Chapter 8: Special Senses Part 2 · Middle Ear • Three auditory ossicles (bones) – malleus...
Transcript of Chapter 8: Special Senses Part 2 · Middle Ear • Three auditory ossicles (bones) – malleus...

Chapter 8: Special SensesPart 2

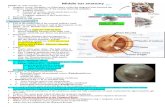
Anatomy of the Ear
• Broken into 3 major parts– External Ear
– Middle Ear (ossicles)
– Internal Ear – Internal Ear

Outer Ear
• Auricle (pinna)
• External auditory canal (meatus)
• Tympanic membrane

Middle Ear
• Three auditory ossicles (bones)– malleus (hammer)– incus (anvil)– stapes (stirrup)– stapes (stirrup)
• Oval window: transmits vibrations from the stapes to the inner ear fluid
• Eustachian tube (auditory tube): connects inner ear to the pharynx; equalizes pressure


Inner Ear
• Bony Labyrinth (filled with perilymph) (membranous labyrinth is enclosed inside the bony labyrinth, filled with endolymph)
Cochlea (Organ of Corti)– Cochlea (Organ of Corti)– Vestibule– Semicircular canal (equilibrium)
• Round Window• Cranial Nerve VIII (Vestibulocochlear)


Path of Hearing
• Sound waves enter the external auditory meatus � pass through the external auditory canal � causes the tympanic membrane to vibrate �malleus, incus, and stapes vibrate in malleus, incus, and stapes vibrate in sequence � oval window vibrate �perilymph in cochlear� endolymph(organ of corti) � hair cells vibrate �auditory nerve � brain’s temporal lobe (interpretation)




Balance and Posture
• Vestibular apparatus and Semicircular canals

Static Equilibrium
• Maculae (sensory receptors for static equilibrium) located inside the vestibular apparatus
• Change in body position � movement of • Change in body position � movement of otoliths � movement of hairs �generate a potential in hair cells �action potential in cranial nerve VIII �pons � cerebellum



Dynamic Equilibrium
• Crista ampullaris: receptors for dynamic equilibrium) located in the ampulla of each semicircular canal
• Change in body position � movement of fluid within canals movement of
• Change in body position � movement of fluid within canals � movement of cupula � movement of hairs �generates potential in hair cells �action potential in cranial nerve VIII �pons � cerebellum


The Sense of Smell (Olfaction)
• Olfaction detects chemicals in solution
• The Olfactory epithelium (organ for smell) is located in the roof of each nasal cavity.nasal cavity.– 5 million olfactory receptor cells
– protected & cushioned by supporting cells



The Chemical Senses
• Taste (gustatory) & Smell (olfactory)
• Chemoreceptors: respond to chemicals in an aqueous solution.– Taste: food chemicals – Taste: food chemicals
– Smell: airborne chemicals
• The receptors of taste & smell complement each other and respond to many of the same stimuli

Olfactory Receptor Cells
• Bipolar neurons, each with thin dendrite that terminates in a knob bearing several long cilia called olfactory hairs
• Olfactory hairs protrude outward and • Olfactory hairs protrude outward and are covered with mucus produced by the olfactory glands.

Olfactory Pathway
• Chemicals (gaseous odors) react with olfactory hairs � impulse in olfactory neurons �olfactory bulb � olfactory tracts � olfactory area of the cerebral tracts � olfactory area of the cerebral cortex (interpretation of smell)





The Sense of Taste
• Taste buds: sensory receptors for taste– Location: tongue, soft palate, cheeks,
pharynx, epiglottispharynx, epiglottis
– 10,000 taste buds (most on the tongue)


The Taste Bud
• Globular structure consisting of 40-60 epithelial cells– supporting cells
– taste cells (gustatory cells)– taste cells (gustatory cells)• Gustatory hairs (microvilli) extend from the cell
through a taste pore
– basal cells • produce new taste cells every 7-10 days



Taste Buds and the Tongue
• Papillae: Projections in the tongue mucosa (taste buds are found here)– gives tongue the abrasive feeling

Types of Papillae
• Circumvallate: – found in the back of the tongue
• Foliate (Filiform)– back sides of tongue– back sides of tongue
• Fungiform:– scattered all over tongue
– mostly at tip & sides


Sensation of Taste
• Sweet (sugar, saccharin, some aa)
• Sour (H+)
• Salty (Metal ions, Na+)
• Bitter (alkaloids such as quinine, nicotine, • Bitter (alkaloids such as quinine, nicotine, caffeine)
• Combinations of the above & the sense of smell (80% taste) give rise to other tastes


Mechanism for Taste
• Chemicals in food dissolve in saliva and diffuse into the taste pore & contact the gustatory hairs.
• Taste cells do not generate action • Taste cells do not generate action potentials, but their receptor potentials summate to trigger an action potential in the associated sensory neurons.

Mechanism for Taste
• Chemicals react with taste hairs �generate action potential in Cranial nerves VII, IX, X � medulla �thalamus � gustatory area of the thalamus � gustatory area of the cerebral cortex (parietal lobe)