated
contraction of the contraction of the bladder muscles and bladder muscles and relaxation of the relaxation of the sphincters, forcing the sphincters, forcing the urine through the urine through the urethra and out urethra and out through the urinary through the urinary meatusmeatus
www.upmccancercenters.com/.../ prostategland.html

MEDICAL SPECIALTIES RELATED TO THE MEDICAL SPECIALTIES RELATED TO THE URINARY SYSTEMURINARY SYSTEM
• Diagnoses and treats diseases and Diagnoses and treats diseases and disorders of the disorders of the kidneyskidneys
• NEPHROLOGISTNEPHROLOGIST• Diagnoses and treats diseases and Diagnoses and treats diseases and
disorders of the disorders of the urinary system of urinary system of females and the genitourinary system females and the genitourinary system of malesof males
• UROLOGISTUROLOGIST

PATHOLOGY OF THE URINARY PATHOLOGY OF THE URINARY SYSTEMSYSTEM
• Renal FailureRenal Failure– Anuria: complete suppression of urine Anuria: complete suppression of urine
formationformation– Uremia: toxic condition caused by excessive Uremia: toxic condition caused by excessive
amount of waste products in bloodstreamamount of waste products in bloodstream– Acute Renal Failure: sudden onset due to injury Acute Renal Failure: sudden onset due to injury
or surgeryor surgery– Chronic Renal Failure: progressive disease, Chronic Renal Failure: progressive disease,
may require dialysis or transplantationmay require dialysis or transplantation– End-Stage Renal Disease: ESRD late stages of End-Stage Renal Disease: ESRD late stages of
renal failurerenal failure• Nephrotic Syndrome: general group of kidney Nephrotic Syndrome: general group of kidney
diseasesdiseases

• KidneysKidneys– GlomerulonephritisGlomerulonephritis– Hydronephrosis: Hydronephrosis:
dilation of renal pelvis dilation of renal pelvis as a result of as a result of obstructionobstruction
– Nephritis: inflammation Nephritis: inflammation of the kidneyof the kidney
– Pyelitis: inflammation of Pyelitis: inflammation of the renal pelvisthe renal pelvis
– Pyelonephritis: Pyelonephritis: inflammation of the inflammation of the renal pelvis and of the renal pelvis and of the kidneykidney

• Stones (calculus)Stones (calculus)– Abnormal mineral Abnormal mineral
depositdeposit– Calculi vary in size Calculi vary in size – Named for the organ or Named for the organ or
tissue where they are tissue where they are locatedlocated• Nephrolithiasis:Nephrolithiasis:
characterized by the characterized by the presence of stones in presence of stones in the kidneythe kidney

• UretersUreters– HydroureterHydroureter: distention of the ureter with : distention of the ureter with
urine due to obstructionurine due to obstruction– Ureterectasis:Ureterectasis: distention of the ureter distention of the ureter – Ureterorrhagia: Ureterorrhagia: discharge of blood from discharge of blood from
the ureterthe ureter– Ureterostenosis:Ureterostenosis: stricture of the ureter stricture of the ureter

• Urinary BladderUrinary Bladder– Cystalgia: pain in the bladderCystalgia: pain in the bladder– Cystitis: inflammation of the bladderCystitis: inflammation of the bladder– Interstitial Cystitis: inflammation of the wall of Interstitial Cystitis: inflammation of the wall of
the bladderthe bladder– Cystocele: hernia of the bladder through the Cystocele: hernia of the bladder through the
vaginal wallvaginal wall– Cystorrhagia: bleeding from the bladderCystorrhagia: bleeding from the bladder– UTI: infections occur more frequently in womenUTI: infections occur more frequently in women– Vesicovaginal Fistula - abnormal opening Vesicovaginal Fistula - abnormal opening
between the bladder and the vaginabetween the bladder and the vagina

• UrethraUrethra– Reflux: Reflux: blockage of blockage of
the urethra causing the urethra causing urine to back up urine to back up into the uretersinto the ureters
– UrethralgiaUrethralgia– Urethrostenosis: Urethrostenosis:
stricture or stenosis stricture or stenosis of the urethraof the urethra
www.med.univ-rennes1.fr/cerf/ iconocerf/P/Doss...

• UrinationUrination– Diuresis:Diuresis: increased excretion of urine increased excretion of urine– Dysuria:Dysuria: difficult or painful urination – difficult or painful urination –
frequently associated with UTI’sfrequently associated with UTI’s– Enuresis:Enuresis: involuntary discharge of urine involuntary discharge of urine
(nocturnal enuresis)(nocturnal enuresis)– Nocturia:Nocturia: excessive urination during the excessive urination during the
nightnight– OliguriaOliguria: scanty urination: scanty urination– Urinary Retention:Urinary Retention: inability to void or empty inability to void or empty
the bladderthe bladder

• IncontinenceIncontinence: the : the inability to control inability to control excretory functionsexcretory functions– Urinary Urinary
IncontinenceIncontinence– Urinary Stress Urinary Stress
IncontinenceIncontinence– Urge Incontinence: Urge Incontinence:
urination occurs urination occurs involuntarily as involuntarily as soon as an urgent soon as an urgent desire to urinate is desire to urinate is feltfelt
www.upmc.edu/minsurg/ UrinaryStress.htm

DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES OF THE DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES OF THE URINARY SYSTEMURINARY SYSTEM
• Catheterization: insertion of a sterile Catheterization: insertion of a sterile catheter through the urethra, into the catheter through the urethra, into the bladderbladder– Performed to withdraw urinePerformed to withdraw urine– To relieve urinary retention pressuresTo relieve urinary retention pressures– To prevent incontinence during surgical To prevent incontinence during surgical
proceduresprocedures– May also be used to place fluids, such as May also be used to place fluids, such as
contrast (VCUG) in bladdercontrast (VCUG) in bladder
www.amershamhealth.com/medcyclopaedia/ Volume%...

• Cystoscopy:Cystoscopy: cysto – visual exam of cysto – visual exam of the urinary bladder using a the urinary bladder using a cystoscopecystoscope
• IVP:IVP: radiographic study of the radiographic study of the kidneys and ureters kidneys and ureters – Iodine is injected into a vein to define Iodine is injected into a vein to define
structures structures
www.hospital.saga-med.ac.jp/.../ gyoumu.htm

TREATMENT PROCEDURES OF THE TREATMENT PROCEDURES OF THE URINARY SYSTEMURINARY SYSTEM
• MedicationsMedications• DialysisDialysis• KidneysKidneys
– TransplantationTransplantation– Nephrolysis: freeing of a kidney from Nephrolysis: freeing of a kidney from
adhesionsadhesions– Nephrostomy: opening between the pelvis of Nephrostomy: opening between the pelvis of
the kidney through its cortex to the outsidethe kidney through its cortex to the outside• Removal of Kidney StonesRemoval of Kidney Stones
– Lithrotripsy: destruction of a stone with the Lithrotripsy: destruction of a stone with the use of ultrasonic waves traveling through use of ultrasonic waves traveling through waterwater
– Nephrolithotomy: surgical removal of kidney Nephrolithotomy: surgical removal of kidney stonestone

TREATMENT PROCEDURES OF THE TREATMENT PROCEDURES OF THE URINARY SYSTEMURINARY SYSTEM
• UretersUreters• Urinary bladderUrinary bladder
– Cystectomy: surgical removal of all or part Cystectomy: surgical removal of all or part of bladderof bladder
– Cystopexy: surgical fixation of bladder to Cystopexy: surgical fixation of bladder to the abdominal wallthe abdominal wall
– Lithotomy: surgical incision for the removal Lithotomy: surgical incision for the removal of a stone, usually from the bladderof a stone, usually from the bladder
– Suprapubic catheter: indwelling catheter Suprapubic catheter: indwelling catheter placed into the bladder through a small placed into the bladder through a small incision through the abdominal wall just incision through the abdominal wall just above the pubic boneabove the pubic bone

nephrectomy
Renal stones
dialysis
cystoscopy
KUB
Urinarycath